|
Kartano
Kartano is the 2nd district of the city of Lahti, in the region of Päijät-Häme, Finland. It borders the districts of Niemi in the north, Kiveriö in the east, Keski-Lahti in the south, Salpausselkä in the southwest and Jalkaranta in the west. The district takes its name from the Fellman Manor; the Finnish word ''kartano'' directly translates to "manor" in English. The population of the statistical district of Kartano was 5,614 in 2019. Hakatornit The Hakatornit are a series of seven nine-floor apartment buildings on the Paasikivenkatu street in Kartano. Designed by architects Mauri Karkulahti and Eino Tuompo and constructed in 1951–1956, the towers have been proclaimed a built cultural environment of national significance by the Finnish Heritage Agency The Finnish Heritage Agency ( fi, Museovirasto, sv, Museiverket), previously known in English as the National Board of Antiquities, preserves Finland's material cultural heritage: collects, studies and distributes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesijärvi Railway Station
The Vesijärvi railway station ( fi, Vesijärven rautatieasema, sv, Vesijärvi järnvägsstation) is located in the city of Lahti, Finland, in the district of Kartano. It was one end of the port and industrial siding that branched off of the Riihimäki–Saint Petersburg railway, on the west side of the Lahti railway station. History As the Riihimäki–Saint Petersburg railway reached Lahti in August 1869, a siding was built to connect the main railway to the shore of lake Vesijärvi, intertwining the railway and the waterborne traffic on the Päijänne. This was made possible not only by the siding, but also by the Vääksy canal being built in 1868-1871, which linked the two waterways together. As with the rest of the Riihimäki–Lahti section of the railway, transport on the Vesijärvi siding was initiated on 1 November 1869. Passenger transit was handled by local trains that passengers would exchange onto at Lahti, after which they could continue their journey toward He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahti Bus Station
The Lahti bus station ( fi, Lahden linja-autoasema) is located in the Kartano district of the city of Lahti, Finland. Architecture The Lahti bus station is a prime example of the functionalist era of station buildings in Finland. Its most notable feature is the 28 meter tall clock tower, which remains a significant landmark in the eastern parts of downtown Lahti. The tower was used by the city authorities as space for advertisements. City Architect Kaarlo Könönen had drawn influence from the Tampere bus station, which was in its final stages of its construction during his design process. This was evident in, for example, the indoor area being cleanly split in just three parts: the entrance hall, commercial area (used for shops as well as a restaurant), and freight wing. A notable feature of the entrance hall was a bench in the shape of a ring, in the centre of which was a small palm tree. The furniture for the restaurant was provided by Asko, a local factory based in Asemant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lahti
Lahti (; sv, Lahtis) is a city and municipality in Finland. It is the capital of the region of Päijänne Tavastia (Päijät-Häme) and its growing region is one of the main economic hubs of Finland. Lahti is situated on a bay at the southern end of lake Vesijärvi about north-east of the capital city Helsinki, south-west of the Heinola town and east of Hämeenlinna, the capital of the region of Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme). It is also situated at the intersection of Highway 4 (between Helsinki and Jyväskylä) and Highway 12 (between Tampere and Kouvola), which are the most significant main roads of Lahti. In English, the Finnish word Lahti literally means ''bay''. Lahti is also dubbed the "Chicago of Finland" due to the early industries of both cities, when they were known as " slaughterhouse cities".Lahti on Suomen Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niemi (Lahti)
Niemi is the 4th district of the city of Lahti, in the region of Päijät-Häme, Finland. It borders the districts of Mukkula in the north, Kivimaa in the east, Kiveriö in the southeast and Keski-Lahti and Kartano in the south, as well as lake Vesijärvi in the west. The population of the statistical district of Niemi was 1,828 in 2019. (under Tilastokanta → Lahti → Väestö → Väkiluku ja ikärakenne → Lahden väkiluku ja ikärakenne alueittain 1999-) References Districts of Lahti {{SouthernFinland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiveriö
Kiveriö is the 5th district of the city of Lahti, in the region of Päijät-Häme, Finland. It borders the districts of Kivimaa in the north, Kytölä in the northeast, Myllypohja in the east, Möysä and Paavola in the south and Keski-Lahti, Kartano Kartano is the 2nd district of the city of Lahti, in the region of Päijät-Häme, Finland. It borders the districts of Niemi in the north, Kiveriö in the east, Keski-Lahti in the south, Salpausselkä in the southwest and Jalkaranta in the ... and Niemi in the west. The population of the statistical district of Kiveriö was 4,337 in 2019. References Districts of Lahti {{SouthernFinland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keski-Lahti
Keski-Lahti ("Central Lahti") is the 1st district of the city of Lahti, in the region of Päijät-Häme, Finland. It covers the downtown areas of the city, circling the Market Square. It borders the districts of Niemi in the north, Kiveriö in the northeast, Paavola and Möysä in the east, Asemantausta in the south, Hennala and Sopenkorpi in the west and Kartano in the northwest. The combined population of the statistical districts of Ydinkeskusta and Pohjoinen keskusta, approximately covering the area of Keski-Lahti, was 12,054 in 2019. Keski-Lahti has been recorded as the most dangerous district in Finland, with almost 80 homicide cases registered within 20 years. History Upon the destruction of the village of Lahti in the fire of 19 June 1877, an initiative to create the first zoning plan for the area that would become Keski-Lahti was started. Governor of the Häme Province Reinhold von Ammondt travelled to the derelict village on the day after the fire, and with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Finland
Finland is divided into 19 regions ( fi, maakunta; sv, landskap)., smn, eennâmkodde, and sms, mäddkåʹdd. The regions are governed by regional councils that serve as forums of cooperation for the Municipalities of Finland, municipalities of each region. The councils are composed of delegates from the municipal councils. The main tasks of regional councils are regional planning, development of enterprises, and education. Between 2004 and 2012 the regional council of Kainuu was elected via popular elections as part of an experimental regional administration. In 2022 new Wellbeing services counties of Finland, wellbeing services counties were established as part of a health care and social services reform. The wellbeing services counties follow the regional borders, and are governed by directly elected county councils. Åland One region, Åland, has a special status and has a much higher degree of autonomy than the others, with its own Parliament of Åland, Parliament and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Päijät-Häme
Päijät-Häme () is a region in Southern Finland south of the lake Päijänne. It borders the regions of Uusimaa, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Pirkanmaa, Central Finland, South Savo and Kymenlaakso. The biggest city in the region is Lahti. Historical provinces Municipalities There are 10 municipalities in Päijänne Tavastia. Cities and towns are marked in bold. Lahti Sub-region: * Asikkala **Population: * Hartola (''Gustav Adolfs'') **Population: * Heinola **Population: * Hollola **Population: * Iitti (''Itis'') **Population: * Kärkölä **Population: * Lahti (''Lahtis'') **Population: * Orimattila **Population: * Padasjoki **Population: * Sysmä **Population: Former municipalities: * Artjärvi (''Artsjö'') ** Consolidated with the town of Orimattila in 2011. * Hämeenkoski ** Consolidated with the municipality of Hollola in 2016. * Heinolan maalaiskunta (''Heinola landskommun'') ** Consolidated with the town of Heinola in 1997. * Nastola ** Conso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Finland
The municipalities ( fi, kunta; sv, kommun) represent the local level of administration in Finland and act as the fundamental, self-governing administrative units of the country. The entire country is incorporated into municipalities and legally, all municipalities are equal, although certain municipalities are called cities or towns ( fi, kaupunki; sv, stad). Municipalities have the right to levy a flat percentual income tax, which is between 16 and 22 percent, and they provide two thirds of public services. Municipalities control many community services, such as schools, health care and the water supply, and local streets. They do not maintain highways, set laws or keep police forces, which are responsibilities of the central government. Government Municipalities have council-manager government: they are governed by an elected council (, ), which is legally autonomous and answers only to the voters. The size of the council is proportional to the population, the extremes bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
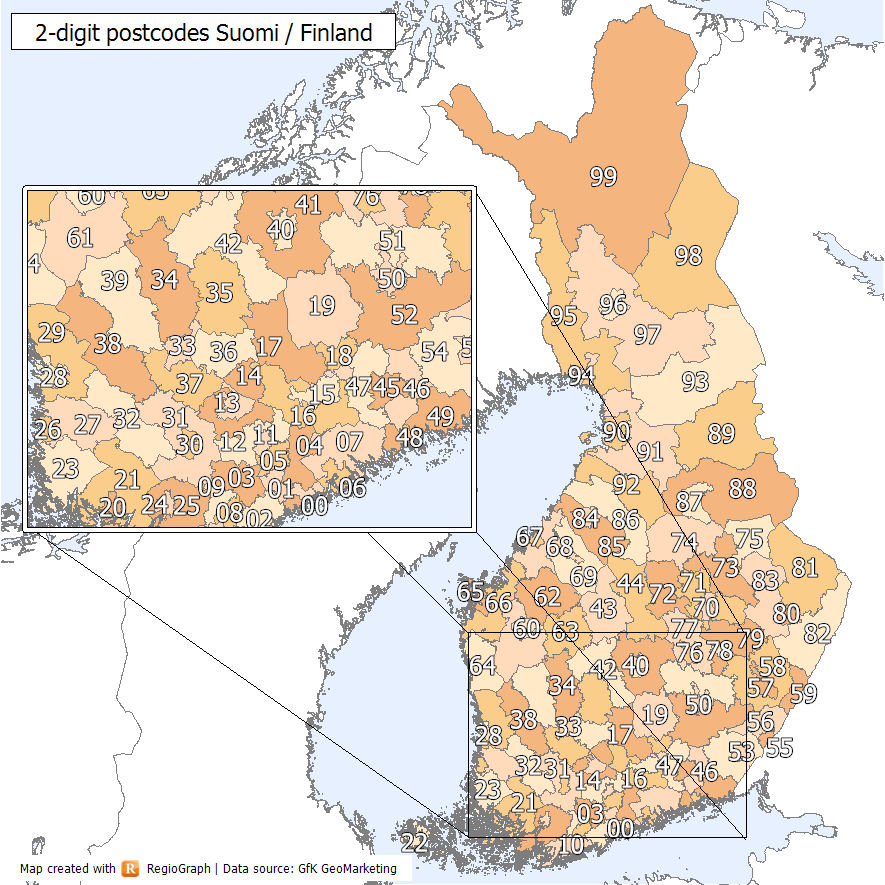
Postal Codes In Finland ...
Finland has used five-digit numeric postal codes since the 1970s. The first and second digits designate the general area of the municipality of the address, while the last three designate a smaller region within that larger area. The numeric postal code is usually accompanied by a written name for the smaller region. Corporations receiving large amounts of mail may have their own postal codes, also consisting of a five-digit numeric code and the name of the company. A special postal code 99999 is used for the residence of the Finnish Joulupukki, Korvatunturi. Notes References * {{Finland-stub Finland Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland across Estonia to the south. Finland covers an area of with a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city, forming a larger metropolitan area with the neighbouring cities of Espoo, Kauniainen, and Vantaa. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. Finnish, alongside Swedish, are the official languages. Swedish is the native language of 5.2% of the population. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to the boreal in the north. The land cover is primarily a boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes. Finland was first inhabited around 9000 BC after the Last Glacial Period. The Stone Age introduced several differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salpausselkä (Lahti)
Salpausselkä (; "Bar Ridge") is an extensive ridge system left by the ice age in Southern Finland. It is a large terminal moraine formation that formed in front of the Baltic ice lake during the Younger Dryas period about 12,250–10,400 years ago. All together the formation is close to from end to end, and the ridges can be as tall as in some places. It runs from Hanko hundreds of kilometers to the east. It traps the extensive river and lake systems of Central Finland known as Finnish Lakeland (, "Lake Finland") and forces the water to flow through few breaches in the ridge. The Vuoksi River flows from lake Saimaa into Lake Ladoga () in Russia. From there the water subsequently flows through river Neva into the Gulf of Finland, bypassing the Salpausselkä. The Kymi River flows from Päijänne into the Gulf of Finland. An artificial breach from the Lakeland is the Saimaa Canal, from Saimaa at Lappeenranta into the Gulf of Finland at Vyborg. Salpausselkä has been used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |