|
Krojanty
Krojanty ( csb, Krojantë, german: Krojanten) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Chojnice, within Chojnice County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies near the Tuchola Forest, approximately north-east of Chojnice and south-west of the regional capital Gdańsk. The village has a population of 461. History On 1 September 1939, the first day of the German invasion of Poland which started World War II, it was the site of the Skirmish of Krojanty which became an Anti-Polish sentiment, anti-Polish propaganda myth of Polish cavalry attacking German tanks. During the subsequent Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German occupation, Krojanty was one of the sites of executions of Polish people, Poles, carried out by the Germans in 1939 as part of the ''Intelligenzaktion''. Local Poles were also among the victims of the massacres in the Igielska Valley near Chojnice, perpetrated by the Germans in October and November 1939, also as part of the ''Intelligen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skirmish Of Krojanty
The charge at Krojanty, battle of Krojanty, the riding of Krojanty or skirmish of Krojanty was a Polish cavalry charge on the evening of 1 September 1939, the first day of the Second World War, near the Pomeranian village of Krojanty. It occurred at the start of the invasion of Poland and was part of the larger Battle of Tuchola Forest. Polish soldiers advanced east along the railway to a railroad crossroads from the town of Chojnice, where elements of the Polish cavalry charged and dispersed a German infantry battalion. Machine gun fire from German armoured cars that appeared from a nearby forest forced the Poles to retreat. However, the attack delayed the German advance, allowing the Polish 1st Rifle Battalion and Czersk Operational Group to withdraw safely. The incident prompted false reports of Polish cavalry attacking German tanks, after journalists saw the bodies of horses and cavalrymen. Nazi propaganda took advantage to suggest that the Poles attacked intentionally since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krojanty Railway Station
Krojanty is a PKP railway station in Krojanty (Pomeranian Voivodeship Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province (Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk. The ...), Poland. Lines crossing the station Train services The station is served by the following service(s): *Regional services (R) ''Chojnice - Czarna Woda - Starogard Gdanski - Tczew''Polregio. Chojnice - Tczew. Timetable valid from 2022.12.11 to 2023.03.1https://polregio.pl/media/21158/pi%C5%82a-g%C5%82%C3%B3wna-chojnice-tczew.pdf/ref> References *Krojanty article aPolish Stations Database URL accessed at 7 March 2006 Railway stations in Pomeranian Voivodeship Chojnice County {{Poland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Cavalry
The Polish cavalry ( pl, jazda, kawaleria, konnica) can trace its origins back to the days of medieval cavalry knights. Poland is mostly a country of flatlands and fields and mounted forces operate well in this environment. The knights and heavy cavalry gradually evolved into many different types of specialised mounted military formations, some of which heavily influenced western warfare and military science. This article details the evolution of Polish cavalry tactics, traditions and arms from the times of mounted knights and heavy winged hussars, through the times of light uhlans to mounted infantry equipped with ranged and mêlée weapons. Early medieval times The first Polish cavalry was created by the Duke of Polans - Mieszko I, who united the West Slav tribes in the area of modern Poland. It's noted in the manuscript of Abraham ben Jacob who traveled in 961–62 in Central Europe. He wrote that the drużyna of Mieszko I had 3000 men, who were paid by the duke. The Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
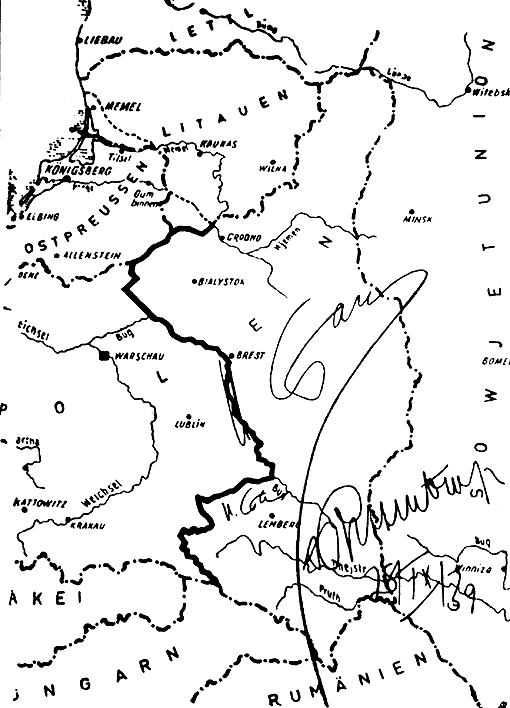
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Chojnice
__NOTOC__ Gmina Chojnice ( csb, Chojnice) is a rural gmina (administrative district) in Chojnice County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. Its seat is the town of Chojnice, although the town is not part of the territory of the gmina. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 16,014. The gmina contains parts of the protected areas of Tuchola Landscape Park and Zaborski Landscape Park. Villages Gmina Chojnice contains the villages and settlements of Angowice, Babilon, Bachorze, Białe Błota, Borne, Charzykowy, Chiny, Chociński Młyn, Chojnaty, Chojniczki, Chojniczki-Wybudowanie, Ciechocin, Cołdanki, Czartołomie, Dębowa Góra, Doręgowice, Drzewicz, Funka, Gockowice, Granowo, Grzampki, Jabłonka, Jakubowo, Jarcewo, Jasnowo, Jeziorki, Józefowo, Kamionka, Kamionka nad jeziorem Zamarte, Karolewo, Klawkowo, Kłodawa, Kłodawka, Klosnowo, Klucza, Kokoszka, Kopernica, Kopernica nad Jeziorem, Krojanty, Kruszka, Kulki, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powiat
A ''powiat'' (pronounced ; Polish plural: ''powiaty'') is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture ( LAU-1, formerly NUTS-4) in other countries. The term "''powiat''" is most often translated into English as "county" or "district" (sometimes "poviat"). In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term ''hrabstwo'' (an administrative unit administered/owned by a ''hrabia'' (count) is also literally translated as "county". A ''powiat'' is part of a larger unit, the voivodeship (Polish ''województwo'') or province. A ''powiat'' is usually subdivided into '' gmina''s (in English, often referred to as "communes" or "municipalities"). Major towns and cities, however, function as separate counties in their own right, without subdivision into ''gmina''s. They are termed " city counties" (''powiaty grodzkie'' or, more formally, ''miasta na prawach powiatu'') and have roughly the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Polish Sentiment
Polonophobia, also referred to as anti-Polonism, ( pl, Antypolonizm), and anti-Polish sentiment are terms for negative attitudes, prejudices, and actions against Poles as an ethnic group, Poland as their country, and their culture. These include ethnic prejudice against Poles and persons of Polish descent, other forms of discrimination, and mistreatment of Poles and the Polish diaspora. This prejudice led to mass killings and genocide or it was used to justify atrocities both before and during World War II, most notably by the German Nazis and Ukrainian nationalists. While Soviet repressions and massacres of Polish citizens were ideologically motivated, the negative attitude of Soviet authorities to the Polish nation is well-attested. Nazi Germany killed between 1.8 to 2.7 million ethnic Poles, 140,000 Poles were deported to Auschwitz where at least half of them perished. Anti-Polish sentiment includes stereotyping Poles as unintelligent and aggressive, as thugs, thieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperial Germany in World War I (1914–1918), as the core element of the of territorial expansion. The most extreme form of this ideology was supported by the Nazi Party and Nazi Germany. was a leading motivation of Nazi Germany to initiate World War II, and it would continue this policy until the end of World War II.Woodruff D. Smith. The Ideological Origins of Nazi Imperialism. Oxford University Press. p. 84. Following Adolf Hitler's rise to power, became an ideological principle of Nazism and provided justification for the German territorial expansion into Central and Eastern Europe. The Nazi policy () was based on its tenets. It stipulated that Germany required a ' necessary for its survival and that most of the indigenous populations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die besetzten polnischen Gebiete), was a German zone of occupation established after the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany, Slovakia and the Soviet Union in 1939 at the onset of World War II. The newly occupied Second Polish Republic was split into three zones: the General Government in its centre, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany in the west, and Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union in the east. The territory was expanded substantially in 1941, after the German Invasion of the Soviet Union, to include the new District of Galicia. The area of the ''Generalgouvernement'' roughly corresponded with the Austrian part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth after the Third Partition of Poland in 1795. The basis for the formation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expulsion Of Poles By Nazi Germany
The Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany during World War II was a massive operation consisting of the forced resettlement of over 1.7 million Poles from the territories of German-occupied Poland, with the aim of their Germanization (see Lebensraum) between 1939 and 1944. The German Government had plans for the extensive colonisation of territories of occupied Poland, which were annexed directly into Nazi Germany in 1939. Eventually these plans grew bigger to include parts of the General Government. The region was to become a "purely German area" within 15–20 years, as explained by Adolf Hitler in March 1941. By that time the General Government was to be cleared of 15 million Polish nationals, and resettled by 4–5 million ethnic Germans. The operation was the culmination of the expulsion of Poles by Germany carried out since the 19th century, when Poland was partitioned among foreign powers including Germany. Racial policies Following the German invasion of the country, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of National Remembrance
The Institute of National Remembrance – Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation ( pl, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej – Komisja Ścigania Zbrodni przeciwko Narodowi Polskiemu, abbreviated IPN) is a Polish state research institute in charge of education and archives with investigative and lustration powers. The IPN was established by the Polish parliament by the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance of 18 December 1998, which incorporated the earlier Main Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation of 1991. IPN itself had replaced a body on Nazi crimes established in 1945. In 2018, IPN's mission statement was amended by the controversial Amendment to the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance to include "protecting the reputation of the Republic of Poland and the Polish Nation". The IPN investigates Nazi and Communist crimes committed between 1917 and 1990, documents its findings, and disseminates them to the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |