|
Kampfgeschwader 77
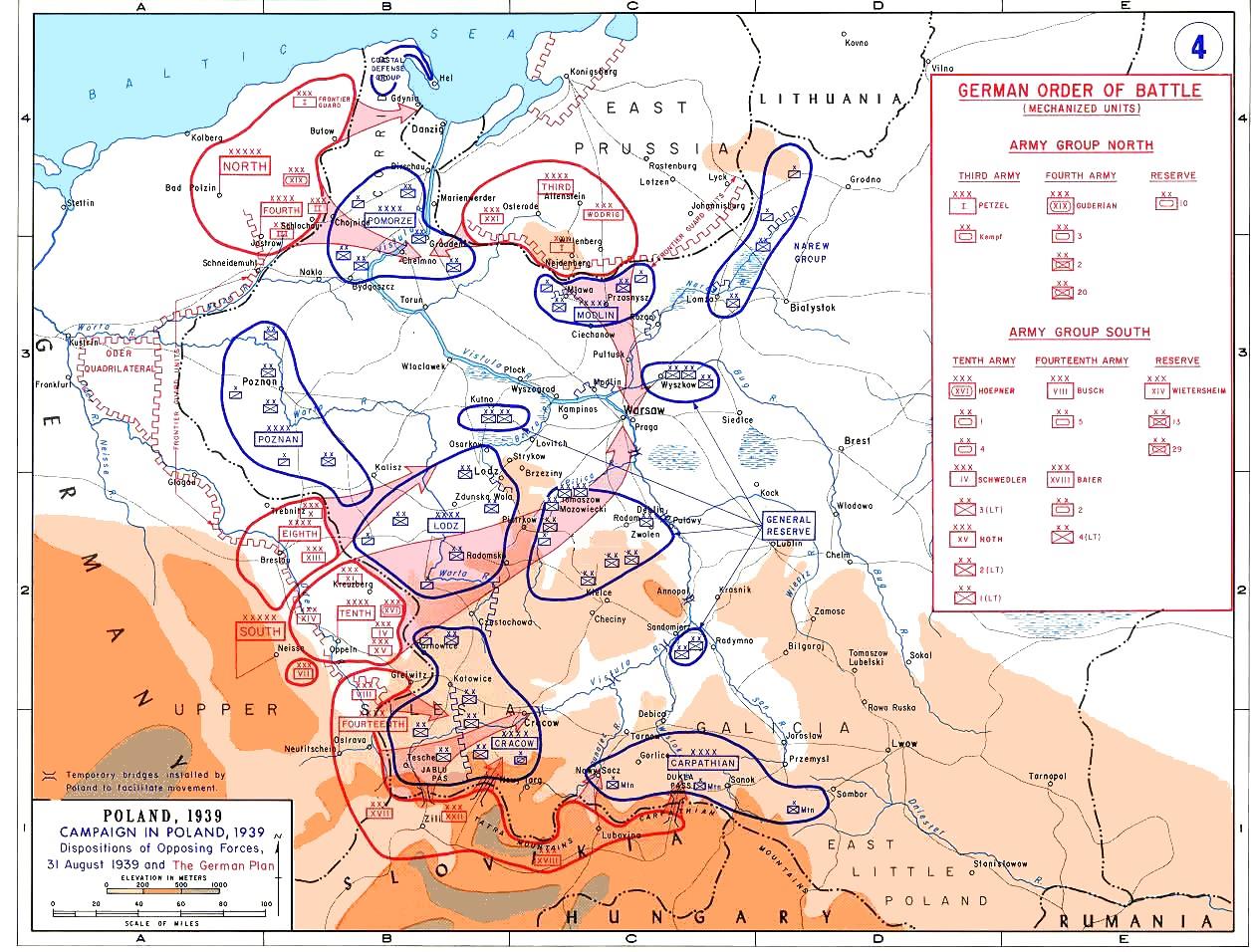
''Kampfgeschwader 77'' (KG 77) was a Luftwaffe bomber wing during World War II. Its units participated on all of the major fronts in the European Theatre until its dissolution in 1944. It operated all three of the major German bomber types; the Dornier Do 17, Heinkel He 111 and the Junkers Ju 88. History Kampfgeschwader 77 was formed on 1 May 1939 at Praha-Kbely, Kampfgeschwader 77 in Czechoslovakia with ''Stab''./KG 77 and I ''Gruppe''. II ''Gruppe'' at Praha-Kbely on the same date. The unit was allocated to ''Luftflotte 4'', and equipped with the Do 17Z, while III./KG 77 was not made operational until 26 August 1939, again in Königgrätz, now Hradec Králové. While training in the summer of 1939 the ''Geschwader'' "worked up" on the Dornier Do 17Z and He 111. Wartime service Polish Campaign During the Polish campaign I. and III. ''Gruppes'' of KG 77 took part in combat operations. Operating from Breslau-Schöngarten (today Copernicus Airport Wrocław), I./KG 77 committed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italy, Italian Caproni Ca 30 and United Kingdom, British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Theatre
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and ending with the Western Allies conquering most of Western Europe, the Soviet Union conquering most of Eastern Europe and Germany's unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945 (9 May in the Soviet Union) but the fighting on the Eastern front continued until 11 May during the Prague offensive and the end of the Battle of Odzak on 25 May. The Allied powers fought the Axis powers on two major fronts ( Eastern Front and Western Front) as well as in a strategic bombing offensive and in the adjoining Mediterranean and Middle East theatre. Preceding events Germany was defeated in World War I, and the Treaty of Versailles placed punitive conditions on the country, including significant financial reparations, the loss of territory (some only temporarily), war gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kielce
Kielce (, yi, קעלץ, Keltz) is a city in southern Poland, and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the banks of the Silnica River, in the northern part of the historical Polish province of Lesser Poland. Kielce has a history back over 900 years, and the exact date that it was founded remains unknown. Kielce was once an important centre of limestone mining and the vicinity is famous for its natural resources like copper, lead and iron, which, over the centuries, were exploited on a large scale. There are several fairs and exhibitions held in Kielce throughout the year. The city and its surroundings are also known for their historic architecture, green spaces and recreational areas like the Świętokrzyski National Park. In sports, the city is known as the home of the top-tier handball club, multiple Polish Champion and one-time EHF Champions Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radom
Radom is a city in east-central Poland, located approximately south of the capital, Warsaw. It is situated on the Mleczna River in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999), having previously been the seat of a separate Radom Voivodeship (1975–1998). Radom is the fourteenth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in its province with a population of 206,946 as of 2021. For centuries, Radom was part of the Sandomierz Province of the Kingdom of Poland and the later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Despite being part of the Masovian Voivodeship, the city historically belongs to Lesser Poland. It was a significant center of administration, having served as seat of the Crown Council which ratified the Pact of Vilnius and Radom between Lithuania and Poland in 1401. The Nihil novi and Łaski's Statute were adopted by the Sejm at Radom's Royal Castle in 1505. In 1976, it was a center of the June 1976 protests. The city is home to the biennial Radom Air Show, the largest air sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicia (Central Europe)
Galicia ()"Galicia" '''' ( uk, Галичина, translit=Halychyna ; pl, Galicja; yi, גאַליציע) is a historical and geographic region spanning what is now southeastern and western , long part of the . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bzura
The Battle of the Bzura (or the Battle of Kutno) was the largest Polish counter-attack of the German invasion of Poland and was fought from 9 to 19 September.''The Second World War: An Illustrated History '', Putnam, 1975, Google Print snippet (p.38)/ref>Sources vary regarding the end date, with some giving 18 September and others 19 September. Brockhaus Multimedial Lexikon gives 19 September 1939 as to the battle's end date. The battle took place west of Warsaw, near the Bzura River. It began as a Polish counter-offensive, which gained initial success, but the Germans outflanked the Polish forces with a concentrated counter-attack. That weakened Polish forces and the Poznań and Pomorze Armies were destroyed. Western Poland was now under German occupation.Zaloga, S.J., ''Poland 1939'', Oxford, Osprey Publishing Ltd., 2002, The battle has been described as "the bloodiest and most bitter battle of the entire Polish campaign". Winston Churchill called the battle an "ever-gloriou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernicus Airport Wrocław
Copernicus Airport Wrocław ( pl, Port Lotniczy Wrocław im. Mikołaja Kopernika, Port lotniczy Wrocław- Strachowice) is an international civil-military airport in Wrocław in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwestern Poland. It is Poland’s 5th busiest airport. The airport is located southwest of the city centre, at Graniczna street 190. It has one runway, one passenger terminal, one cargo terminal and one general aviation terminal. Wrocław airport is also often used by Polish Air Force, US Air Force, NATO air force and Heavy Airlift Wing. History Early years The airport was built in 1938 as ''Flugplatz Breslau-Schöngarten'' Airport for German military purposes before World War II, when the city was still part of Germany. It was the site of a military aviation school, the ''Luftkriegsschule Breslau-Schöngarten'', later renamed ''Luftkriegsschule 5''. Among the Luftwaffe units stationed here just before the war were the Sturzkampfgeschwader 77, Kampfgeschwader 76, and Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hradec Králové
Hradec Králové (; german: Königgrätz) is a city of the Czech Republic. It has about 91,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of the Hradec Králové Region. The historic centre of Hradec Králové is well preserved and is protected by law as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument reservations, urban monument reservation, the wider centre is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, urban monument zone. Administrative parts Hradec Králové is made up of 21 city parts: *Březhrad *Hradec Králové *Nový Hradec Králové *Kukleny *Malšova Lhota *Malšovice *Moravské Předměstí *Piletice *Plácky *Plačice *Plotiště nad Labem *Pouchov *Pražské Předměstí *Roudnička *Rusek *Slatina *Slezské Předměstí *Svinary *Svobodné Dvory *Třebeš *Věkoše Etymology The city was originally named Hradec, which is a diminutive of ''hrad'' (i.e. "castle"). Later, when it was owned by Bohemian queens, the Králové attribute (from ''král, král ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftflotte 4
''Luftflotte'' 4For an explanation of the meaning of Luftwaffe unit designation see Luftwaffe Organisation (Air Fleet 4) was one of the primary divisions of the German Luftwaffe in World War II. It was formed on March 18, 1939, from Luftwaffenkommando Österreich in Vienna. The ''Luftflotte'' was redesignated on 21 April 1945, to ''Luftwaffenkommando'' 4, and became subordinated to Luftflotte 6. It was the Luftflotte 4, that was responsible for the bombing campaign of Stalingrad, where ca. 40,000 civilians died. This Luftwaffe detachment was based in Romania, Bulgaria, Southeast Poland, Hungary, Ukraine and Russian occupied territories, for supporting Axis forces; with command offices in Morczyn, Hungary, during 26 June 1944, Eastern Front. See Organization of the Luftwaffe (1933–1945) for explanation of abbreviations used below. Strategic reconnaissance *2.(F)/11 ( Jasionka) *2.(F)/22 ( Focşani) *2.(F)/100 (Lublin) Transports (special duties) *14 St./Transportgeschwader 4 (O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czechoslovakia , life_span = 1918–19391945–1992 , p1 = Austria-Hungary , image_p1 = , s1 = Czech Republic , flag_s1 = Flag of the Czech Republic.svg , s2 = Slovakia , flag_s2 = Flag of Slovakia.svg , image_flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia.svg , flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia , flag_type = Flag(1920–1992) , flag_border = Flag of Czechoslovakia , image_coat = Middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia.svg , symbol_type = Middle coat of arms(1918–1938 and 1945–1961) , image_map = Czechoslovakia location map.svg , image_map_caption = Czechoslovakia during the interwar period and the Cold War , national_motto = , anthems = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)