|
Kyzylart
Kyzylart Pass (russian: Кызыл-Арт; ky, Кызыл-Арт ашуусу) is a mountain pass and border crossing in the Trans-Alay Range on the border of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. The highest point is 4,280 m (14,042 ft). The border checkpoint on the Kyrgyz side is Bor-Döbö. accessed 31 January 2022. The area is typically rugged and dry. It is crossed by the which leads south from in the up onto the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamir Highway
The M41, known informally and more commonly as the Pamir Highway (russian: Памирский тракт, translit=Pamirsky Trakt ), is a road traversing the Pamir Mountains through Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan with a length of over 1,200 km. It is the only continuous route through the difficult terrain of the mountains and is the main supply route to Tajikistan's Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region. The route has been in use for millennia, as there are a limited number of viable routes through the high Pamir Mountains. The road formed one link of the ancient Silk Road trade route. M41 is the Soviet road number, but no road number is generally signposted along the road today, only destinations. Route description Sources disagree on the termini of the highway, with Mazari Sharif, Afghanistan; Termiz, Uzbekistan; Dushanbe, Tajikistan; and Khorog, Tajikistan all being offered as the beginning of the highway. All sources, however, agree that the highway e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Central Asia. It has an area of and an estimated population of 9,749,625 people. Its capital and largest city is Dushanbe. It is bordered by Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east. It is separated narrowly from Pakistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor. The traditional homelands of the Tajiks include present-day Tajikistan as well as parts of Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. The territory that now constitutes Tajikistan was previously home to several ancient cultures, including the city of Sarazm of the Neolithic and the Bronze Age and was later home to kingdoms ruled by people of different faiths and cultures, including the Oxus civilization, Andronovo culture, Buddhism, Nestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Alay Range
russian: Заалайский хребет , etymology = , photo = Alai Valley 1.jpg , photo_caption = Trans-Alay Range and Alay Valley , photo_size = 250 , country = Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan , state = , region = Osh Province, Gorno-Badakshan , district = , border = , highest = Lenin Peak , elevation_m = 7134 , range_coordinates = , length_km = 250 , length_orientation = E-W , width_km = 40 , width_orientation = N-S , area_km2 = , geology = Limestone and schist , orogeny = , period = Paleozoic and Mesozoic , coordinates = , map = Tajikistan , map_caption = Location in Tajikistan , label_position = none , language = ky The Trans-Alay Range ( ky, Чоң Алай кырка тоосу, Chong Alay kyrka toosu; russian: Заалайский хребет, translit=Zaalaisky Khrebet; also 'Trans Alai') is the northernmost range of the Pamir Mountain System. Geography The Trans-Alay is located in the area where the Pamirs and the Tian Shan come together. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
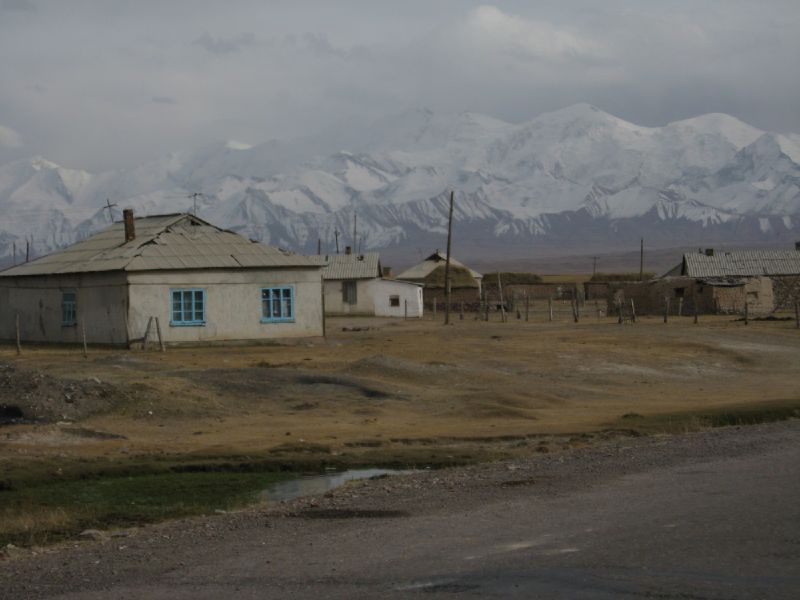
Sary-Tash
, native_name_lang = ky , settlement_type = , image_skyline = Sary Tash, Kirghizstan.jpg , image_alt = , image_caption = Sary Tash village with the Pamir mountains , image_flag = , flag_alt = , image_seal = , seal_alt = , image_shield = , shield_alt = , nickname = , motto = , image_map = , map_alt = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Kyrgyzstan , pushpin_label_position = , pushpin_map_alt = , pushpin_map_caption = , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Kyrgyzstan , subdivision_type1 = Region , subdivision_name1 = Osh Region , subdivision_type2 = District , subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. Its capital and largest city is Bishkek. Ethnic Kyrgyz make up the majority of the country's seven million people, followed by significant minorities of Uzbeks and Russians. The Kyrgyz language is closely related to other Turkic languages. Kyrgyzstan's history spans a variety of cultures and empires. Although geographically isolated by its highly mountainous terrain, Kyrgyzstan has been at the crossroads of several great civilizations as part of the Silk Road along with other commercial routes. Inhabited by a succession of tribes and clans, Kyrgyzstan has periodically fallen under larger domination. Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many Turkic states. It was first established as the Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate later i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since many of the world's mountain ranges have presented formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human and animal migration throughout history. At lower elevations it may be called a hill pass. A mountain pass is typically formed between two volcanic peaks or created by erosion from water or wind. Overview Mountain passes make use of a gap (landform), gap, saddle (landform), saddle, col or notch (landform), notch. A topographic saddle is analogous to the mathematical concept of a saddle surface, with a saddle point marking the highest point between two valleys and the lowest point along a ridge. On a topographic map, passes are characterized by contour lines with an hourglass shape, which indicates a low spot between two higher points. In the high mountains, a difference of between the summit and the mountain is defined as a mountain pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alay Valley
The Alay Valley ( ky, Алай өрөөнү, ) is a broad, dry valley running east–west across most of southern Osh Region, Kyrgyzstan. It spreads over a length of east–west. The valley extends in north–south direction with varying width of in the west, in the central part, and in the east. The altitude of the valley ranges from near Karamyk to at Toomurun Pass with an average altitude of about . The area of the valley is . The north side is the Alay Mountains which slope down to the Ferghana Valley. The south side is the Trans-Alay Range along the Tajikistan border, with Lenin Peak, (). The western or so is more hills than valley. On the east there is the low Tongmurun pass and then more valley leading to the Irkestam border crossing to China. The eastern Kyzyl-Suu ('Red River') flows from the Tongmurun rise past Irkestam toward Kashgar. The western Kyzyl-Suu flows west from the Tongmurun rise and drains most of the valley, flowing on the north side. It exits th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
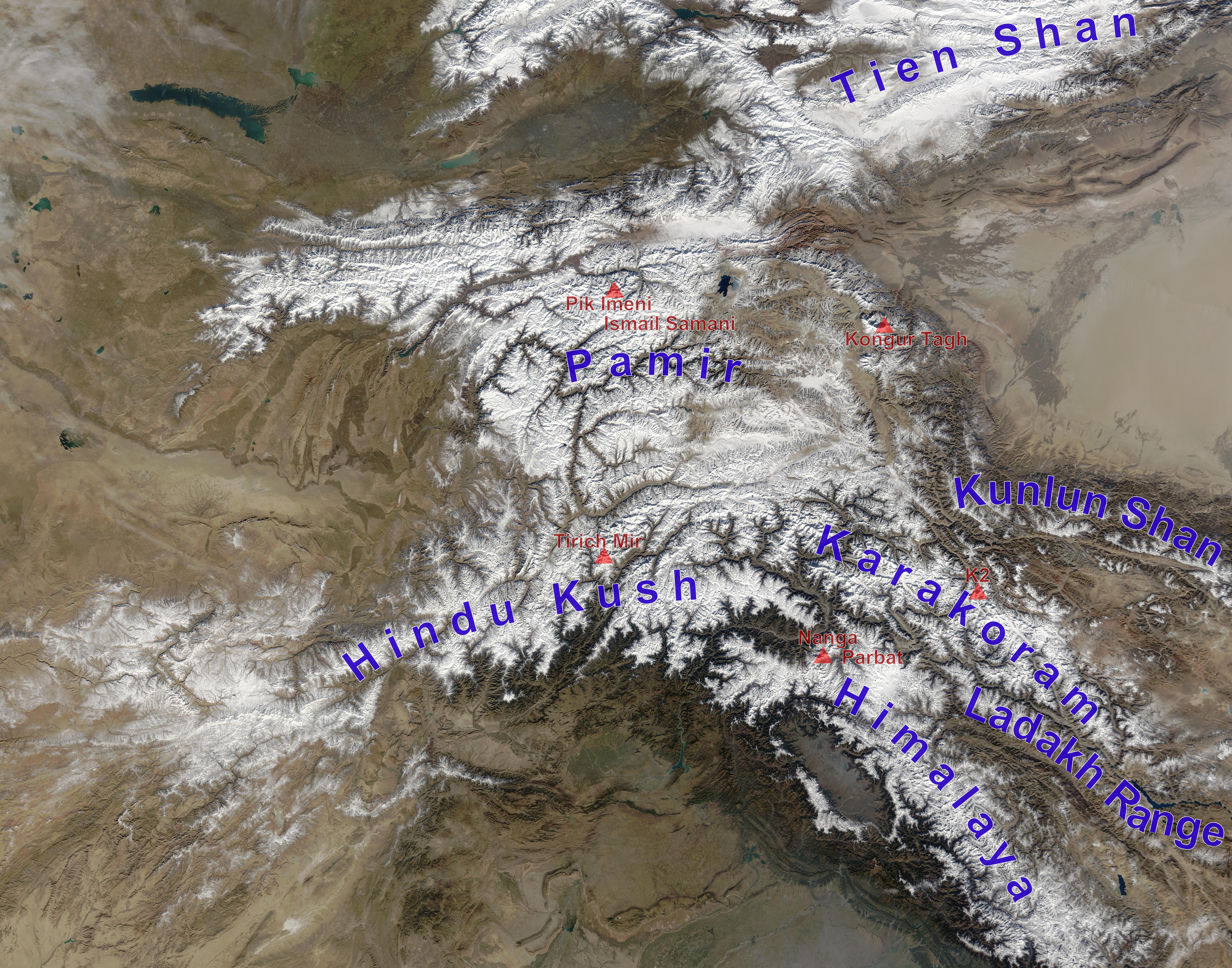
Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains. Much of the Pamir Mountains lie in the Gorno-Badakhshan Province of Tajikistan. To the south, they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in Badakhshan Province, Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan regions of Pakistan. To the north, they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the east, they extend to the range that includes China's Kongur Tagh, in the "Eastern Pamirs", separated by the Yarkand valley from the Kunlun Mountains. Name and etymology Since Victorian times, they have been known as the " Roof of the World", presumably a translation from Persian. Names In other languages they are called: ps, , ; ky, Памир тоолору, , ; fa, , Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakul (Tajikistan)
Karakul, Qarokul (Kyrgyz for "black lake", replacing the older Tajik name Siob; russian: Каракуль; tg, Қарокӯл) is a diameter lake within a rather large impact crater. It is located in the Tajik National Park in the Pamir Mountains in Tajikistan. Impact crater Karakul lies within a circular depression interpreted as an impact crater with a rim diameter of . Some estimates give its age as relatively recent. Preliminarily, it was thought to be c. 25 Ma or less than 23 Ma. However, it may even be from the recent Pliocene (5.3 to 2.6 Ma). The Earth Impact Database (EID) also lists it as younger than 5 Ma. It is larger than the Eltanin impact (2.5 Ma), which has already been suggested as a contributor to the cooling and ice cap formation in the Northern Hemisphere during the late Pliocene. The Karakul impact structure was first identified around 1987 through studies of imagery taken from space. Lake description The lake/crater lies at an el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murghab, Tajikistan
Murghob ( tg, Мурғоб) or Murghab (russian: Мургаб, from the Persian word ''margh-ab'', meaning 'prairie river') is the capital of Murghob District in the Pamir Mountains of Gorno-Badakhshan, Tajikistan. With a population of just under 7,500, Murghob is the only significant town in the eastern half of Gorno-Badakhshan. It is the highest town in Tajikistan (and of the former Soviet Union) at 3,650 meters above sea level. It is where the Pamir Highway crosses the Bartang river.Jamoat-level basic indicators United Nations Development Programme in Tajikistan, accessed 5 October 2020 The Pamir Highway goes north to Sary-Tash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Passes Of Tajikistan
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Passes Of Kyrgyzstan
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |