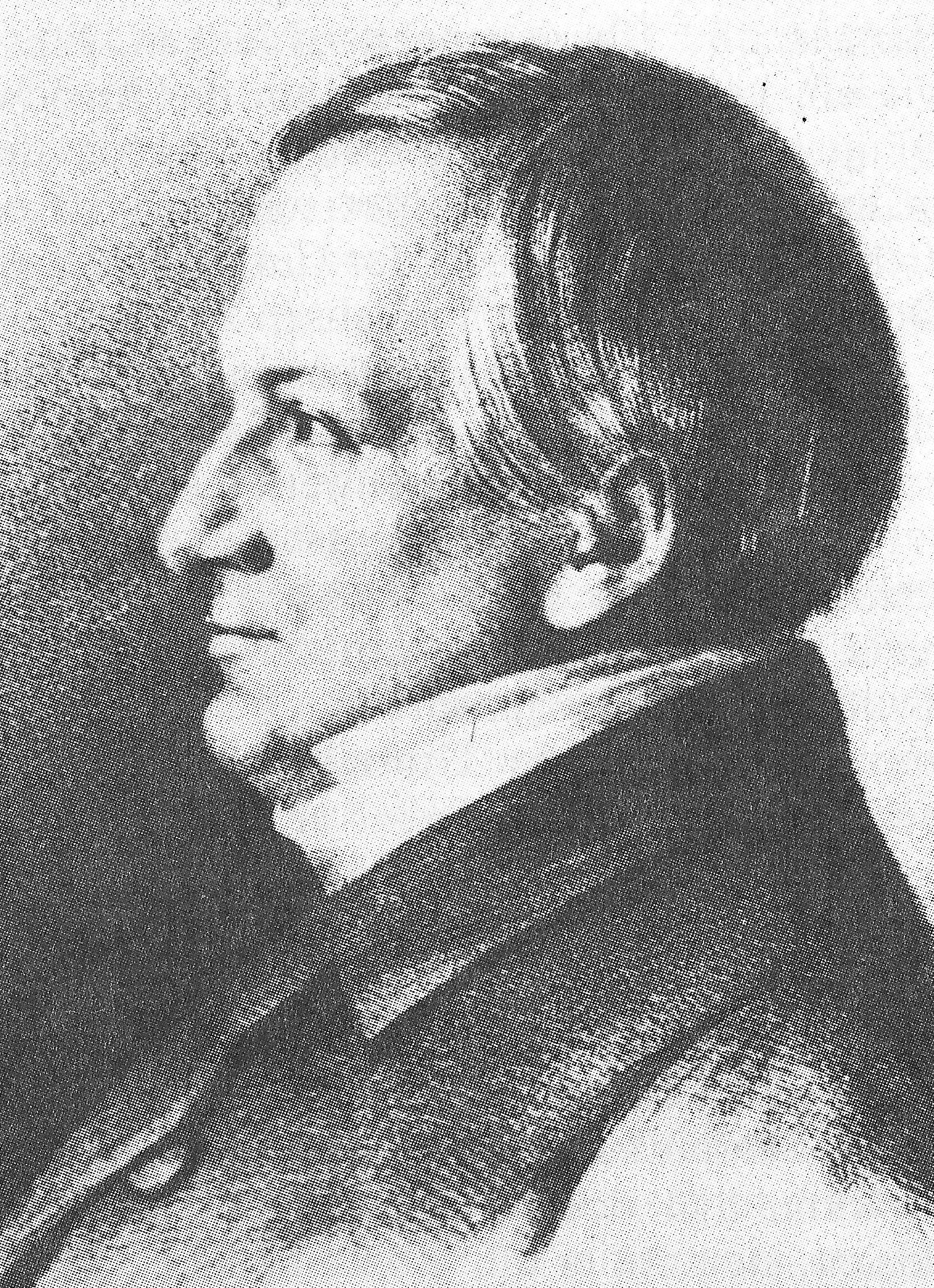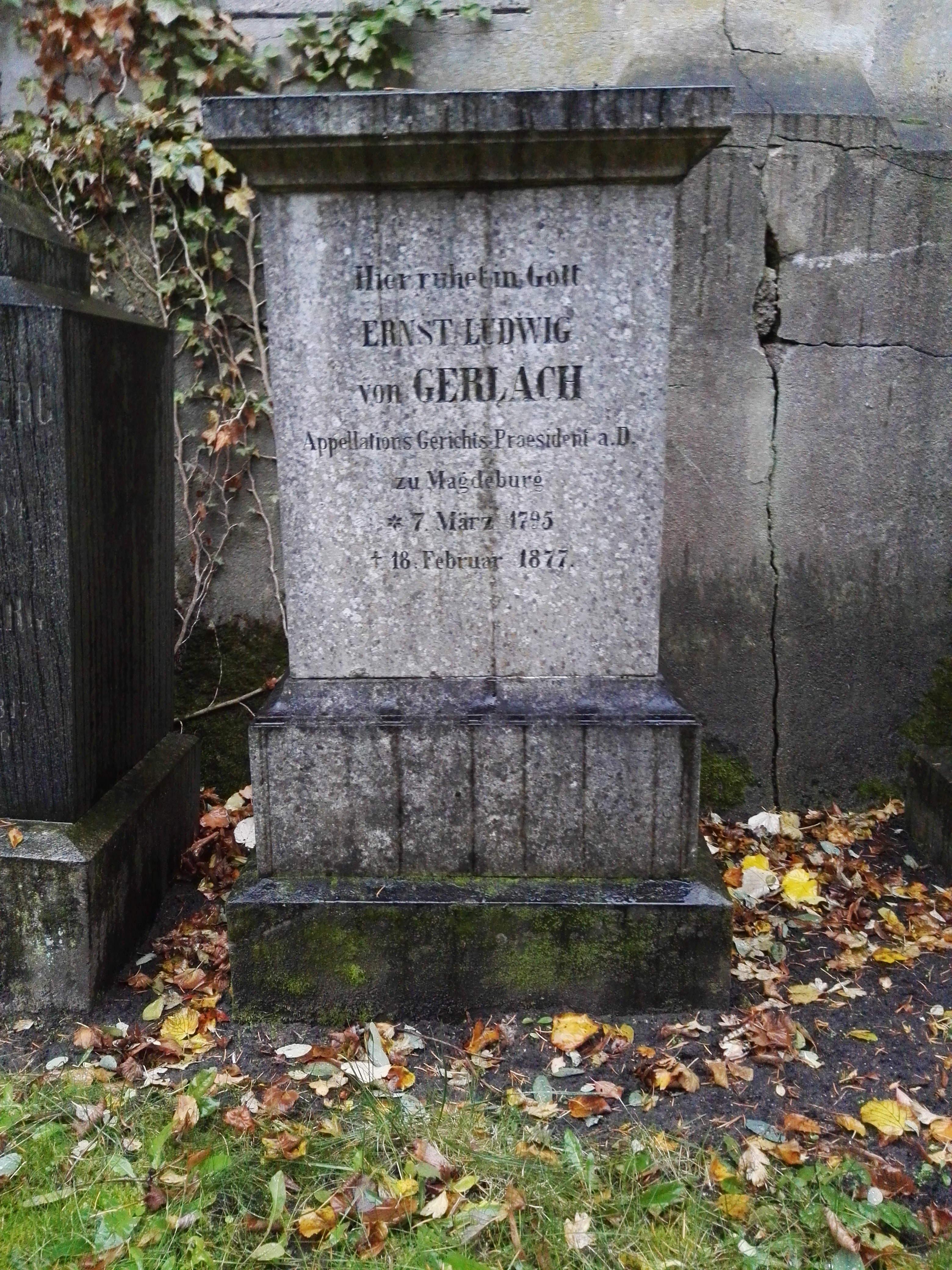|
Kreuzzeitung
The ''Kreuzzeitung'' was a national daily newspaper published between 1848 and 1939 in the Kingdom of Prussia and then during the German Empire, the Weimar Republic and into the first part of the Nazi Germany, Third Reich. The paper was a voice of the conservative upper class, although it was never associated with any political party and never had more than 10,000 subscribers. Its target readership was the nobility, military officers, high-ranking officials, industrialists and diplomats. Because its readers were among the elite, the ''Kreuzzeitung'' was often quoted and at times very influential. It had connections to officials in the highest levels of government and business and was especially known for its foreign reporting. Most of its content consisted of carefully researched foreign and domestic news reported without commentary. Its original name was officially the (''New Prussian Newspaper''), although because of the Iron Cross as its emblem in the title, it was simply calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreuzzeitung Titel Ab 1848
The ''Kreuzzeitung'' was a national daily newspaper published between 1848 and 1939 in the Kingdom of Prussia and then during the German Empire, the Weimar Republic and into the first part of the Nazi Germany, Third Reich. The paper was a voice of the conservative upper class, although it was never associated with any political party and never had more than 10,000 subscribers. Its target readership was the nobility, military officers, high-ranking officials, industrialists and diplomats. Because its readers were among the elite, the ''Kreuzzeitung'' was often quoted and at times very influential. It had connections to officials in the highest levels of government and business and was especially known for its foreign reporting. Most of its content consisted of carefully researched foreign and domestic news reported without commentary. Its original name was officially the (''New Prussian Newspaper''), although because of the Iron Cross as its emblem in the title, it was simply calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
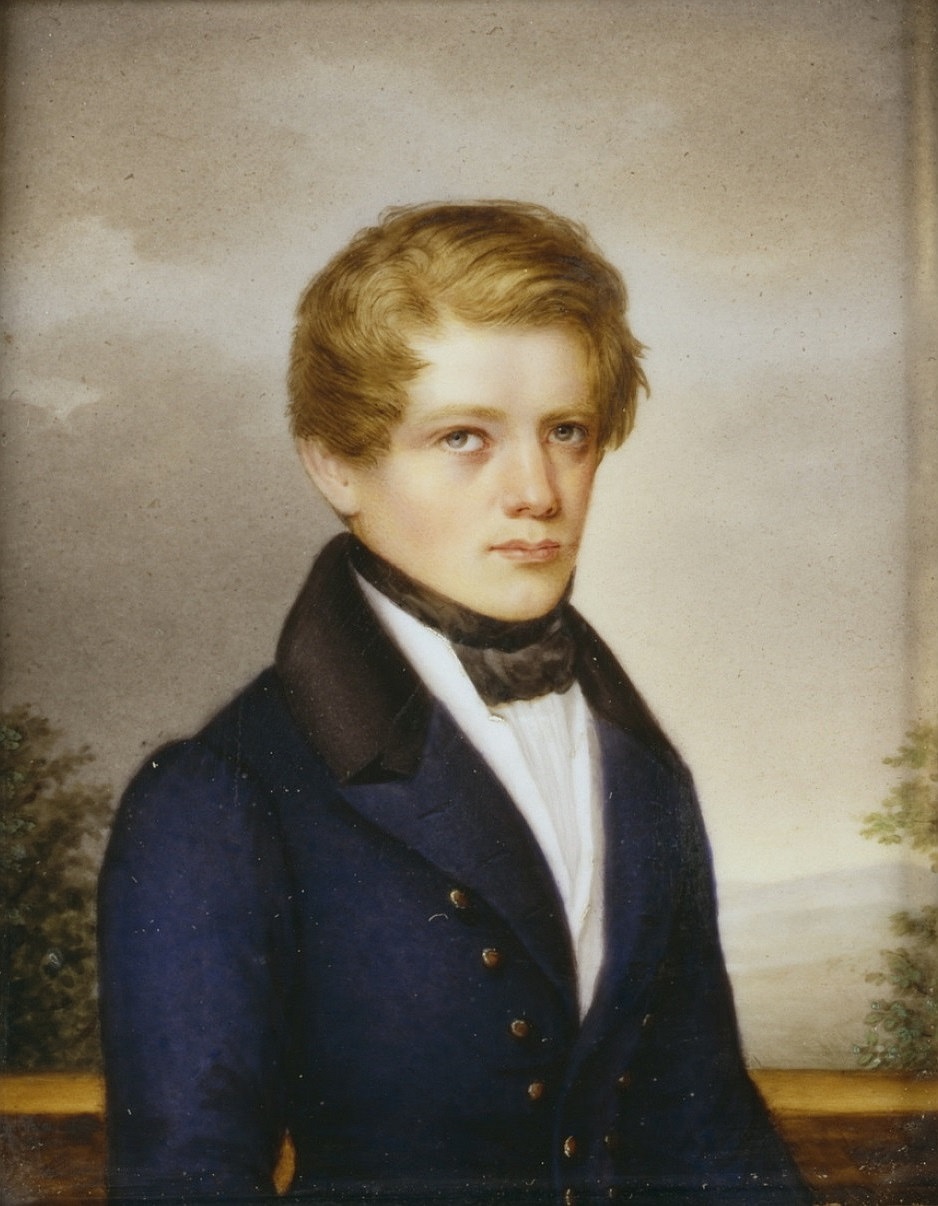
Ernst Ludwig Von Gerlach
Ernst Ludwig von Gerlach (7 March 1795 – 18 February 1877) was a Prussian politician, editor and judge. He is considered one of the main founders and leading thinkers of the Conservative Party in Prussia and was for many years its leader in the Prussian House of Representatives. Like his brother Leopold von Gerlach, he belonged to the circle that formed around the ''Neue Preußische Zeitung'' (New Prussian Newspaper), in the founding of which he also played a leading role. Life Origins and youth Gerlach was born in Berlin in 1795 to a family of Prussian bureaucratic gentry, the fourth child of the mayor of Berlin, Carl Friedrich Leopold von Gerlach. Among his brothers were the later general and adjutant to the Prussian king Leopold von Gerlach and the theologian and court chaplain Otto von Gerlach. Between 1810 and 1815 Ernst Ludwig studied law, with interruptions, at the newly founded University of Berlin, then later in Göttingen and Heidelberg. From 1813 to 1815 he fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
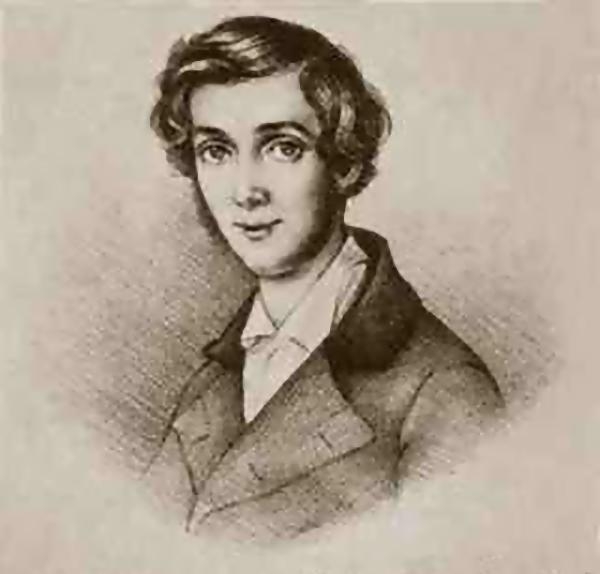
Hermann Wagener
Friedrich Wilhelm Hermann Wagener (March 8, 1815 in Segeletz (now Wusterhausen) – April 22, 1889 in Friedenau (now part of Berlin)) was a Prussian jurist, chief editor of the Kreuzzeitung (The "New Prussian Newspaper") and was a politician and minister from the Prussian Conservative Party. Life Wagenar was the son of a country priest from Neuruppin. After studies and graduation in Salzwedel in 1835 he studied legal science in Berlin. He was interested in the judicial philosophy of Friedrich Julius Stahl and the economic theories of Karl Ludwig von Haller regarding political legitimacy. He followed the usual legal career, becoming a law clerk in 1838 at the Higher Regional Court of Frankfurt (Oder) under vice president Ludwig von Gerlach and worked from 1844 to 1847 as an attorney at the Prussian land-improvement bureau and later at the consistory at the province of Saxony. In 1847 he became an appellate court attorney representing the consistory in Madeburg where he was as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of Junker landowners, Bismarck rose rapidly in Prussian politics, and from 1862 to 1890 he was the minister president and foreign minister of Prussia. Before his rise to the executive, he was the Prussian ambassador to Russia and France and served in both houses of the Prussian Parliament. He masterminded the unification of Germany in 1871 and served as the first Chancellor of the German Empire until 1890, in which capacity he dominated European affairs. He had served as the chancellor of the North German Confederation from 1867 to 1871, alongside his responsibilities in the Kingdom of Prussia. He cooperated with King Wilhelm I of Prussia to unify the various German states, a partnership that would last for the rest of Wilhelm's life. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Friedrich Leopold Von Gerlach
(Ludwig Friedrich) Leopold von Gerlach (17 September 1790 – 10 January 1861) was a Prussian army general, adjutant to King Frederick William IV of Prussia and a Protestant conservative associate of Otto von Bismarck. Ancestry He was the son of Carl Friedrich Leopold von Gerlach (1757–1813) and his wife Agnes, née von Raumer (1762–1831). His father was mayor of Berlin and later District President and President of the War and Domains Chamber of the Electoral March of Brandenburg. Military career Gerlach attended the Joachimsthal Gymnasium in Berlin and in 1803 was commissioned as a corporal in the infantry regiment "von Arnim" in the Prussian Army. After his promotion to ensign, he took part in the Battle of Auerstedt in 1806 during the War of the Fourth Coalition. He was taken prisoner but was released on his word of honor and placed on inactive status. After the Peace of Tilsit, he studied law in Göttingen and in Heidelberg and in 1812 was appointed a junior l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Julius Stahl
Friedrich Julius Stahl (16 January 1802 – 10 August 1861), German constitutional lawyer, political philosopher and politician. Biography Born at Würzburg, of Jewish parentage, as Julius Jolson, he was brought up strictly in the Jewish religion and was allowed to attend the gymnasium. As a result of its influence, he was at the age of seventeen converted to Christianity and baptized into the Lutheran Church at Erlangen on November 6, 1819. To this faith he clung with earnest devotion and persistence until his death. Having studied law at Würzburg, Heidelberg and Erlangen, Stahl, on taking the degree of ''doctor juris'', established himself as ''Privatdozent'' in Munich, was appointed (1832) ordinary professor of law at Würzburg, and in 1840 received the chair of ecclesiastical law and polity at Berlin. Here he immediately made his mark as an ecclesiastical lawyer, and was appointed a member of the first chamber of the general synod. Elected in 1850 a member of the short-liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Fontane
Theodor Fontane (; 30 December 1819 – 20 September 1898) was a German novelist and poet, regarded by many as the most important 19th-century German-language realist author. He published the first of his novels, for which he is best known today, only at age 58 after a career as a journalist. Fontane's novels are known for their complex, often sceptical view of society in the German empire; he shows different social and political parts of society meeting and sometimes clashing. Other trademarks of Fontane's work are their strongly drawn female characters (such as ''Effi Briest'' and '' Frau Jenny Treibel''), tender irony and vivid conversations between characters. Life Youth Fontane was born in Neuruppin, a town 30 miles northwest of Berlin, into a Huguenot family. At the age of sixteen he was apprenticed to an apothecary, his father's profession. He became an apothecary himself and in 1839, at the age of 20, wrote his first work (''Heinrichs IV. erste Liebe'', now lost). Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thaler
A thaler (; also taler, from german: Taler) is one of the large silver coins minted in the states and territories of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy during the Early Modern period. A ''thaler'' size silver coin has a diameter of about and a weight of about 25 to 30 grams (roughly 1 ounce). The word is shortened from ''Joachimsthaler'', the original ''thaler'' coin minted in Joachimstal, Bohemia, from 1520. While the first standard coin of the Holy Roman Empire was the '' Guldengroschen'' of 1524, its longest-lived coin was the '' Reichsthaler (Reichstaler)'', which contained Cologne Mark of fine silver (or 25.984 g), and which was issued in various versions from 1566 to 1875. From the 17th century a lesser-valued '' North German thaler'' currency unit emerged, which by the 19th century became par with the '' Vereinsthaler''. The ''thaler'' silver coin type continued to be minted until the 20th century in the form of the Mexican peso until 1914, the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhart Koselleck
Reinhart Koselleck (23 April 1923 – 3 February 2006) was a German historian. He is widely considered to be one of the most important historians of the twentieth century. He occupied a distinctive position within history, working outside of any pre-established 'school', while making pioneering contributions to conceptual history (Begriffsgeschichte), the epistemology of history, linguistics, the foundations of an anthropology of history and social history, and the history of law and government. Biography Koselleck volunteered to serve as a German soldier during World War II, having previously joined the Hitler Youth, the youth organisation of the German Nazi Party. In May 1945 he was captured by the Red Army and was sent for debris removal to the Auschwitz concentration camp, before being transported to Kazakhstan and held there as a prisoner of war for 15 months until he was returned to Germany on medical grounds. He claimed that his personal experiences during the war were form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Question
The "German question" was a debate in the 19th century, especially during the Revolutions of 1848, over the best way to achieve a unification of all or most lands inhabited by Germans. From 1815 to 1866, about 37 independent German-speaking states existed within the German Confederation. The ("Greater German solution") favored unifying all German-speaking peoples under one state, and was promoted by the Austrian Empire and its supporters. The ("Little German solution") sought only to unify the northern German states and did not include any part of Austria (either its German-inhabited areas or its areas dominated by other ethnic groups); this proposal was favored by the Kingdom of Prussia. The solutions are also referred to by the names of the states they proposed to create, and ("Little Germany" and "Greater Germany"). Both movements were part of a growing German nationalism. They also drew upon similar contemporary efforts to create a unified nation state of people who sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postil
A postil or postill ( la, postilla; german: Postille) was originally a term for Bible commentaries. It is derived from the Latin ''post illa verba textus'' ("after these words from Scripture"), referring to biblical readings. The word first occurs in the chronicle (with reference to examples of 1228 and 1238) of Nicolas Trivetus, but later it came to mean only homiletic exposition, and thus became synonymous with the homily in distinction from the thematic sermon. Finally, after the middle of the fourteenth century, it was applied to an annual cycle of homilies. Early Lutheran postils From the time of Martin Luther, who published the first part of his postil under the title ''Enarrationes epistolarum et evangeliorum quas postillas vocant'' (Wittenberg, 1521), every annual cycle of sermons on the lessons, whether consisting of homilies or formal sermons, is termed a ''postil''. A few of the most famous Lutheran postils are those of M. Luther (''Kirchenpostille'', Wittenberg, 1527; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Allgemeine Zeitung
''Deutsche Allgemeine Zeitung'' (often abbreviated to DAZ) was a German newspaper that appeared between 1861 and 1945. Until 1918 the title of the paper was ''Norddeutsche Allgemeine Zeitung''. Although Wilhelm Liebknecht, one of the founders of SPD and close associate of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, was member of the founding editorial board in 1861, the paper became soon a conservative flagship of the German press ("Bismarcks Hauspostille"). At the end of the First World War, the name was changed to "Deutsche Allgemeine Zeitung", under the intention to form a conservative and democratic equivalent to the British newspaper ''The Times'' in Germany and give the Reich a more democratic image. Various liberal and conservative writers worked for DAZ at that time, Otto Flake was head of the Cultural Section ( called "Feuilleton" in German newspapers ), people like the historian Egmont Zechlin, the journalist Dr. Friedrich Schrader and his Swiss colleague from Constantinople ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |