|
Kutch Embroidery
The Kutch Embroidery is a handicraft and textile signature art tradition of the tribal community of Kutch District in Gujarat and Sindh. This embroidery with its rich designs has made a notable contribution to the Indian embroidery traditions. The embroidery, practiced normally by women is generally done on fabrics of cotton, in the form of a net using cotton or silk threads. In certain patterns, it is also crafted over silk and satin. The types of stitches adopted are “square chain, double buttonhole, pattern darning, running stitch, satin and straight stitches”. The signature effect of the colorful embroidery sparkles when small mirrors called ''abhla'' are sewn over the geometrically shaped designs. Depending on the tribal sub groups of Rabari, Garasia Jat, and Mutava involved with this craft work many hand embroidered ethnic styles have evolved. These six styles: Suf, khaarek, paako, Rabari, Garasia Jat, and Mutava. This embroidery product of Kutch has been registered for p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat And Sindh
Gujarat (, ) is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories of India by area, fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the List of states and union territories of India by population, ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujarati people, Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state List of Indus Valley civilisation sites#List of Indus Valley sites discovered, encompas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mochi (Hindu)
The Mochi are a Hindu caste found mainly in North India. They are the traditional shoemakers of South Asia. History and origin Historically, the community was involved in the manufacture of protective leather crafts. Gangaramji Dhuldhoye worked for their upliftment in Central India. Present circumstances In Gujarat, the Mochi caste is categorised as OBC in Bakshi Panch. They belong to the Rajput Clan and are mostly from Saurashtra (Kathiyawad). The Mochi are involved in the manufacture of leather shoes. The community has a traditional caste council, as is common among many North Indian artisan communities. This caste council acts as an instrument of social control, by punishing those who contravene community norms. Each caste council is headed by a Chaudhary, a position that tends to be hereditary. The Mochi live in multi-caste villages, but occupy their own distinct quarters. The Mochi of Haryana claim to have migrated from Rajasthan, and are found mainly in the canto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Culture
The culture of Gujarat is both ancient, new, and modern. Gujarati engagement ceremony ''In many Gujarati communities, the engagement ceremony is known as 'Gol Dhana', which does not include a ring ceremony''. (in Gujarati alphabet, Gujarati script, ગોળ-ધાણા), which literally means "Jaggery and Coriander seeds" and refers to the practice of distributing a small amount of jaggery mixed with coriander seeds. Gujarati Hindu ceremony Marriage is a highly auspicious occasion in Indian culture. According to the Vedas, the Hindu scriptures, marriage is a sacred lifelong commitment between a man and a woman. It is considered to be the strongest of all social bonds and is the initiation into a lifetime of togetherness. The Vedic wedding ceremony consists of prayers, invocations, and vows recited in Sanskrit, the most ancient surviving language. The Vedic wedding ceremony dates back to over five thousand years and is performed under a decorated canopy, the ''mandap''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embroidery In India
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on caps, hats, coats, overlays, blankets, dress shirts, denim, dresses, stockings, scarfs, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. Some of the basic techniques or stitches of the earliest embroidery are chain stitch, buttonhole or blanket stitch, running stitch, satin stitch, and cross stitch. Those stitches remain the fundamental techniques of hand embroidery today. History Origins The process used to tailor, patch, mend and reinforce cloth fostered the development of sewing techniques, and the decorative possibilities of sewing led to the art of embroidery. Indeed, the remarkable stability of basic embroidery stitches has been noted: The art of embroidery has been found worldwide and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silk In The Indian Subcontinent
Silk In India, about 97% of the raw mulberry silk is produced in the Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. Mysore and North Bangalore, the upcoming site of a US$20 million "Silk City", contribute to a majority of silk production. Another emerging silk producer is Tamil Nadu where mulberry cultivation is concentrated in Salem, Erode and Dharmapuri districts. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh and Gobichettipalayam, Tamil Nadu were the first locations to have automated silk reeling units. History Indus Valley Civilisation Recent archaeological discoveries in Harappa and Chanhudaro suggest that sericulture, employing wild silk threads from native silkworm species, existed in South Asia during the time of the Indus Valley civilisation dating between 2450 BC and 2000 BC. The Indus silks were obtained from more than one species ''Antheraea'' and ''Philosamia'' (eri silk). ''Antheraea assamensis'' and '' A. paphia'' were widely used. These findings were pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embroidered Hanging, Kutch (western India
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on caps, hats, coats, overlays, blankets, dress shirts, denim, dresses, stockings, scarfs, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. Some of the basic techniques or stitches of the earliest embroidery are chain stitch, buttonhole or blanket stitch, running stitch, satin stitch, and cross stitch. Those stitches remain the fundamental techniques of hand embroidery today. History Origins The process used to tailor, patch, mend and reinforce cloth fostered the development of sewing techniques, and the decorative possibilities of sewing led to the art of embroidery. Indeed, the remarkable stability of basic embroidery stitches has been noted: The art of embroidery has been found worldwide a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Rajput covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities. Over time, the Rajputs emerged as a social class comprising people from a variety of ethnic and geographical backgrounds. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the membership of this class became largely hereditary, although new claims to Rajput status continued to be made in the later centuries. Several Rajput-ruled kingdoms played a significant role in many regions of central and northern India from seventh century onwards. The Rajput population and the former Rajput stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
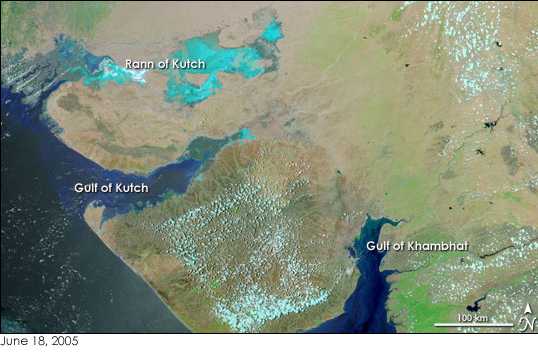
Great Rann Of Kutch
The Great Rann of Kutch (or Rann of Kutch seasonal salt marsh) is a salt marsh in the Thar Desert in the Kutch District of Gujarat, India. It is about 7500 km2 (2900 sq miles) in area and is reputed to be one of the largest salt deserts in the world. This area has been inhabited by the Kutchi people. The Hindi word is derived from Sanskrit/Vedic word ' (इरिण) attested in the Rigveda and Mahabharata. It is an extension of the Thar Desert. Location and description The Little Rann of Kutch, including the Banni grasslands on its southern edge, is situated in the district of Kutch and comprises some between the Gulf of Kutch and the mouth of the Indus River in southern Pakistan. The marsh can be accessed from the village of Kharaghoda in Surendranagar District. The Great Rann of Kutch together with the Little Rann of Kutch is called Rann of Kutch. In India's summer monsoon, the flat semi-desert of salty clay and mudflats, which average 15 meters above sea lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banni Grasslands Reserve
Banni Grasslands Reserve or Banni grasslands form a belt of arid grassland ecosystem on the outer southern edge of the desert of the marshy salt flats of Rann of Kutch in Kutch District, Gujarat State, India. They are known for rich wildlife and biodiversity and are spread across an area of 3,847 square kilometres. They are currently legally protected under the status as a protected or reserve forest in India. Though declared a protected forest more than half a century ago Gujarat state's forest department has recently proposed a special plan to restore and manage this ecosystem in the most efficient way. Wildlife Institute of India (WII) has identified this grassland reserve as one of the last remaining habitats of the cheetah in India and a possible reintroduction site for the species. The word 'Banni' comes from Hindi word 'banai', meaning made. The land here was formed from the sediments that were deposited by the Indus and other rivers over thousands of years. Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harijan
Dalit (from sa, दलित, dalita meaning "broken/scattered"), also previously known as untouchable, is the lowest stratum of the castes in India. Dalits were excluded from the four-fold varna system of Hinduism and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Dalits now profess various religious beliefs, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, Islam. Scheduled Castes is the official term for Dalits as per the Constitution of India. History The term ''Dalit'' is a self-applied concept for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste hierarchy. Economist and reformer B. R. Ambedkar (1891–1956) said that untouchability came into Indian society around 400 CE, due to the struggle for supremacy between Buddhism and Brahmanism (an ancient term for Brahmanical Hinduism). Some Hindu priests befriended untouchables and were demoted to low-caste ranks. Eknath, another excommunicated Brahmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_according_to_Indian_Caste_System_-_1942.jpg)