|
Korea Aerospace Research Institute
The Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), established in 1989, is the aeronautics and space agency of South Korea. Its main laboratories are located in Daejeon, in the Daedeok Science Town. KARI's vision is to continue building upon indigenous launch capabilities, strengthen national safety and public service, industrialize satellite information and applications technology, explore the moon, and develop environmentally-friendly and highly-efficient cutting-edge aircraft and core aerospace technology. Current projects include the KSLV-2 launcher. Past projects include the 1999 Arirang-1 satellite. The agency was founded in 1989. Prior to South Korea's entry into the Institute for Advanced Engineering (IAE) in 1992, it focused primarily on aerospace technology. Background KARI began on October 10, 1989, as a national aerospace research institute with the purpose of contributing to sound development of the national economy and enhancement of people's lives through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daejeon
Daejeon () is South Korea's fifth-largest metropolis, with a population of 1.5 million as of 2019. Located in the central-west region of South Korea alongside forested hills and the Geum River, the city is known both for its technology and research institutions, and for celebrating its natural environment, with most mountains, hot springs, and rivers freely open for public use. Daejeon serves as a hub of transportation for major rail and road routes, and is approximately 50 minutes from the capital, Seoul, by KTX or SRT high speed rail. Daejeon (along with Seoul, Gwacheon and Sejong City) are collectively South Korea's administration hubs. The city is home to 23 universities and colleges, including Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Chungnam National University, as well as government research institutes, and research and development centers for global companies such as Samsung, LG, mostly located in the city's Daedeok Science Town. Occupied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller and a system of communications with the UAV. The flight of UAVs may operate under remote control by a human operator, as remotely-piloted aircraft (RPA), or with various degrees of autonomy, such as autopilot assistance, up to fully autonomous aircraft that have no provision for human intervention. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications.Hu, J.; Bhowmick, P.; Jang, I.; Arvin, F.; Lanzon, A.,A Decentralized Cluster Formation Containment Framework for Multirobot Systems IEEE Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
중앙일보
''The JoongAng'', formally known as ''JoongAng Ilbo'', is a South Korean daily newspaper published in Seoul, South Korea. It is one of the three biggest newspapers in South Korea, and a newspaper of record for South Korea. The paper also publishes an English edition, ''Korea JoongAng Daily'', in alliance with the ''International New York Times''. It is often regarded as the holding company of JoongAng Group chaebol as it is owner of various affiliates, such as the broadcast station and drama producing company JTBC, and movie theatres chain Megabox (movie theaters), Megabox. History It was first published on September 22, 1965, by Lee Byung-chul, the founder of Samsung Group which once owned the Tongyang Broadcasting Company (TBC). In 1980, ''JoongAng Ilbo'' gave up TBC and TBC merged with KBS. ''JoongAng Ilbo'' is the pioneer in South Korea for the use of horizontal copy layout, topical sections, and specialist reporters with investigative reporting teams. Since April 15, 1995 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KSLV-II
Nuri (; , meaning "world" in native Korean), also known as KSLV-II (Korean Space Launch Vehicle-II), is a three-stage launch vehicle, the second one developed by South Korea and the successor to Naro-1 (KSLV-1). Nuri is developed by Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI). All three stages use indigenously developed launch vehicle engines, making Nuri the first indigenously developed South Korean orbital launch vehicle (the Naro-1 launch vehicle used a Russian-made first stage). The South Korean government has set SpaceX as a "role model", striving to develop relatively cheap and reliable rockets competitive enough for the commercial launch market. On 21 October 2021, Nuri made its initial orbital launch attempt at 08:00 UTC and it launched a dummy satellite payload into what was planned to be a Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO). However, despite the payload reaching the targeted apogee (700 km), the third stage shut down about 46 seconds earlier than planned and the paylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
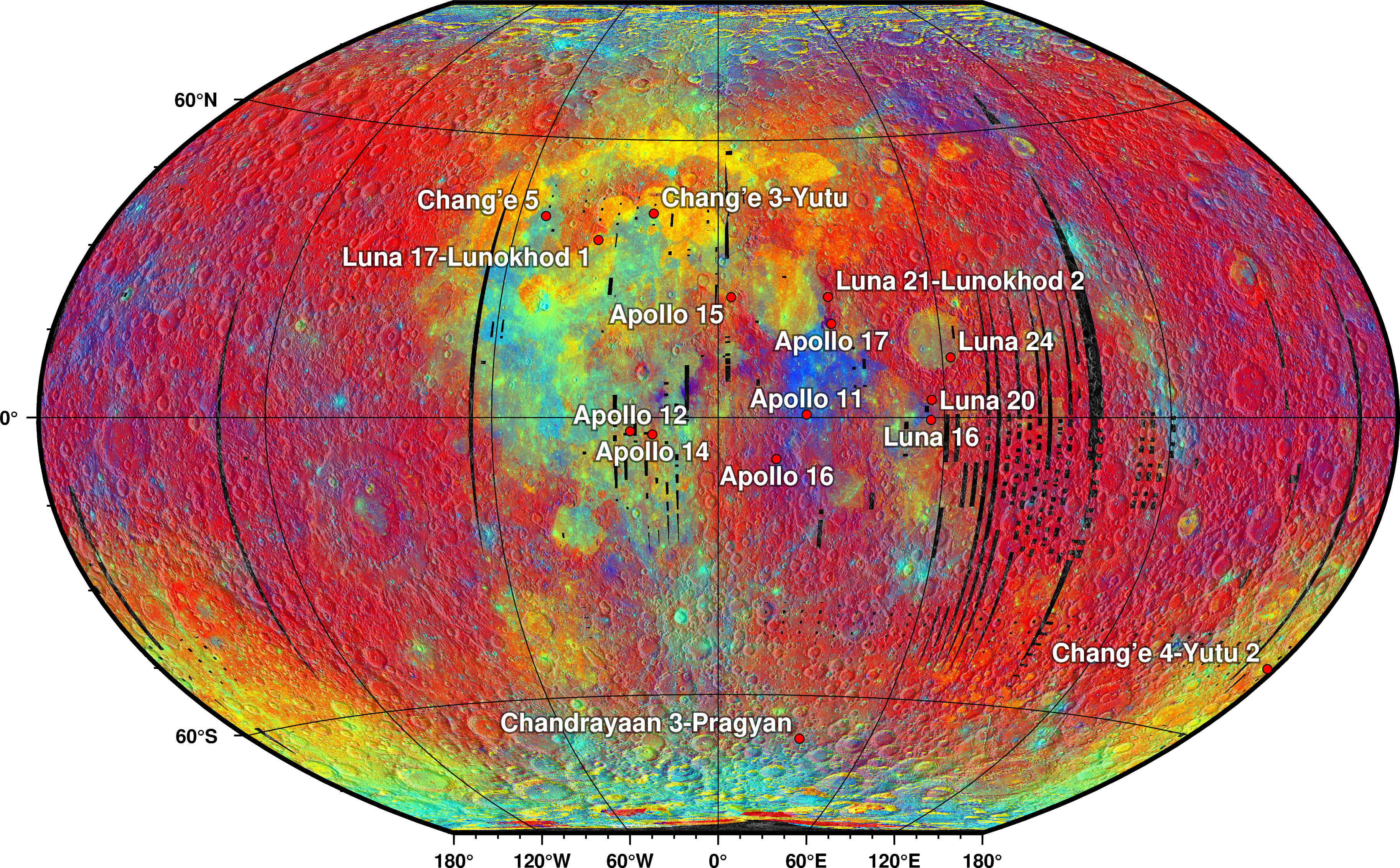
Lunar Rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rovers have been partially or fully autonomous robots, such as the Soviet Union's Lunokhods and the Chinese '' Yutus''. Three countries have had operating rovers on the Moon: the Soviet Union, the United States and China. An Indian mission failed while Japan and Greece currently have planned missions. Past missions Lunokhod 1 Lunokhod 1 (Луноход) was the first of two polycrystalline-panel-powered robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program after a previous unsuccessful attempt of a launch probe with Lunokhod 0 (No.201) in 1969. The spacecraft which carried Lunokhod 1 was named Luna 17. The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains on November 1970. Lunokhod was the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Lander
A lunar lander or Moon lander is a spacecraft designed to land on the surface of the Moon. As of 2021, the Apollo Lunar Module is the only lunar lander to have ever been used in human spaceflight, completing six lunar landings from 1969 to 1972 during the United States' Apollo Program. The design requirements for these landers depend on factors imposed by the payload, flight rate, propulsive requirements, and configuration constraints. Other important design factors include overall energy requirements, mission duration, the type of mission operations on the lunar surface, and life support system if crewed. The relatively high gravity and lack of lunar atmosphere negates the use of aerobraking, so a lander must use propulsion to decelerate and achieve a soft landing. Several studies indicate the potential for both scientific and technological benefits from sustained lunar surface exploration that would culminate in the utilization of lunar resources, or in the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation Satellite
An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others. The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs; some EO satellites may perform remote sensing without forming pictures, such as in GNSS radio occultation. The first occurrence of satellite remote sensing can be dated to the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, by the Soviet Union on October 4, 1957. Sputnik 1 sent back radio signals, which scientists used to study the ionosphere. The United States Army Ballistic Missile Agency launched the first American satellite, Explorer 1, for NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on January 31, 1958. The information sent back from its radiation detector led to the discovery of the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center
KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC; ko, 인공위성연구센터), is a university based research center for satellite technology and applications research. Space Programme SaTReC, which is located within the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), promotes the education and training of satellite engineers through research programs in satellite engineering, space science and remote sensing. In 1992, SaTReC developed and launched the first satellite of Korea, KITSAT-1, a scientific microsatellite. Since then, SaTReC continues to develop satellites with scientific and technology demonstration missions. Satellite Missions * Development and Operations of Kitsat-1 * Development and Operations of Kitsat-2 * Development and Operations of Kitsat-3 KITSAT-3 was a South Korean remote sensing minisatellite which carried MEIS (Multispectral Earth Imaging System) and SENSE (Space ENvironment Scientific Experiment) instruments to low Earth orbit (LE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KARI KSR-3
KSR-3 or KSR-III (Korean Sounding Rocket-3) is South Korean liquid sounding rocket designed by Korea Aerospace Research Institute. It was launched successfully on November 28, 2002, a rocket for scientific surveillance purposes. The first test flight of KSR-III was carried out by the KARI rocketry team from Anheung Proving Ground, reaching an altitude of and flying over . Spec * Payload: 150 kg * Apogee: 42.7 km * Range: 79 km * Thrust: 13 t * Weight: 6.1 t * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 13.5 m * Burn time: 53 sec * Launch: November 28, 2002 See also * KSLV-I * KSLV-II * KARI KSR-1 * KARI KSR-2 KSR-2 (Korean Sounding Rocket-2) is a South Korean sounding rocket designed by KARI. Spec * Payload: 150 kg * Apogee: 160 km * Thrust: 86 kN * Weight: 2000 kg * Diameter: 0.42 m * Length: 11.04 m * Launch: July 9, 1997 (1st)/June 11, 1998 (2nd) ... References Further reading * Encyclopedia AstronauticKSR-III. KSR-III Sounding rockets of South Korea {{ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was registered as a trademark by Canadian geologist and inventor Abraham Gesner in 1854 before evolving into a generic trademark. It is sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage. The term kerosene is common in much of Argentina, Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Nigeria, and the United States, while the term paraffin (or a closely related variant) is used in Chile, eastern Africa, South Africa, Norway, and in the United Kingdom. The term lamp oil, or the equivalent in the local languages, is common in the majority of Asia and the Southeastern United States. Liquid paraffin (called mineral oil in the US) is a more viscous and highly refined product which is used as a laxative. Paraffin wax is a waxy solid extracted from pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which has continued to the present. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a pale blue color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 under and , and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in liquid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STSAT-2A
STSat-2A (Science and Technology Satellite-2A) was a satellite launched by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), the national space agency of South Korea, from the Naro Space Center in Goheung County, South Jeolla using the Naro-1 (KSLV-1) launch vehicle. Spacecraft The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) developed STSat-2A as a Sun observation, satellite laser ranging and engineering and technology demonstration sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology. It was expected to be operational for about two years, and was scheduled to be launched between 2005 and 2007. The Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA) instrument was intended to measure the orbit of STSAT-2A, in order to investigate variations in its orbit. It was a follow-up to STSat-1, which was launched using a Kosmos-3M rocket on 27 September 2003. Originally a Dual-channel Radiometers for Earth and Atmosphere Monitoring (DREAM) microwave radiometer was intended as the principal payload of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)