|
Kolhabi
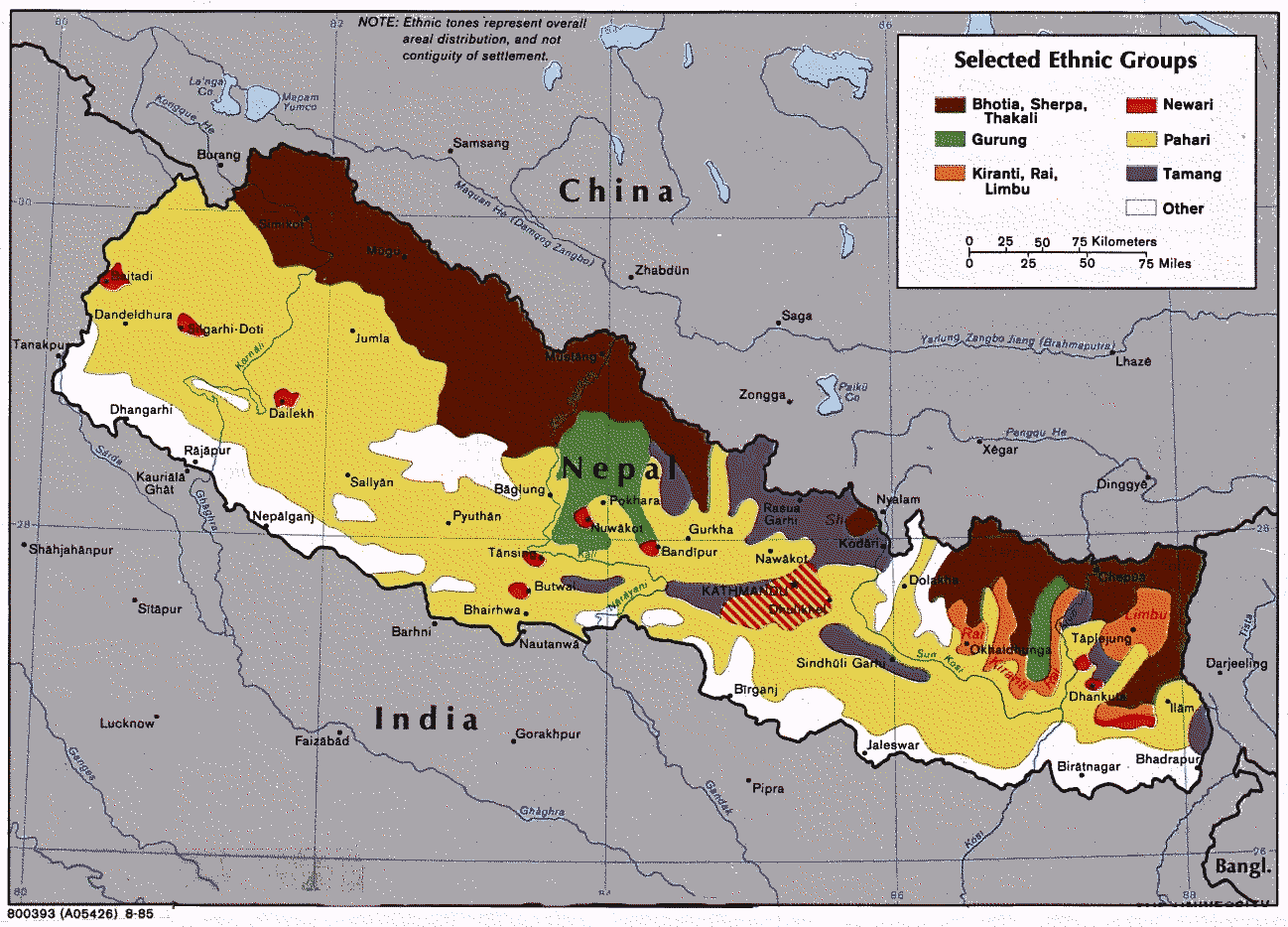
Kolhabi (Nepali: कोल्हवी ) is a municipality in Bara District in the Madhesh Province of Nepal. It was formed in 2016 occupying current 11 sections (wards) from previous 11 former VDCs. It occupies an area of 157.4 km2 with a total population of 43,036. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Kolhabi Municipality had a population of 44,082. Of these, 50.8% spoke Tharu, 24.0% Bhojpuri, 16.5% Nepali, 4.2% Maithili, 1.9% Tamang, 1.0% Urdu, 0.9% Newar and 0.5% Magar as their first language. In terms of ethnicity/caste, 59.3% were Tharu, 8.1% Hill Brahmin, 5.1% Musahar, 4.6% Chhetri, 3.6% Chamar/Harijan/Ram, 2.4% Tamang, 2.2% Musalman, 1.7% Dusadh/ Paswan/Pasi, 1.5% Teli, 1.4% Newar, 1.1% Magar, 1.0% Mallaha, 0.8% Bin, 0.8% Kami, 0.7% Kalwar, 0.6% Kanu, 0.5% Hajjam/Thakur, 0.5% Majhi, 0.5% Nuniya, 0.4% Koiri/Kushwaha, 0.3% Terai Brahmin, 0.3% Damai/Dholi, 0.3% other Terai, 0.3% Thakuri, 0.2% Kathabaniyan, 0.2% Sanyasi/Dasnami, 0.2% Sonar, 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bara District
Bara District ( ne, बारा जिल्ला ) is one of the seventy–seven districts of Nepal, located in the western part of the Madhesh Province. The district is third richest district in Nepal after Kathmandu and Morang with 3.3% share of total GDP of Nepal and highest per capita income in Madhesh province. Kalaiya serves as the district's headquarter. Bakaiya, Jamuniya, Pasaha, Dudhaura and Bangari are the main rivers of Bara. The main languages spoken in the district are Bhojpuri, Bajjika, Tharu and Nepali. History Simraungadh is major part of Bara district. It is a historical place in Nepal and famous for agricultural products. Here people grow wheat, maize, and various green vegetables ( cauliflower, tomato, banana (raw), beetroot, bitter gourd, bottle gourd, brinjal, cabbage, carrot, cauliflower, chilli (green), chilli (dry red), coriander leaves, cucumber, potato and so on). Bara district is famous for the Gadhimai Temple, particularly as every five yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the governing body of a given municipality. A municipality is a general-purpose administrative subdivision, as opposed to a special-purpose district. The term is derived from French and Latin . The English word ''municipality'' derives from the Latin social contract (derived from a word meaning "duty holders"), referring to the Latin communities that supplied Rome with troops in exchange for their own incorporation into the Roman state (granting Roman citizenship to the inhabitants) while permitting the communities to retain their own local governments (a limited autonomy). A municipality can be any political jurisdiction, from a sovereign state such as the Principality of Monaco, to a small village such as West Hampton Dunes, New York. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamang (Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāng'') is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken mainly in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% to 63%. For comparison, lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese, is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar People
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars form a linguistic and cultural community of primarily Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman ethnicities following Hinduism and Buddhism with Nepal Bhasa as their common language. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, art and literature, trade, agriculture and cuisine. Today, they consistently rank as the most economically and socially advanced community of Nepal, according to the annual Human Development Index published by UNDP. Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teli
Teli is a caste traditionally occupied in the pressing of oil in India, Nepal and Pakistan. Members may be either Hindu or Muslim; Muslim Teli are called Roshandaar or Teli Malik. The Jewish community of Maharashtra (called Bene Israel) was also known to be a sub-group in the Teli caste called Shanivar Teli meaning ''Saturday oil pressers'' for their Jewish custom of abstention from work on Shabbat. History In the Early Medieval period in some parts of south India, Teli community used to work on their own oil presses to produce oil to be supplied to the temples. The emergence of "Temple towns" in various parts of south India was instrumental in the improvement of social status of some of the communities who were associated with the supply of essential items for cultural activities. The communities like ''Malakar'' (garland makers), and ''Telikars'' (oil pressers) thus became important for the functioning of such towns. Some of them even became prosperous enough to make donation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paswan
The Paswan, also known as Dusadh, are a Dalit community from eastern India. They are found mainly in the states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand. The Urdu word ''Paswan'' means bodyguard or "one who defends". The origin of the word, per the belief of the community, lies in their participation in the battle against Siraj-ud-daulah, the Nawab of Bengal at the behest of British East India Company, after which they were rewarded with the post of '' Chowkidars'' and lathi wielding tax collector for the ''Zamindars''. They follow certain rituals such as walking on fire to assert their valour. Etymology The Paswans claim their origin from a number of folk and epic characters in order to seek upliftment in their social status. Some Paswan believe that they have originated from Rahu, a superhuman and one of the planets in Hindu mythology, while others claim their origin from Dushasana, one of the Kaurava princes. Claims regarding origin from "Gahlot Kshatriya" are also persistent amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepalese Muslims
Nepalese Muslims ( ne, नेपाली मुसलमान; ''Nepali Musalman'') are Nepalis who follow Islam. Their ancestors arrived in Nepal from different parts of South Asia, Central Asia and Tibet during different epochs, and have since lived amidst the numerically dominant Hindus and Buddhists. About 97% of the Muslim community live in the Terai region, while the other 4% are found mainly in the city of Kathmandu and Gorkha and the western hills. The community numbers 971,056, about 3.8% of the total population of Nepal. Districts with large Muslim population include Sarlahi (9.9%), Rautahat (17.2%), Bara (11.9%), and Parsa (17.3%) in the central Terai region bordering the Indian state of Bihar, Kapilbastu (16.8%) and Banke (16%) in the western Terai and Siraha (7%) and Sunsari (10%) and Saptari (10%) eastern Terai Gorkha (2.8%) hill. History Muslims have lived in Nepal for long period of time and have shared common historical experiences with the Hindu majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang People
The Tamang (; Devanagari: तामाङ; ''tāmāṅ'') are an Tibeto-Burmese ethnic group of Nepal. In Nepal Tamang/Moormi people constitute 5.6% of the Nepalese population at over 1.3 million in 2001, increasing to 1,539,830 as of the 2011 census. Tamang people are also found in significant numbers in the Indian state of Sikkim and districts of Darjeeling and Kalimpong in West Bengal state of India and various districts in the southern foothills of the Kingdom of Bhutan. Such districts include the Tsirang District, the Dagana District, the Samtse District, the Chukha District, the Sarpang District and the Samdrup Jongkhar District. Emergent North-East : A Way Forward By H. C. Sadangi Tamang language is the fifth most-spoken language in Nepal. Etymology ''Tamang'' may be derived from the word ''Tamang'', where ''Ta'' means "horse" and ''Mak'' means "warrior" in Tibetan. However, there are no written documentations of Horse Riders. Some scientific research claims Tamangs ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamar
Chamar is a Dalit community classified as a Scheduled Caste under modern India's system of affirmative action. Historically subject to untouchability, they were traditionally outside the Hindu ritual ranking system of castes known as varna. They are found throughout the Indian subcontinent, mainly in the northern states of India and in Pakistan and Nepal. History Ramnarayan Rawat posits that the association of the Chamar community with a traditional occupation of tanning was constructed, and that the Chamars were instead historically agriculturists. The term ''chamar'' is used as a pejorative word for dalits in general. It has been described as a casteist slur by the Supreme Court of India and the use of the term to address a person as a violation of the Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989. Chamars have remained one of the most discriminated community within Hinduism. In reference to villages of Rohtas and Bhojpur district of Bihar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhetri
Chhetri (Kshetri, Kshettri, Kshetry or Chhettri), ( ne, क्षेत्री ; IAST: ''Kṣetrī'') historically called Kshettriya or Kshetriya or Khas are Nepali speakers of Khas community, some of whom trace their origin to migration from medieval India. Chhetri was a caste of administrators, governor and military elites in the medieval Khas Kingdom and Gorkha Kingdom (later unified Kingdom of Nepal). The nobility of the Gorkha Kingdom mainly originated from Chhetri families. They also had a strong presence in civil administration affairs. The bulk of prime ministers of Nepal before the democratization of Nepal belonged to this caste as a result of the old Gorkhali aristocracy. Gorkha-based aristocratic Chhetri families included the Pande dynasty, the Basnyat dynasty, the Kunwar family, and the Thapa dynasty, (Rana dynasty and other Kunwars). Khas Chhetris were traditionally considered a division of the Khas people with Khas Brahmin (commonly called Khas Bahun). They m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musahar
Musahar or Mushahar are a Dalit community found in the eastern Gangetic plain and the Terai. They are also known as ''Banbasi''.The other names of the Musahar are Bhuiyan and Rajawar Their name literally means 'rat-eater' due to their main former occupation of catching rats, and there are many who are still forced to do this work due to destitution and poverty. Origins and history In Bihar, the word Musahar is said to be derived from the Bhojpuri ''mūs+ahar'' (literally ''rat eater''), on account of their traditional occupation as rat catchers. According to a local legend, Lord Brahma created man and gave him the horse to ride. The first Musahar decided to dig holes in the belly of the horse to fix his feet as he rode. This offended Lord Brahma, who cursed him and his descendants to be rat-catchers. Herbert Hope Risley, in his 1881 survey of castes and tribes of Bengal, speculated that the Musahars were an offshoot of the hunter-gatherer Bhuiya from the Chota Nagpur Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahun
Bahun ( ne, बाहुन) or Khas Brahmin ( ne, खस ब्राह्मण) is a caste ( ''Varna'') among Khas people of Nepal. Their origins are from the Indo-Aryan Khasa tribe of Nepal and South Asia. According to the 2011 Nepal census, Bahun is the second most populous group after Chhetri, another Varna within the hill Hindus in Nepal. According to 1854 ''Muluki Ain'' (Nepalese Legal Code), Bahuns were regarded as caste among sacred thread bearers (Tagadhari) and twice-born Hindus. Origin Traditionally, Bahuns were members of the Khas community together with Chhetris and Hill Dalits. Possibly due to political power of the Khasa Malla kingdom, Khas Bahun and Khas Rajput (Chhetris) had high social status like plain Brahmins and Rajputs in the present-day western Nepal. Bahuns, regarded as upper class Khas group together with Chhetri, were associated mostly with the Gorkha Kingdom. Bahuns were original inhabitants of Karnali region of Nepal. The immigration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |