|
Kaldbaksbotnur
Kaldbaksbotnur is a village on the island of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands. Geography Kaldbaksbotnur is located on the east coast of Streymoy. The village consists two farms. One farm is located in the bottom of Kaldbaksfjørður on the western side of the river and this farm is also called Northern part of Sund. The other is on the eastern side of the river and relates to Kaldbak. When the road to Tórshavn opened in 1980 this connected both Kaldbaksbotnur and Kaldbak to the island's road network. In 1992 the 2816m tunnel ''Kollfjarðartunnilin'' was opened from Kaldbaksbotnur to Kollafjørður and this is now the main route from Tórshavn to the villages in the north of the island. Throughout the 1990s Kaldbaksbotnur was served by bus route 4 operated by the blue Bygdaleiðir country buses which passed through the village on their route from Tórshavn to Kaldbak. Route 5, added in 2001, also ran from Tórshavn through Kaldbaksbotnur to the township of Kollafjørður. Since 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaldbaksbotnur
Kaldbaksbotnur is a village on the island of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands. Geography Kaldbaksbotnur is located on the east coast of Streymoy. The village consists two farms. One farm is located in the bottom of Kaldbaksfjørður on the western side of the river and this farm is also called Northern part of Sund. The other is on the eastern side of the river and relates to Kaldbak. When the road to Tórshavn opened in 1980 this connected both Kaldbaksbotnur and Kaldbak to the island's road network. In 1992 the 2816m tunnel ''Kollfjarðartunnilin'' was opened from Kaldbaksbotnur to Kollafjørður and this is now the main route from Tórshavn to the villages in the north of the island. Throughout the 1990s Kaldbaksbotnur was served by bus route 4 operated by the blue Bygdaleiðir country buses which passed through the village on their route from Tórshavn to Kaldbak. Route 5, added in 2001, also ran from Tórshavn through Kaldbaksbotnur to the township of Kollafjørður. Since 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streymoy
Streymoy ( da, Strømø) is the largest and most populated island of the Faroe Islands. The capital, Tórshavn, is located on its southeast coast. The name means "island of currents". It also refers to the largest region of the country that also includes the islands of Hestur, Koltur and Nólsoy. Geography The island is oblong in shape and stretches roughly in northwest–southeast direction with a length of and a width of around . There are two deeply-indented fjords in the southeast: Kollafjørður and Kaldbaksfjørður. The island is mountainous (average height is 337 meter ), especially in the northwest, with the highest peak being Kopsenni (). That area is dominated by over cliffs. The area is known as Vestmannabjørgini, which means Cliffs of Vestmanna. The beaches of Tórshavn, Vestmanna, Leynar, Kollafjørður, Hvalvík (meaning Whale Bay) and Tjørnuvík are officially approved ''grind'' beaches for whaling. Like the rest of the Faroe Islands there are numerous shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tórshavn Municipality
Tórshavn Municipality (Tórshavnar kommuna) is the municipality of the Faroese capital Tórshavn and its surroundings. The municipality covers the southern half of Streymoy island and adjacent minor islands and has an area of 173 km2. It became an independent municipality in 1866 and is the largest in the Faroes. The municipality has a population of about 23,071 (August 2022) or 40.5% of the total population of the islands. It contains the following towns and villages: *Tórshavn *Argir *Hoyvík * Hvítanes *Kaldbak * Kaldbaksbotnur *Kirkjubøur *Velbastaður *Kollafjørður *Oyrareingir *Signabøur * Sund *Norðradalur *Syðradalur *Nólsoy *Hestur *Koltur Koltur ( da, Kolter) is an island in the Faroe Islands, located to the west of Streymoy and to the north-west of Hestur. The name 'Koltur' means ' colt', in contrast with the name of the larger island to the south-east, 'Hestur', which means 'hors ... Population progression Progression of the population of Tórshav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns In The Faroe Islands ...
This is a list of villages (and towns) of the Faroe Islands. :fo:Býir í Føroyum :de:Liste der Städte und Orte auf den Färöern References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Towns In The Faroe Islands Towns Faroe Islands The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark. They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two North American. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implemented the North Atlantic Treaty, signed in Washington, D.C., on 4 April 1949. NATO is a collective security system: its independent member states agree to defend each other against attacks by third parties. During the Cold War, NATO operated as a check on the perceived threat posed by the Soviet Union. The alliance remained in place after the dissolution of the Soviet Union and has been involved in military operations in the Balkans, the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa. The organization's motto is ''animus in consulendo liber'' (Latin for "a mind unfettered in deliberation"). NATO's main headquarters are located in Brussels, Belgium, while NATO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroese Language
Faroese ( ; ''føroyskt mál'' ) is a North Germanic language spoken as a first language by about 72,000 Faroe Islanders, around 53,000 of whom reside on the Faroe Islands and 23,000 in other areas, mainly Denmark. It is one of five languages descended from Old West Norse spoken in the Middle Ages, the others being Norwegian, Icelandic, and the extinct Norn and Greenlandic Norse. Faroese and Icelandic, its closest extant relative, are not mutually intelligible in speech, but the written languages resemble each other quite closely, largely owing to Faroese's etymological orthography. History Around 900 AD, the language spoken in the Faroes was Old Norse, which Norse settlers had brought with them during the time of the settlement of Faroe Islands () that began in 825. However, many of the settlers were not from Scandinavia, but descendants of Norse settlers in the Irish Sea region. In addition, women from Norse Ireland, Orkney, or Shetland often married native Scandinavian m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teitur Lassen
Teitur Lassen (, 4 January 1977) is a Faroese musician, composer, singer-songwriter and producer. He is a winner of multiple Danish Music Awards and has toured globally since his debut release, ''Poetry & Aeroplanes'', in 2003. Teitur was born in Hoyvík. Since 2001 he has dedicated himself to playing and writing music in English full-time, and has released six studio albums as a solo artist. He has additionally produced, written for, or worked with multiple international artists including Seal, Corinne Bailey Rae, Netherlands Wind Ensemble, Emilie Simon, International Contemporary Ensemble (ICE), Holland Baroque Society, Nolwenn Leroy, Nico Muhly, and Ane Brun. His songs have appeared on major motion picture soundtracks and numerous compilations. Studio albums ''Poetry and Aeroplanes'' After finding both a publishing deal with Windswept Pacific and a record contract with Universal Records in the United States, the Faroe Islands awarded him its 2004 " Businessman of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordenite
Mordenite is a zeolite mineral with the chemical formula, ( Ca, Na2, K2) Al2 Si10 O24·7 H2O. and it is one of the six most abundant zeolites and is used commercially. It was first described in 1864 by Henry How. He named it after the small community of Morden, Nova Scotia, Canada, along the Bay of Fundy, where it was first found. Mordenite is orthorhombic (a,b,c unequal & all angles 90 degree). It crystallizes in the form of fibrous aggregates, masses, and vertically striated prismatic crystals. It may be colorless, white, or faintly yellow or pink. It has Mohs hardness of 5 and a density of 2.1 g/cm3. When it forms well developed crystals they are hairlike; very long, thin, and delicate. Mordenite’s molecular structure is a framework containing chains of five-membered rings of linked silicate and aluminate tetrahedra (four oxygen atoms arranged at the points of a triangular pyramid about a central silicon or aluminium atom). Its high ratio of silicon to aluminum atoms m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
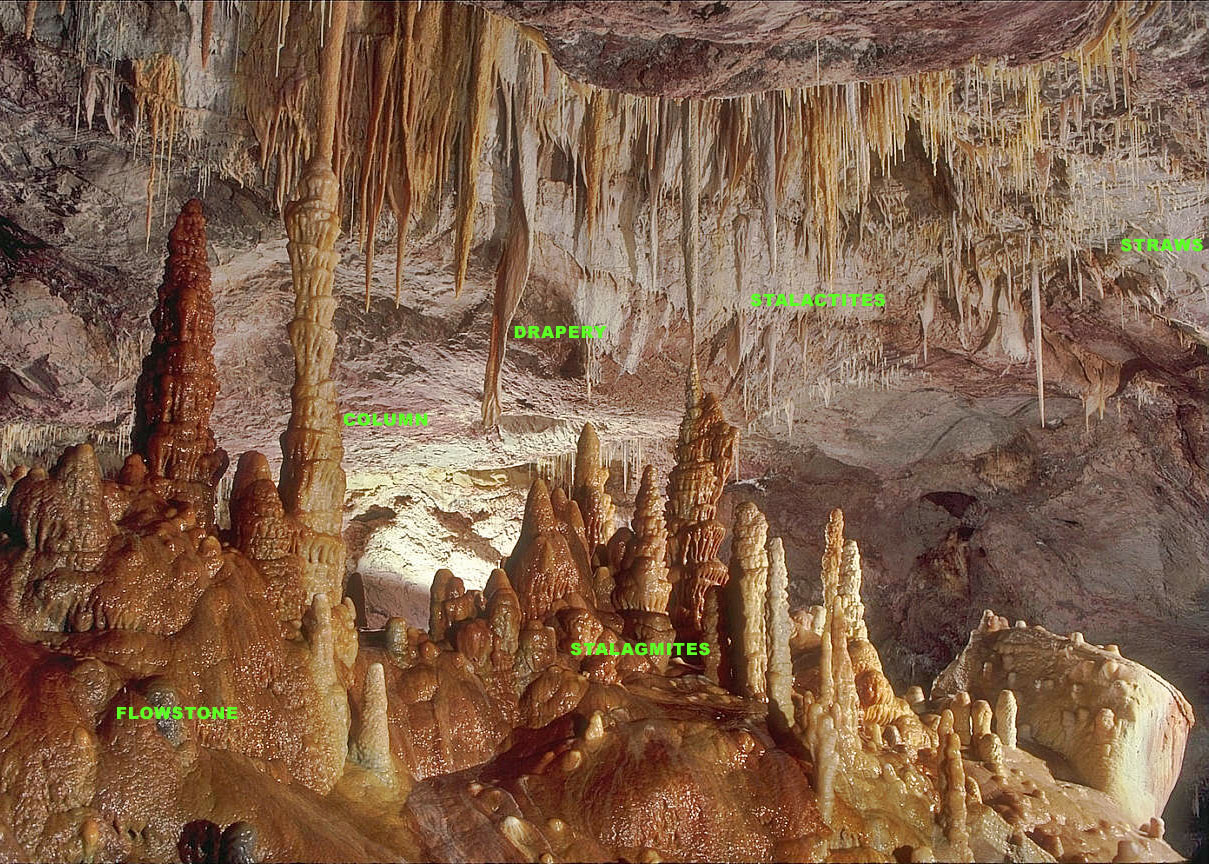
Stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling") is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically composed of calcium carbonate, but may consist of lava, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). The corresponding formation hanging down from the ceiling of a cave is a stalactite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground", another is that, as with ants in the pants, the mites go up and the tights (tites) come down. Formation and type Limestone stalagmites The most common stalagmites are speleothems, which usually form in limestone caves. Stalagmite formation occurs only under certain pH conditions within the cavern. They form through deposition of calcium carbonate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)