|
Kura–Araxes Culture
The Kura–Araxes culture (also named ''Kur–Araz culture, Mtkvari–Araxes culture, Early Transcaucasian culture, Shengavitian culture'') was an archaeological culture that existed from about 4000 BC until about 2000 BC, which has traditionally been regarded as the date of its end; in some locations it may have disappeared as early as 2600 or 2700 BC. The earliest evidence for this culture is found on the Ararat plain; it spread north in the Caucasus by 3000 BC. Altogether, the early Transcaucasian culture enveloped a vast area approximately 1,000 km by 500 km, and mostly encompassed the modern-day territories of the Armenia, eastern Georgia, Azerbaijan, northwestern Iran, the northeastern Caucasus, eastern Turkey, and as far as northern Syria.K. Kh. Kushnareva[The Southern Caucasus in Prehistory: Stages of Cultural and Socioeconomic Development from the Eighth to the Second Millennium B.C."UPenn Museum of Archaeology, 1 Jan. 1997. p 44Antonio Sagona, Paul Zimansky"A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Caucasus
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, Georgia (country), Georgia, and Azerbaijan, which are sometimes collectively known as the Caucasian States. The total area of these countries measures about . The South Caucasus and the North Caucasus together comprise the larger Caucasus geographical region that divides Eurasia. The South Caucasus is a dynamic and complex region where the three countries have pursued distinct geopolitical pathways. Geography The South Caucasus spans the southern portion of the Caucasus Mountains and their lowlands, straddling the border between the continents of Europe and Asia, and extending southwards from the southern part of the Main Caucasian Range of southwestern Russia to the Turkey, Turkish and Armenian borders, and from the Black Sea in the west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norşuntepe
Norşuntepe is a tell, or archaeological settlement mound, in Elazığ Province (Turkey). The site was occupied between the Chalcolithic and Iron Age and is now partially submerged by Lake Keban. It was excavated between 1968 and 1974. The site and its environment Before it was flooded, Norşuntepe was located on the Altınova Plain near the mouth of the Murat River (downstream from the town of Palu, Elazığ). It is now partially submerged by the reservoir created by the Keban Dam; its top is still above the water level. The site consists of a central hill or "acropolis" measuring and high, making it the largest tell in the area. The central hill is surrounded by lower terraces encompassing an area of . History Norşuntepe was occupied from the Chalcolithic to the Iron Age. The excavators have recognized 40 different occupation levels ranging in date from the fifth millennium BC to ca. 600 BC. Its occupation levels overlap to a large degree with those excavated at nearb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic (, ) is a landlocked country, landlocked Enclave and exclave, exclave of the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a population of 459,600. It is bordered by Armenia to the east and north, Iran to the southwest, and Turkey to the west. It is the sole autonomous republic of Azerbaijan, governed by Supreme Assembly (Nakhchivan), its own elected legislature. The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan (city), Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BC. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the Provinces of the kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), cantons of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Kingdom of Armenia. Historically, the Persians, Armenians, Mongols, and Turkic peoples, Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran in the 16th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedentism
In anthropology, sedentism (sometimes called sedentariness; compare sedentarism) is the practice of living in one place for a long time. As of , the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and archaeology, ''sedentism'' takes on a slightly different sub-meaning, often applying to the transition from nomadic society to a lifestyle that involves remaining in one place permanently. Essentially, sedentism means living in groups permanently in one place. The invention of agriculture led to sedentism in many cases, but the earliest sedentary settlements were pre-agricultural. Initial requirements for permanent, non-agricultural settlements For small-scale nomadic societies it can be difficult to adopt a sedentary lifestyle in a landscape without on-site agricultural or livestock breeding resources, since sedentism often requires sufficient year-round, easily accessible local natural resources. Non-agricultural sedentism requires goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhchivan Region
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic (, ) is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a population of 459,600. It is bordered by Armenia to the east and north, Iran to the southwest, and Turkey to the west. It is the sole autonomous republic of Azerbaijan, governed by its own elected legislature. The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BC. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the cantons of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia. Historically, the Persians, Armenians, Mongols, and Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran in the 16th century. The semi-autonomous Nakhchivan Khanate was established there in the mid-18th century. In 1828, after the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Highlands
The Armenian highlands (; also known as the Armenian upland, Armenian plateau, or Armenian tableland)Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century''. Richard G. Hovannisian (ed.) New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997, pp. 1–17 comprise the most central and the highest of the three plateaus that together form the northern sector of West Asia. Clockwise starting from the west, the Armenian highlands are bounded by the Anatolia, Anatolian plateau, the Caucasus, the Kur-Araz Lowland, Kura-Aras lowlands, the Iranian Plateau, and Mesopotamia. The highlands are divided into western and eastern regions, defined by the Ararat Plain, Ararat Valley where Mount Ararat is located. Western Armenia is nowadays referred to as Eastern Anatolia. On the other hand, Eastern Armenia is part of Lesser Caucasus or Caucasus Minor, which was historically known by some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khirbet Kerak
Khirbet Kerak ( , "the ruin of the fortress") or Beth Yerah (, "House of the Moon (god)") (also Khirbat al-Karak) is a Tell (archaeology), tell (archaeological mound) located on the southern shore of the Sea of Galilee in modern-day Israel. The tell spans an area of over 50 acres—one of the largest in the Levant—and contains remains dating from the Early Bronze Age (c. 3000 BCE - 2000 BCE) and from the Achaemenid Empire, Persian period (c. 450 BCE) through to the Early Islamic period (c. 1000 CE).''The Holy Land: An Archaeological Guide from Earliest Times to 1700,'' Jerome Murphy O'Connor, Oxford University Press, 1980, p.159 Khirbet Kerak ware is a type of Early Bronze Age Syro-Palestinian archaeology#Ceramics analysis, Syro-Palestinian pottery first discovered at this site. It is also found in other parts of the Levant, including Jericho, Beth Shan, Tell Judeideh, and Ugarit. Khirbet Kerak culture appears to have been a Levantine version of the Kura–Araxes culture, Early T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
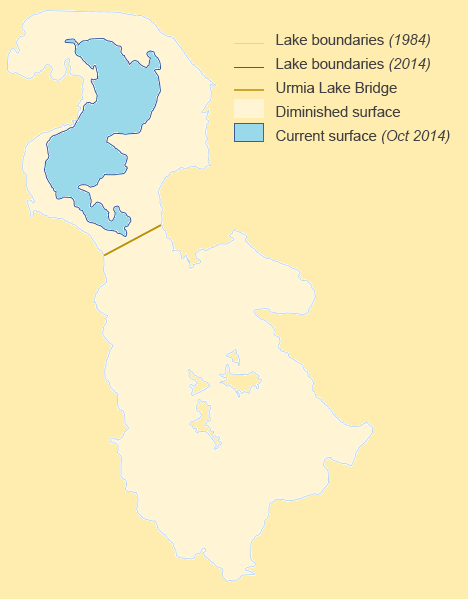
Lake Urmia
Lake Urmia is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East. It is the sixth-largest saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately , a length of , a width of , and a maximum depth of . By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size (and 1/60 of water volume in 1998) due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again, due to both increased rain and water diversion from the Zab River under the Urmia Lake Research Programme. Lake Urmia, along with its approximately 102 (former) islands, is protected as a national park by the Iranian Department of Environment. Names and et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakyol, Çemişgezek
Sakyol () is a village in the Çemişgezek District, Tunceli Province, Turkey. The village is populated by Kurds of the Şikakî tribe and by Turks. It had a population of 54 in 2021. The hamlet of Yuvacık is attached to the village. Archaeology Pulur (Sakyol) is an important prehistoric archaeological site near the village ( :tr:Pulur / Sakyol Höyük) that had been flooded by the Keban Dam. Rescue excavations were conducted here by Hamit Z. Koşay from 1968 to 1971 before the artificial lake was created. Artifacts of the Kura–Araxes culture were found, as well as some religious-oriented structures. In front of the altars, terracotta cult hearths were located, which were unique to Kura-Araxes culture. Their inner space resembled a ship bow divided into three parts; the upper platforms were red-painted and decorated with geometric figures. Statuette of women and men, as well as of worship animals, such as horses, bulls and rams were found near these hearths. The horseshoe- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a List of cities in Turkey, city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010. It is the site of ancient Theodosiopolis. The city uses the double-headed eagle as its coat-of-arms, a motif that has been a common symbol throughout Anatolia since the Bronze Age. Erzurum has winter sports facilities, hosted the 2011 Winter Universiade, and the 2023 Winter Deaflympics (in March 2024). Name and etymology The city was originally known in Armenian language, Armenian as Karno K'aghak' (), meaning city of Karin, to distinguish it from the district of Karin (wikt:Կարին, Կարին). It is presumed its name was derived from a local tribe called the Karenitis. Darbinian, M. "Erzurum," Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1978, vol. 4, p. 93. An alternate theory contends that a local princely family, the Kams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |