|
KO-theory
In mathematics, topological -theory is a branch of algebraic topology. It was founded to study vector bundles on topological spaces, by means of ideas now recognised as (general) K-theory that were introduced by Alexander Grothendieck. The early work on topological -theory is due to Michael Atiyah and Friedrich Hirzebruch. Definitions Let be a compact Hausdorff space and k= \R or \Complex. Then K_k(X) is defined to be the Grothendieck group of the commutative monoid of isomorphism classes of finite-dimensional -vector bundles over under Whitney sum. Tensor product of bundles gives -theory a commutative ring structure. Without subscripts, K(X) usually denotes complex -theory whereas real -theory is sometimes written as KO(X). The remaining discussion is focused on complex -theory. As a first example, note that the -theory of a point is the integers. This is because vector bundles over a point are trivial and thus classified by their rank and the Grothendieck group of the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
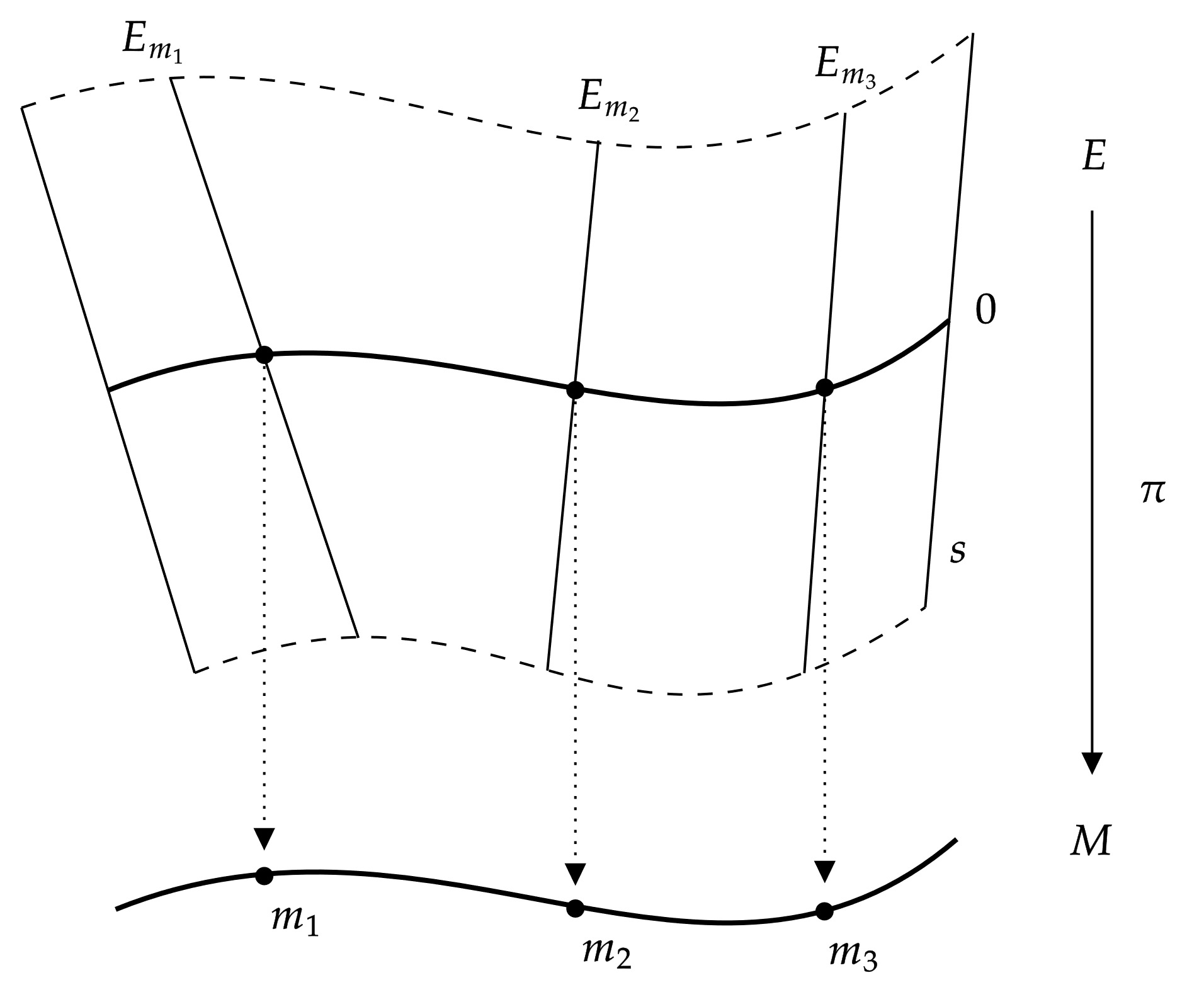
Vector Bundle
In mathematics, a vector bundle is a topological construction that makes precise the idea of a family of vector spaces parameterized by another space X (for example X could be a topological space, a manifold, or an algebraic variety): to every point x of the space X we associate (or "attach") a vector space V(x) in such a way that these vector spaces fit together to form another space of the same kind as X (e.g. a topological space, manifold, or algebraic variety), which is then called a vector bundle over X. The simplest example is the case that the family of vector spaces is constant, i.e., there is a fixed vector space V such that V(x)=V for all x in X: in this case there is a copy of V for each x in X and these copies fit together to form the vector bundle X\times V over X. Such vector bundles are said to be ''trivial''. A more complicated (and prototypical) class of examples are the tangent bundles of smooth (or differentiable) manifolds: to every point of such a manifold w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bott Periodicity Theorem
In mathematics, the Bott periodicity theorem describes a periodicity in the homotopy groups of classical groups, discovered by , which proved to be of foundational significance for much further research, in particular in K-theory of stable complex vector bundles, as well as the stable homotopy groups of spheres. Bott periodicity can be formulated in numerous ways, with the periodicity in question always appearing as a period-2 phenomenon, with respect to dimension, for the theory associated to the unitary group. See for example topological K-theory. There are corresponding period-8 phenomena for the matching theories, (real) KO-theory and ( quaternionic) KSp-theory, associated to the real orthogonal group and the quaternionic symplectic group, respectively. The J-homomorphism is a homomorphism from the homotopy groups of orthogonal groups to stable homotopy groups of spheres, which causes the period 8 Bott periodicity to be visible in the stable homotopy groups of spheres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitney Sum
In mathematics, a vector bundle is a topological construction that makes precise the idea of a family of vector spaces parameterized by another space X (for example X could be a topological space, a manifold, or an algebraic variety): to every point x of the space X we associate (or "attach") a vector space V(x) in such a way that these vector spaces fit together to form another space of the same kind as X (e.g. a topological space, manifold, or algebraic variety), which is then called a vector bundle over X. The simplest example is the case that the family of vector spaces is constant, i.e., there is a fixed vector space V such that V(x)=V for all x in X: in this case there is a copy of V for each x in X and these copies fit together to form the vector bundle X\times V over X. Such vector bundles are said to be ''trivial''. A more complicated (and prototypical) class of examples are the tangent bundles of smooth (or differentiable) manifolds: to every point of such a manifold w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernel Of A Homomorphism
In algebra, the kernel of a homomorphism (function that preserves the structure) is generally the inverse image of 0 (except for groups whose operation is denoted multiplicatively, where the kernel is the inverse image of 1). An important special case is the kernel of a linear map. The kernel of a matrix, also called the ''null space'', is the kernel of the linear map defined by the matrix. The kernel of a homomorphism is reduced to 0 (or 1) if and only if the homomorphism is injective, that is if the inverse image of every element consists of a single element. This means that the kernel can be viewed as a measure of the degree to which the homomorphism fails to be injective.See and . For some types of structure, such as abelian groups and vector spaces, the possible kernels are exactly the substructures of the same type. This is not always the case, and, sometimes, the possible kernels have received a special name, such as normal subgroup for groups and two-sided ideals fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unitary Group
In mathematics, the unitary group of degree ''n'', denoted U(''n''), is the group of unitary matrices, with the group operation of matrix multiplication. The unitary group is a subgroup of the general linear group . Hyperorthogonal group is an archaic name for the unitary group, especially over finite fields. For the group of unitary matrices with determinant 1, see Special unitary group. In the simple case , the group U(1) corresponds to the circle group, consisting of all complex numbers with absolute value 1, under multiplication. All the unitary groups contain copies of this group. The unitary group U(''n'') is a real Lie group of dimension ''n''2. The Lie algebra of U(''n'') consists of skew-Hermitian matrices, with the Lie bracket given by the commutator. The general unitary group (also called the group of unitary similitudes) consists of all matrices ''A'' such that ''A''∗''A'' is a nonzero multiple of the identity matrix, and is just the product of the unitary gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colimit
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, the abstract notion of a limit captures the essential properties of universal constructions such as products, pullbacks and inverse limits. The dual notion of a colimit generalizes constructions such as disjoint unions, direct sums, coproducts, pushouts and direct limits. Limits and colimits, like the strongly related notions of universal properties and adjoint functors, exist at a high level of abstraction. In order to understand them, it is helpful to first study the specific examples these concepts are meant to generalize. Definition Limits and colimits in a category C are defined by means of diagrams in C. Formally, a diagram of shape J in C is a functor from J to C: :F:J\to C. The category J is thought of as an index category, and the diagram F is thought of as indexing a collection of objects and morphisms in C patterned on J. One is most often interested in the case where the category J is a small or even finite category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum (homotopy Theory)
In algebraic topology, a branch of mathematics, a spectrum is an object representing a generalized cohomology theory. Every such cohomology theory is representable, as follows from Brown's representability theorem. This means that, given a cohomology theory\mathcal^*:\text^ \to \text,there exist spaces E^k such that evaluating the cohomology theory in degree k on a space X is equivalent to computing the homotopy classes of maps to the space E^k, that is\mathcal^k(X) \cong \left , E^k\right/math>.Note there are several different categories of spectra leading to many technical difficulties, but they all determine the same homotopy category, known as the stable homotopy category. This is one of the key points for introducing spectra because they form a natural home for stable homotopy theory. The definition of a spectrum There are many variations of the definition: in general, a ''spectrum'' is any sequence X_n of pointed topological spaces or pointed simplicial sets together with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contractible Space
In mathematics, a topological space ''X'' is contractible if the identity map on ''X'' is null-homotopic, i.e. if it is homotopic to some constant map. Intuitively, a contractible space is one that can be continuously shrunk to a point within that space. Properties A contractible space is precisely one with the homotopy type of a point. It follows that all the homotopy groups of a contractible space are trivial. Therefore any space with a nontrivial homotopy group cannot be contractible. Similarly, since singular homology is a homotopy invariant, the reduced homology groups of a contractible space are all trivial. For a topological space ''X'' the following are all equivalent: *''X'' is contractible (i.e. the identity map is null-homotopic). *''X'' is homotopy equivalent to a one-point space. *''X'' deformation retracts onto a point. (However, there exist contractible spaces which do not ''strongly'' deformation retract to a point.) *For any space ''Y'', any two maps ''f'',''g'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homotopy Category
In mathematics, the homotopy category is a category built from the category of topological spaces which in a sense identifies two spaces that have the same shape. The phrase is in fact used for two different (but related) categories, as discussed below. More generally, instead of starting with the category of topological spaces, one may start with any model category and define its associated homotopy category, with a construction introduced by Quillen in 1967. In this way, homotopy theory can be applied to many other categories in geometry and algebra. The naive homotopy category The category of topological spaces Top has objects the topological spaces and morphisms the continuous maps between them. The older definition of the homotopy category hTop, called the naive homotopy category for clarity in this article, has the same objects, and a morphism is a homotopy class of continuous maps. That is, two continuous maps ''f'': ''X'' → ''Y'' are considered the same in the naive hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contravariant Functor
In mathematics, specifically category theory, a functor is a mapping between categories. Functors were first considered in algebraic topology, where algebraic objects (such as the fundamental group) are associated to topological spaces, and maps between these algebraic objects are associated to continuous maps between spaces. Nowadays, functors are used throughout modern mathematics to relate various categories. Thus, functors are important in all areas within mathematics to which category theory is applied. The words ''category'' and ''functor'' were borrowed by mathematicians from the philosophers Aristotle and Rudolf Carnap, respectively. The latter used ''functor'' in a linguistic context; see function word. Definition Let ''C'' and ''D'' be categories. A functor ''F'' from ''C'' to ''D'' is a mapping that * associates each object X in ''C'' to an object F(X) in ''D'', * associates each morphism f \colon X \to Y in ''C'' to a morphism F(f) \colon F(X) \to F(Y) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coboundary
In mathematics, a chain complex is an algebraic structure that consists of a sequence of abelian groups (or modules) and a sequence of homomorphisms between consecutive groups such that the image of each homomorphism is included in the kernel of the next. Associated to a chain complex is its homology, which describes how the images are included in the kernels. A cochain complex is similar to a chain complex, except that its homomorphisms are in the opposite direction. The homology of a cochain complex is called its cohomology. In algebraic topology, the singular chain complex of a topological space X is constructed using continuous maps from a simplex to X, and the homomorphisms of the chain complex capture how these maps restrict to the boundary of the simplex. The homology of this chain complex is called the singular homology of X, and is a commonly used invariant of a topological space. Chain complexes are studied in homological algebra, but are used in several areas of math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |