|
Kyaswa
Kyaswa ( my, ကျစွာ, ; 1198–1251) was the king of the Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1235 to 1251. Kyaswa succeeded his father Htilominlo and was even more devout.Harvey 1925: 59Coedès 1968: 183 Kyaswa's reign like his father's was largely peaceful but the depletion of the royal treasury due to large tax-free religious landholdings became more pronounced. The royal treasury was so depleted that Kyaswa had trouble completing a temple. The empire founded by Anawrahta over two centuries earlier was still peaceful but already on its last legs, unprepared for the internal disorders and external forces that were to come. Early life Kyaswa was born to Prince Zeya Theinkha and his wife Eindawthe. An inscription donated by his maternal aunt (younger sister of his mother) states that Kyaswa was born on Monday, 4 May 1198 at 4 o'clock in the morning.Kala Vol. 1 2006: 232, per footnote #2 by the Universities Historical Research The date is two weeks later than 20 April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Heirs To The Burmese Thrones
This is a list of the individuals who were, at any given time, considered the next in line to succeed the Burmese monarch to inherit the throne of various History of Burma, Burmese kingdoms (849–1885). Those who actually succeeded at any future time are shown in bold. Pagan Kingdom Pinya Kingdom Sagaing Kingdom Ava Kingdom Hanthawaddy Kingdom, Ramanya Prome Kingdom Toungoo Dynasty The dates after 1582 are according to the Gregorian calendar. Konbaung Dynasty Thibaw Min was deposed and exiled in 1885. He died in exile in India in 1916. He was succeeded as head of the family by his daughter Myat Phaya (1925–1956). From 1956 to 2019, the claimant to the throne was Taw Phaya, the second son of Princess Myat Phaya Galay. References Bibliography * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Heirs To The Burmese Thrones, List Of Lists of Burmese people, Burmese monarchs Lists of Burmese monarchs Heirs to the Burmese throne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazathingyan Of Pagan
Yazathingyan ( my, ရာဇသင်္ကြန်, ; also spelled Yaza Thingyan or Yazathinkyan; 1198/1199–1260) was the chief minister of kings Kyaswa, Uzana, and Narathihapate of the Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). He was also the commander-in-chief of the Royal Burmese Army from 1258 until his death in 1260. Ava kings from Swa Saw Ke to Narapati II and all Konbaung kings were descended from him. Background He was a descendant of the 11th-century general Nyaung-U Hpi.Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 360 That he was married to a daughter of King Kyaswa and that he became the chief minister show that he hailed from a (distant) branch of the royal family.(Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 360): He was married to Saw Khin Htut, daughter of King Kyaswa by queen Yaza Dewi. Per (Aung-Thwin 1985: 130–131), ministers of the court were usually drawn from more distant branches of the royal family. Their subordinates were not royal but usually hailed from top official families. He was born c. 1198/99.B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzana Of Pagan
Uzana ( my, ဥဇနာ, ; also known as Sithu III; 1213–1256) was king of Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1251 to 1256.Coedès 1968: 183 He assumed the regnal name "Śrī Tribhuvanāditya Dhammarājajayasūra" (ၐြီတြိဘုဝနာဒိတျဓမ္မရာဇဇယသူရ). Although his actual reign lasted only five years, Uzana was essentially the power behind the throne during his predecessor Kyaswa's reign, 1235–1251. Kyaswa, a devout Buddhist and scholar, had given Uzana full royal authority to govern the kingdom to the business of governing the country.Harvey 1925: 59 However Uzana reportedly cared more about chasing elephants, and drinking liquor than governing during his father's or his reign. As king, he left the task of governing to his chief minister Yazathingyan. The king was accidentally killed at Dala (modern Twante) in May 1256 while hunting elephants.Htin Aung 1967: 65 His death was followed by a brief power struggle for the throne. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Htilominlo
Htilominlo ( my, ထီးလိုမင်းလို, ; also called Nadaungmya or Zeya Theinkha Uzana; 1175 – 1235) was king of Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1211 to 1235. His 24-year reign marked the beginning of the gradual decline of Pagan dynasty. It was the first to see the impact of over a century of continuous growth of tax-free religious wealth, which had greatly reduced the potential tax base. Htilominlo was the last of the temple builders although most of his temples were in remote lands not in the Pagan region, reflecting the deteriorating state of royal treasury.Htin Aung 1967: 50–54 All the royal chronicles say he was succeeded by his son Kyaswa. But two contemporary inscriptions indicate that another son of his Naratheinga Uzana was at least acting as the regent towards the end of his reign.Htin Aung 1970: 43Than Tun 1964: 131–132 Early life Htilominlo was born to King Sithu II and his queen Saw Mya Kan. Chronicles do not agree on the birth, dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eindawthe (Htilominlo)
, image = , caption = , reign = , coronation = , succession = , predecessor = , successor = , spouse = Htilominlo , issue = Naratheinga Uzana Kyaswa , issue-link = , full name = , house = Pagan , father = Theinkhathu , mother = , birth_date = 1170s , birth_place = , death_date = 11 May 1198 , death_place = Pagan (Bagan)? , date of burial = , place of burial = , religion = Theravada Buddhism , signature = Eindawthe ( my, အိမ်တော်သည်, ) was a wife of Prince Zeya Theinkha (later King Htilominlo). She was the mother of Regent Naratheinga Uzana (r. 1231–35) and King Kyaswa Kyaswa ( my, ကျစွာ, ; 1198–1251) was the king of the Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burmese Monarchs
This is a list of the monarchs of Burma (Myanmar), covering the monarchs of all the major kingdoms that existed in the present day Burma (Myanmar). Although Burmese chronicles, Burmese chronicle tradition maintains that various monarchies of Burma (Mon people, Mon, Bamar people, Burman, Rakhine people, Arakanese), began in the 9th century Common Era, BCE, historically verified data date back only to 1044 CE at the accession of Anawrahta of Pagan dynasty, Pagan. The farther away the data are from 1044, the less verifiable they are. For example, the founding of the city of Pagan (Bagan) in the 9th century is verifiable–although the accuracy of the actual date, given in the Chronicles as 849, remains in question–but the founding of early Pagan dynasty, given as the 2nd century, is not.Harvey 1925: 364 For early kingdoms, see List of early and legendary monarchs of Burma. The reign dates follow the latest available dates as discussed in each section. Early kingdoms * See List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naratheinga Uzana
Naratheinga Uzana ( my, နရသိင်္ဃ ဥဇနာ, ; also known as Naratheinkha Uzana; 1190s–1235) was the regent of Pagan from c. 1231 to 1235. He was crown prince prior to his regency. He is regarded by some historians G.H. Luce and Than Tun as king between 1231 and 1235 but others Htin Aung and Michael Aung-Thwin Michael Aung-Thwin (1946 – August 14, 2021) was a Burmese American historian and emeritus professor at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, specializing in early Southeast Asian and Burmese history. Early life and education Aung-Thwin wa ... do not accept him as king.Htin Aung 1970: 43Than Tun 1964: 131–132Aung-Thwin and Aung-Thwin 2012: 99 One contemporary stone inscription identifies him as the crown prince, and another identifies him as the king. Neither inscription provides any regnal dates but they were conjecturally dated c. 1230 or c. 1231 by Luce. Luce and Than Tun accept that he was king. It is not universally accepted. Htin Aung d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saw Khin Htut Of Pagan
Saw Khin Htut ( my, စောခင်ထွတ်, ) was a princess of the Pagan Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). She was a daughter of King Kyaswa, and the mother of Queen Saw Soe.Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 360 Her husband was Yazathingyan who served as the chief minister of her father, and his two successors. She had at least two children Saw San and Saw Soe with Yazathingyan. She may also be the mother of Yazathingyan's two other children Ananda Pyissi and Yanda Pyissi Yanda Pyissi ( my, ရန္တ ပစ္စည်း, ; also spelled Rantapyissi; 1240s – 1284) was a minister in the service of King Narathihapate of the Pagan Dynasty of Burma (Myanmar). He was also a general in the Royal Burmese Army under ..., who were generals in the Pagan army, although chronicles do not explicitly identify her as the mother. References Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Khin Htut, Saw Pagan dynasty 13th-century Burmese women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaza Dewi Of Pagan
Yaza Dewi ( my, ရာဇဒေဝီ, ) was the chief queen consort of King Kyaswa of Pagan Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. .... Her personal name was Shin Pwa Oo (ရှင်ဘွားဦး).Hmannan Vol. 1 2003: 360 References Bibliography * * * {{Queens consort of Pagan Chief queens consort of Pagan 13th-century Burmese women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thonlula
Ti Lawka Sanda II , image = , caption = , reign = May 1251 – May 1256 , coronation = , succession = Chief queen consort of Burma , predecessor = Yaza Dewi , successor = Yadanabon II , suc-type = Successor , reg-type = , regent = , spouse = Uzana of Pagan , issue = Thihathu of Pagan , issue-link = , full name = , house = Pagan , father = Kyaswa , mother = Yaza Dewi , birth_date = 1220s , birth_place = Pagan (Bagan) , death_date = ? , death_place = Pagan , date of burial = , place of burial = , religion = Theravada Buddhism , signature = Ti Lawka Sanda ThonlulaThonlula is the direct translation of Ti Lawka Sanda, which is the Burmese transcription of Pali Ti-Loka Canda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
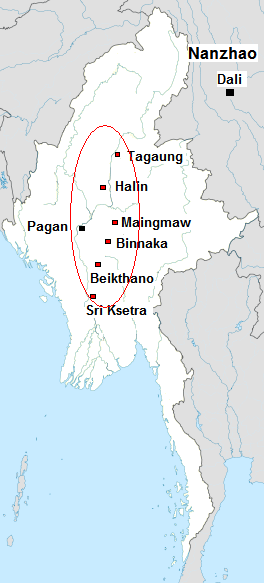
Pagan Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazawin Thit
''Maha Yazawin Thit'' ( my, မဟာ ရာဇဝင် သစ်, ; ; also known as ''Myanmar Yazawin Thit'' or ''Yazawin Thit'') is a national chronicle of Burma (Myanmar). Completed in 1798, the chronicle was the first attempt by the Konbaung court to update and check the accuracy of ''Maha Yazawin'', the standard chronicle of the previous Toungoo Dynasty. Its author Twinthin Taikwun Maha Sithu consulted several existing written sources, and over 600 stone inscriptions collected from around the kingdom between 1783 and 1793.Thaw Kaung 2010: 44–49 It is the first historical document in Southeast Asia compiled in consultation with epigraphic evidence.Woolf 2011: 416 The chronicle updates the events up to 1785, and contains several corrections and critiques of earlier chronicles. However, the chronicle was not well received, and ultimately rejected by the king and the court who found the critiques of earlier chronicles excessively harsh.Thaw Kaung 2010: 50–51 It became kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |