|
Kambo Cleanse
Kambo, also known as vacina-do-sapo, or sapo (from Portuguese "sapo", Literal translation, lit. meaning "toad"), is the dried skin secretions of the Phyllomedusa bicolor, kambô, a species of frog, used as a transdermal medicine. Kambo is usually used in a group setting, called a Kambo circle or Kambo ceremony. The effects on humans usually include tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, and Diarrhoea, diarrhea, however, a meta-review of 50 studies in which 11 cases of acute intoxication were examined found that extreme cases may include psychosis (occasionally severe), SIADH, kidney damage (including acute renal failure), pancreas damage, Liver disease, liver damage including toxic hepatitis, dermatomyositis, esophageal rupture, seizures, and death, although evidence for these is limited. Kambo, which originated as a folk medicine practice among Indigenous peoples of the Amazon, the Amazon indigenous peoples, is also administered as an alternative medicine treatment in the West, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literal Translation
Literal translation, direct translation or word-for-word translation, is a translation of a text done by translating each word separately, without looking at how the words are used together in a phrase or sentence. In Translation studies, translation theory, another term for "literal translation" is ''metaphrase'' (as opposed to ''paraphrase'' for an Analogy, analogous translation). Literal translation leads to mistranslating of idioms, which is a serious problem for machine translation. The term as used in translation studies Usage The term "literal translation" often appeared in the titles of 19th-century English language, English translations of classical, Bible and other texts. Cribs Word-for-word translations ("cribs," "ponies" or "trots") are sometimes prepared for a writer who is translating a work written in a language they do not know. For example, Robert Pinsky is reported to have used a literal translation in preparing his translation of Dante's ''Inferno (Dante), I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detoxification (alternative Medicine)
Detoxification (often shortened to detox and sometimes called body cleansing) is a type of alternative-medicine treatment which aims to rid the body of unspecified "toxins" – substances that proponents claim accumulate in the body over time and have undesirable short-term or long-term effects on individual health. Activities commonly associated with detoxification include dieting, fasting, consuming exclusively or avoiding specific foods (such as fats, carbohydrates, fruits, vegetables, juices, herbs), colon cleansing, chelation therapy, and the removal of dental fillings containing amalgam. Scientists and health organizations have criticized the concept of detoxification for its unsound scientific basis and for the lack of evidence for claims made. The "toxins" usually remain undefined, with little to no evidence of toxic accumulation in the patient. The British organisation Sense About Science has described some detox diets and commercial products as "a waste of time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panoan Language
Panoan (also Pánoan, Panoano, Panoana, Páno) is a family of languages spoken in Peru, western Brazil, and Bolivia. It is possibly a branch of a larger Pano–Tacanan family. Genetic relations The Panoan family is generally believed to be related to the Tacanan family, forming with it Pano–Tacanan, though this has not yet been established (Loos 1999). Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Kechua, Mapudungun, Moseten-Tsimane, Tukano, Uru-Chipaya, Harakmbet, Arawak, Kandoshi, and Pukina language families due to contact. Languages There are some 18 extant and 14 extinct Panoan languages.Fleck, David. 2013. Panoan Languages and Linguistics'. Anthropological Papers of the American Museum of Natural History 99. In the list of Panoan languages below adapted from Fleck (2013), (†) means extinct, and (*) obsolescent (no longer spoken daily). Dialects are listed in parentheses. *Mayoruna ** Tabatinga Mayoruna ost divergent† * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the world by discharge volume of water. The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse. Etymology The river's name is derived from the Warao term for "a place to paddle", itself derived from the terms ''güiri'' (paddle) and ''noko'' (place) i.e. a navigable place. History The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Christopher Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his third voyage. Its source at the Cerro Delgado–Chalbaud, in the Parima range, was not explored until 453 years later, in 1951. The source, near the Venezuelan–Brazilian border, at ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. or Amazonia is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin encompasses , of which are covered by the rainforest. This region includes territory belonging to nine nations and 3,344 formally acknowledged Indigenous territory (Brazil), indigenous territories. The majority of the forest is contained Amazônia Legal, within Brazil, with 60% of the rainforest, followed by Peruvian Amazonia, Peru with 13%, Amazon natural region, Colombia with 10%, and with minor amounts in Bolivia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela. Four nations have "Amazonas (other), Amazonas" as the name of one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese (' ), also Portuguese of Brazil (', ) or South American Portuguese (') is the set of varieties of the Portuguese language native to Brazil and the most influential form of Portuguese worldwide. It is spoken by almost all of the 214 million inhabitants of Brazil and spoken widely across the Brazilian diaspora, today consisting of about two million Brazilians who have emigrated to other countries. With a population of over 214 million, Brazil is by far the world's largest Portuguese-speaking nation and the only one in the Americas. Brazilian Portuguese differs, particularly in phonology and prosody, from varieties spoken in Portugal and Portuguese-speaking African countries. In these latter countries, the language tends to have a closer connection to contemporary European Portuguese, partly because Portuguese colonial rule ended much more recently there than in Brazil, partly due to the heavy indigenous and African influence on Brazilian Portuguese. Despite t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huni Kuin
The Huni Kuin (also known as: ''Kaxinawá'', ''Cashinahua'', ''Kaschinawa'', ''Kashinawa'', ''Caxinauás'') are an indigenous people of Brazil and Peru. Their villages are located along the Purus and Curanja Rivers in Peru and the Tarauacá, Jordão, Breu, Muru, Envira, Humaitã, and Purus Rivers in Brazil."Kaxinawá: Location." ''Povos Indígenas no Brasil.'' Retrieved 8 Dec 2011. In the Peruvian Amazon rainforest, some Huni Kuin live on the Alto Purús Indigenous Territory with the Kulina people. Name The name ''Huni Kuin'' means "true people" or "people with t ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
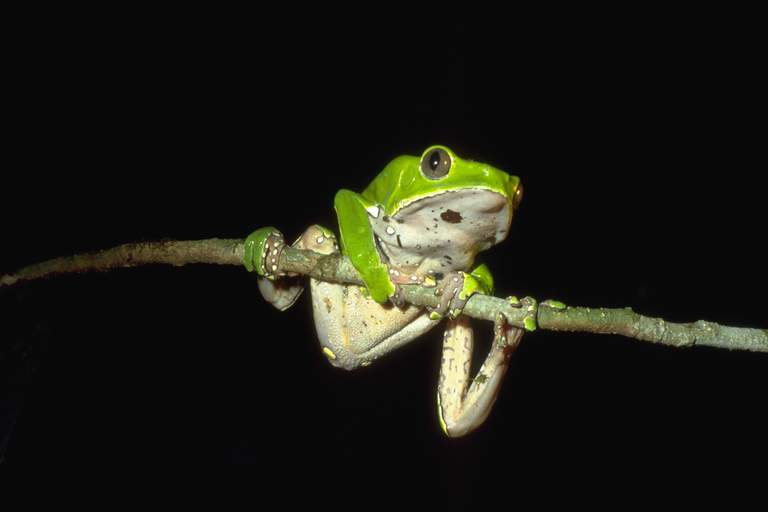
Phyllomedusa Bicolor01a
''Phyllomedusa'' is a genus of tree frogs in the subfamily Phyllomedusinae found in tropical and subtropical South America (south to northern Argentina) and Panama. It has 16 recognised species. Taxonomy The following species are recognised in the genus ''Phyllomedusa'': * ''Phyllomedusa bahiana'' * ''Phyllomedusa bicolor'' - giant leaf frog * ''Phyllomedusa boliviana'' * ''Phyllomedusa burmeisteri'' - Burmeister's leaf frog * '' Phyllomedusa camba'' * ''Phyllomedusa chaparroi'' * '' Phyllomedusa coelestis'' * '' Phyllomedusa distincta'' * ''Phyllomedusa iheringii'' * ''Phyllomedusa neildi'' * ''Phyllomedusa sauvagii'' - waxy monkey leaf frog * '' Phyllomedusa tarsius''- tarsier leaf frog * '' Phyllomedusa tetraploidea'' * ''Phyllomedusa trinitatis'' * ''Phyllomedusa vaillantii'' - white-lined leaf frog * '' Phyllomedusa venusta'' Several other species formerly included in this genus are now placed in two other phyllomedusid genera: ''Callimedusa'' and ''Pithecopus''. Ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
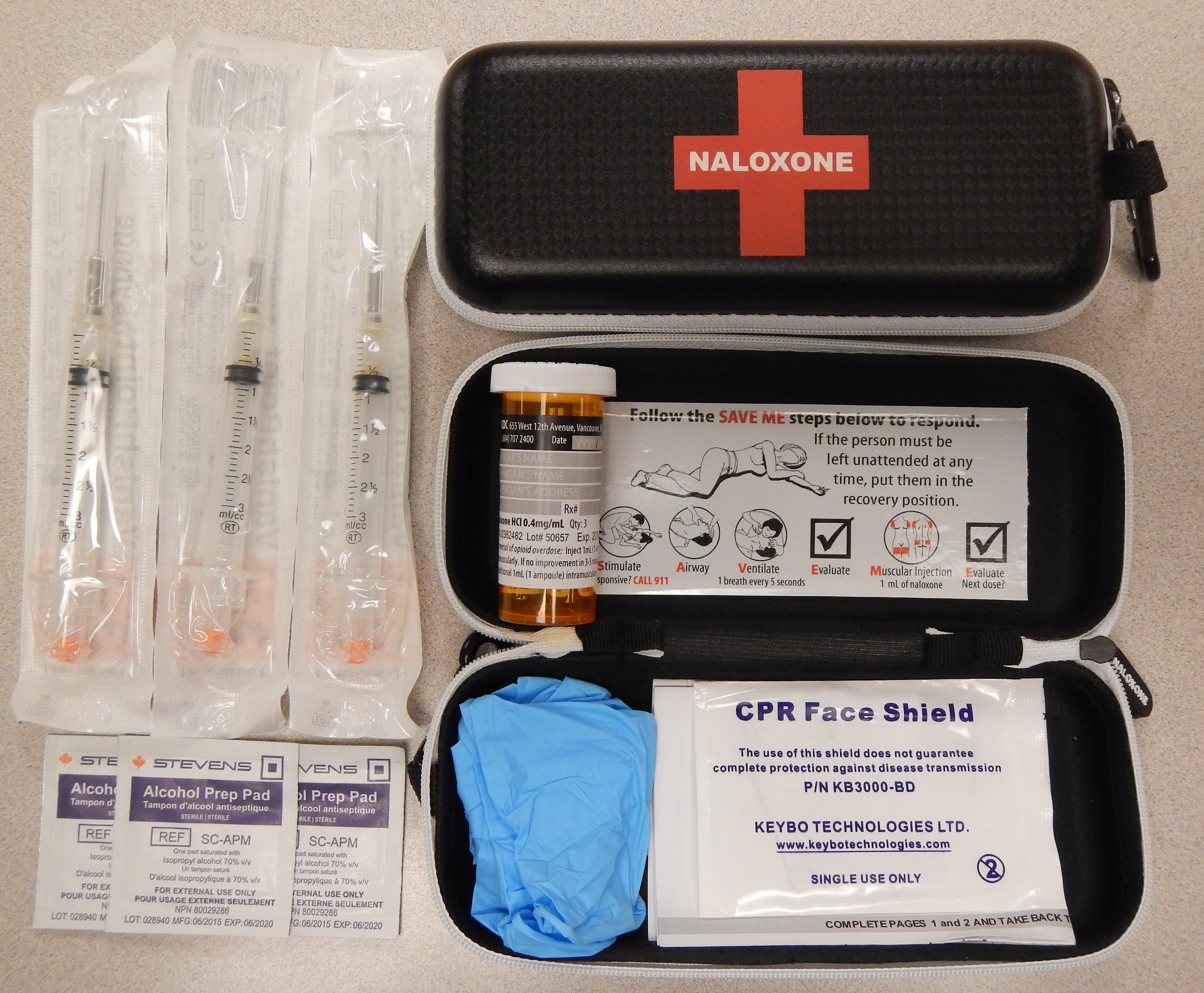
Naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin within two minutes when given intravenously, and within five minutes when injected into a muscle. The medicine can also be administered by spraying it into a person's nose. Naloxone commonly blocks the effects of opioids for 30 to 90 minutes. Multiple doses may be required, as the duration of action of some opioids is greater than that of naloxone. Administration to opioid-dependent individuals may cause symptoms of opioid withdrawal, including restlessness, agitation, nausea, vomiting, a fast heart rate, and sweating. To prevent this, small doses every few minutes can be given until the desired effect is reached. In those with previous heart disease or taking medications that negatively affect the heart, further heart problems have occurred. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or softening of the bones. Causes include alcohol use disorder, refeeding in those with malnutrition, recovery from diabetic ketoacidosis, burns, hyperventilation, and certain medications. It may also occur in the setting of hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, and Cushing syndrome. It is diagnosed based on a blood phosphate concentration of less than 0.81 mmol/L (2.5 mg/dL). When levels are below 0.32 mmol/L (1.0 mg/dL) it is deemed to be severe. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Phosphate may be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. Hypophosphatemia occurs in about 2% of people within hospital and 70% of people in the intensive care unit (ICU). Signs and symptoms * Muscle dysfunction and weakness – This occurs in major muscles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)