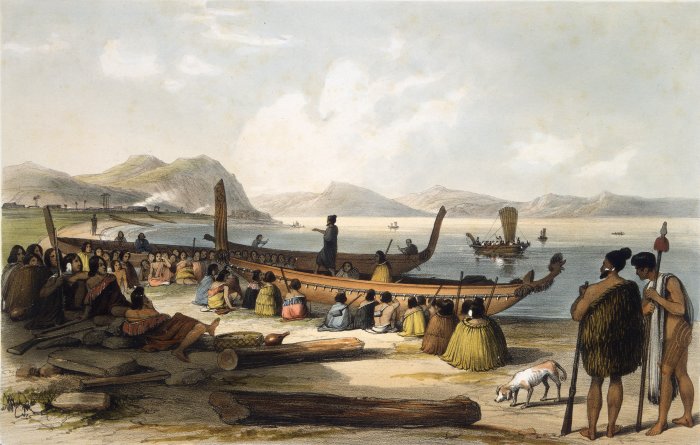|
Kai-ihu
Kai-ihu (or possibly Kaih┼½) was a M─üori people, M─üori rangatira (chief) in the Tainui confederation of tribes, based at K─üwhia, New Zealand. He is best known for his part in a raid on Te Huaki in revenge for the murder of his father, Te-Ata-i-┼Źrongo. He probably lived in the early seventeenth century. Sources The earliest record of the story is a manuscript from the collection of Governor George Grey (GNZMMSS 31) composed sometime before 1854. Elsdon Best records a version which he was told in 1894 by Te Karehana Whakataki of Ng─üti Toa. A version by Wirihana Te Aoterangi, a chief from Raglan who died in 1907, forms the basis of the account by Pei Te Hurinui Jones. Life Kai-ihu was a male-line descendant of Hoturoa, leader of the ''Tainui (canoe), Tainui'' ''waka'' through his father Te-Ata-i-┼Źrongo, son of Uetapu / Uenuku-tuhatu, the son of Whatihua. Murder of Te-Ata-i-┼Źrongo Te-Ata-i-┼Źrongo married Rangi-waea who came from ┼īkoro but had been raised at Tairutu near Te ─ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whatihua
Whatihua was a M─üori rangatira (chief) in the Tainui confederation of tribes, based at K─üwhia, New Zealand. He quarrelled with his brother, T┼½rongo, and as a result Tainui was split between them, with Whatihua receiving the northern Waikato region, including K─üwhia. He probably lived in the early sixteenth century. Life Whatihua was a male-line descendant of Hoturoa, leader of the ''Tainui'' ''waka'' through his father T─üwhao. T─üwhao married two daughters of Te Aorere, another descendant of Hoturoa, P┼½nui-a-te-kore and Maru-t─ō-hiakina. Whatihua was the first-born son, but his mother was the younger of T─üwhao's wives, Maru-t─ō-hiakina. His younger brother T┼½rongo was born to the senior wife, P┼½nui-a-te-kore. As a result, the relative status of the two sons was unclear and they competed for pre-eminence. As youths, Whatihua and T┼½rongo went hunting ''k┼½aka'' (Bar-tailed godwits) on Kaiwhai island off K─üwhia. At first, all the birds came to T┼½rongo and he caught grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M─üori People
The M─üori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). M─üori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early M─üori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Initial contact between M─üori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; M─üori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising tensions over disputed land sales led to conflict in the 1860s, and massive land confiscations, to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato River
The Waikato River is the longest river in New Zealand, running for through the North Island. It rises on the eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu, joining the Tongariro River system and flowing through Lake Taup┼Ź, New Zealand's largest lake. It then drains Taup┼Ź at the lake's northeastern edge, creates the Huka Falls, and flows northwest through the Waikato Plains. It empties into the Tasman Sea south of Auckland, at Port Waikato. It gives its name to the Waikato region that surrounds the Waikato Plains. The present course of the river was largely formed about 17,000 years ago. Contributing factors were climate warming, forest being reestablished in the river headwaters and the deepening, rather than widening, of the existing river channel. The channel was gradually eroded as far up river as Piarere, leaving the old Hinuera channel through the Hinuera Gap high and dry. The remains of the old course are seen clearly at Hinuera, where the cliffs mark the ancient river edges. The Wai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiki
In Polynesian mythology, (also rendered as in Cook Islands M─üori, in Samoan, in Tahitian, in Hawaiian) is the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in many M─üori stories. Anne Salmond states ''Havaii'' is the old name for Raiatea, the homeland of the M─üori. When British explorer James Cook first sighted New Zealand in 1769, he had Tupaia on board, a Raiatean navigator and linguist. Cook's arrival seemed to be a confirmation of a prophecy by Toiroa, a priest from M─ühia. At Tolaga Bay, Tupaia conversed with the ''tohunga'' associated with the school of learning located there, called Te Rawheoro. The priest asked about the Maori homelands, 'Rangiatea' (Ra'iatea), 'Hawaiki' (Havai'i, the ancient name for Ra'iatea), and 'Tawhiti' (Tahiti). Etymology Linguists have reconstructed the term to Proto- Nuclear Polynesian ''*sawaiki''. The M─üori word figures in legends about the arrival of the M─üori in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ng─ütoro-i-rangi
In M─üori tradition, Ng─ütoro-i-rangi (Ng─ütoro) is the name of a tohunga (priest) prominent during the settling of New Zealand ( Aotearoa) by the M─üori people, who came from the traditional homeland Hawaiki on the '' Arawa'' canoe. He is the ancestor of Ng─üti T┼½wharetoa and his travels around Lake Taup┼Ź and up onto the Volcanic Plateau are the basis of Ng─üti T┼½wharetoa's claim to those regions. Rangi─ütea Ng─ütoro-i-rangi was the son of Rakauri and Hineruarangi and was raised at Te Vaitoa in Rangi─ütea. He was descended from the Ng─üti Ohomairangi tribe and was direct successor to the high priest of Taputapuatea marae at Rangi─ütea. He also had ancestral connections to Aitutaki, Rarotonga, Rangi─ütea (Ra'iatea) and other islands in the area. Puha-o-rangi, the father of Ohomairangi, was the progenitor of all of the Te Arawa people. He was trained at Taputapu─ütea marae as a priest and navigator and was renowned for his skills and status. He made a number of journeys around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utu (M─üori Concept)
''Utu'' is a M─üori concept of reciprocation or balance. To retain ''mana'', both friendly and unfriendly actions require an appropriate response, hence ''utu'' covers both the reciprocation of kind deeds, and the seeking of revenge. ''Utu'' can also be used in reference to monetary repayments, paying or repaying. Cultural references * ''Utu'', a 1983 New Zealand film loosely based on events from Te Kooti's War Te Kooti's War was among the last of the New Zealand Wars, the series of 19th century conflicts in New Zealand between the M─üori and the colonising European settlers. It was fought in the East Coast region and across the heavily forested centra ... "Amazon's "one-click" patent reconsidered"- a modern example of the term's use within New Zealand society References External links An exploration of utu as a legal concept M─üori words and phrases M─üori society {{maori-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are M─üori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka t─½wai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in M─üori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") are large canoes manned by up to 80 paddlers and are up to in length. Large waka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakia
Karakia are M─üori incantations and prayers, used to invoke spiritual guidance and protection. With the nineteenth-century introduction of Christianity to New Zealand, M─üori adopted (or wrote new) karakia to acknowledge the new faith. Modern karakia tend to contain a blend of Christian and traditional influence, and their poetic language may make literal translations into English not always possible.Karakia , Otago University website. Retrieved 23 July 2019. In modern M─üori society, performances of ''karakia'' frequently open important meetings and ceremonies, both within a M─üori context (such as tribal , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lice
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result of developments in phylogenetic research. Lice are obligate parasites, living externally on warm-blooded hosts which include every species of bird and mammal, except for monotremes, pangolins, and bats. Lice are vectors of diseases such as typhus. Chewing lice live among the hairs or feathers of their host and feed on skin and debris, while sucking lice pierce the host's skin and feed on blood and other secretions. They usually spend their whole life on a single host, cementing their eggs, called nits, to hairs or feathers. The eggs hatch into nymphs, which moult three times before becoming fully grown, a process that takes about four weeks. Genetic evidence indicates that lice are a highly modified lineage of Psocoptera (now called Ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapu (Polynesian Culture)
Tapu is a Polynesian traditional concept denoting something holy or sacred, with " spiritual restriction" or "implied prohibition"; it involves rules and prohibitions. The English word ''taboo'' derives from this later meaning and dates from Captain James Cook's visit to Tonga in 1777. The concept exists in many societies, including traditional M─üori, Samoan, Kiribati, Rapanui, Tahitian, Hawaiian, and Tongan cultures, in most cases using a recognisably similar word (from Proto-Polynesian '' *tapu''), though the Rotuman term for this concept is "ha'a". In Hawaii, a similar concept is known as "kapu". Outside Polynesian The root also exists outside Polynesian languages, in the broader Austronesian family: e.g. Fijian ''tabu'', Hiw (Vanuatu) ''toq'' ŌĆśholy, sacredŌĆÖ, Mwotlap ''ne-teq'' ŌĆścemeteryŌĆÖŌĆ” Fran├¦ois (2022). Whether Polynesian or not, all modern forms go back to a Proto-Oceanic etymon reconstructed as *''tabu'' . As for cognates outside Oceanic, they seem to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raglan, New Zealand
Raglan is a small beachside town located 48 km west of Hamilton, New Zealand on State Highway 23. It is known for its surfing, and volcanic black sand beaches. History The Ngāti Māhanga iwi occupied the area around Raglan in the late 18th century. There are at least 81 archaeological sites in the area, mainly near the coast. Limited radiocarbon dating puts the earliest sites at about 1400AD. The Māori people named the site ("the long pursuit"). One tradition says that Tainui priest, Rakataura, crossed Whāingaroa on his way to Kāwhia. Another says it was among the places the early Te Arawa explorer, Kahumatamomoe, with his nephew Īhenga, visited on their expedition from Maketū. The first Europeans to settle in the area, the Rev James and Mary Wallis, Wesleyan missionaries, were embraced and welcomed by local Māori in 1835. European settlement, including large scale conversion of land to pasture, began in the mid-1850s after a large sale of land by Chief Wirem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost
A ghost is the soul or spirit of a dead person or animal that is believed to be able to appear to the living. In ghostlore, descriptions of ghosts vary widely from an invisible presence to translucent or barely visible wispy shapes, to realistic, lifelike forms. The deliberate attempt to contact the spirit of a deceased person is known as necromancy, or in spiritism as a ''s├®ance''. Other terms associated with it are apparition, haunt, phantom, poltergeist, shade, specter or spectre, spirit, spook, wraith, demon, and ghoul. The belief in the existence of an afterlife, as well as manifestations of the spirits of the dead, is widespread, dating back to animism or ancestor worship in pre-literate cultures. Certain religious practicesŌĆöfuneral rites, exorcisms, and some practices of spiritualism and ritual magicŌĆöare specifically designed to rest the spirits of the dead. Ghosts are generally described as solitary, human-like essences, though stories of ghostly armies and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |