|
Kolarian
Kolarian is a word first used by George Campbell. He described it as one of the three non-Aryan language families of India, which he made up, along with the Tibeto-Burman and the Dravidian. It is group of Munda languages of Austro-asiatic languages in India. The following languages as belonging to the group: * Bondo * Gadaba * Ho * Juang * Kharia * Korku * Korwa * Mundari * Santali * Savara Savara may refer to: *Savara people or Sora people * Savara language (Munda), or Sora, in India * Savara language (Dravidian), in India * ''Savara'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Erebidae *Savara, a planet in the computer game ''Tyrian Tyr ... References {{reflist Languages of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munda Languages
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about nine million people in India and Bangladesh. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages. The family is generally divided into two branches: North Munda, spoken in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Odisha, and South Munda, spoken in central Odisha and along the border between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. North Munda, of which Santali is the most widely spoken, has twice as many speakers as South Munda. After Santali, the Mundari and Ho languages rank next in number of speakers, followed by Korku and Sora. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korku Language
Korku (also known as ''Kurku,'' or ''Muwasi'') is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Korku tribe of central India, in the states of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra. It is isolated in the midst of the Gondi people, who are Dravidian, while its closest relatives are in eastern India. It is the westernmost Austroasiatic language. Korkus are also closely associated with the Nihali people, many of whom have traditionally lived in special quarters of Korku villages. Korku is spoken by around 700,000 people, mainly in four districts of southern Madhya Pradesh (Khandwa, Harda, Betul, Hoshangabad) and three districts of northern Maharashtra (Rajura and Korpana tahsils of Chandrapur district, Manikgarh pahad area near Gadchandur in Chandrapur district) (Amravati, Buldana, Akola). The name Korku comes from ''Koro-ku'' (-''ku'' is the animate plural), ''Koro'' 'person, member of the Korku community' (Zide 2008). Sociolinguistics The Indian national census of 2011 reported 727 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
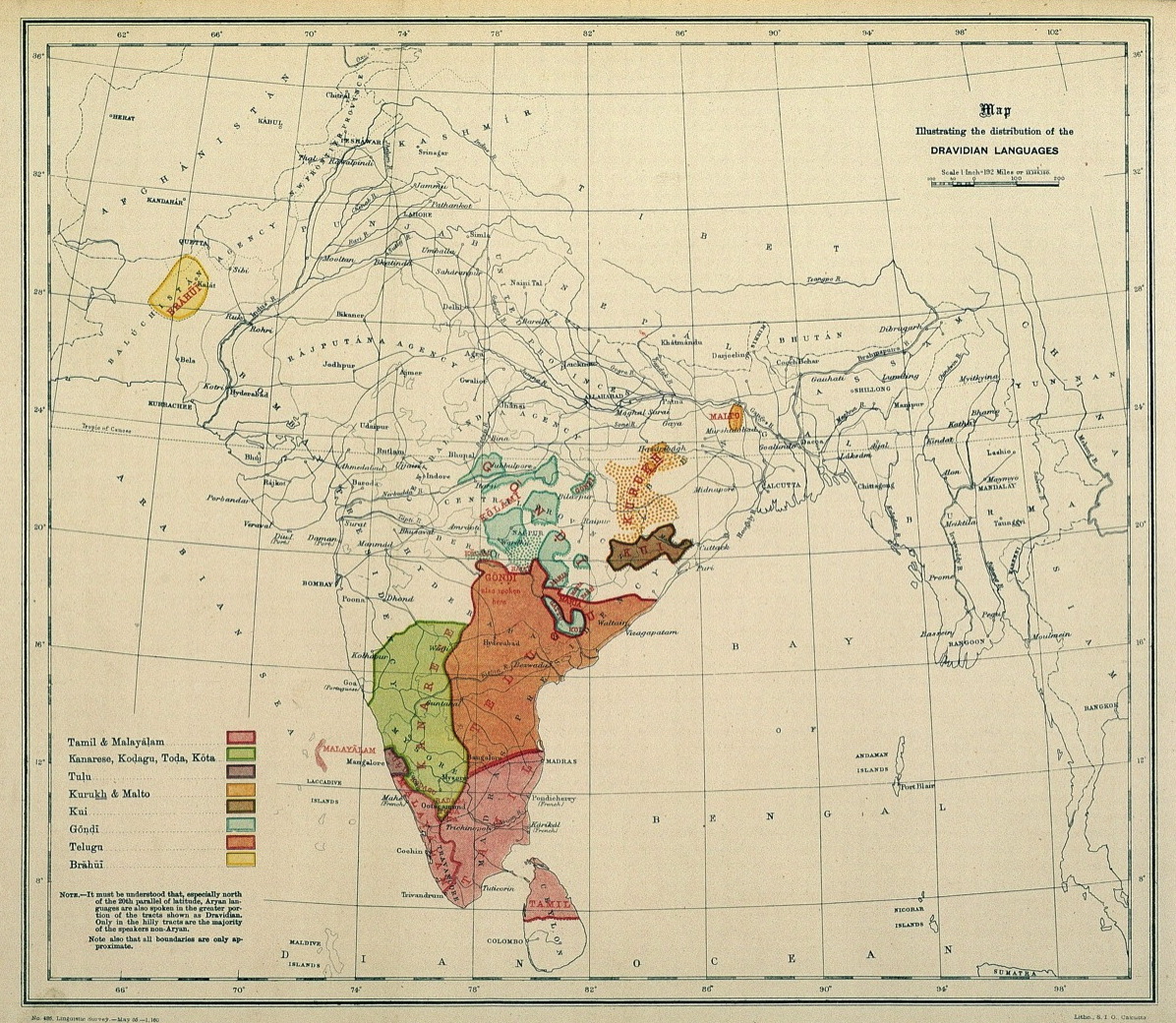
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-asiatic Languages
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status. '' Ethnologue'' identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bondo Language
The Bonda language, also known as Bondo or Remo, is a south Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken in Odisha, formerly known as Southern Odisha, in India. It had 2,568 speakers, all in Odisha, according to the 1951 Census of India,N. Gopalakrishnan, Linguistic Survey of India', p. 271 increasing to approximately 9,000 speakers in 2002 according to SIL. Classification The Bonda language is an indigenous language belonging to the Southern subgroup of the Munda branch of the Austroasiatic language family. Bonda is a spoken language with no traditional written system recorded. Bonda is a part of the Gutob-Remo branch, due to the similarities Bonda shares with another Southern Munda Language named Gutob History The Bonda language derives its name from the tribe of the Bonda people, an indigenous group located in Odisha known as the Bonda Highlanders. In their native language, the Bonda people regard themselves as "Remo', which translates to human, and derive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutob Language
The Gutob or Bodo Gadaba language is a south Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family of India, with the greatest concentrations of speakers being found in Koraput district of Odisha and Visakhapatnam district of Andhra Pradesh. It is also known simply as the Gadaba language, but it is different from the Dravidian Gadaba language. Other names for the Bodo Gadaba language include Gadba, Gutop, Gudwa, Godwa, Gadwa, and Boi Gadaba. Classification The Gutob language belongs to the South Munda subgroup of the Munda branch of the Austroasiatic language family. It is most closely related to the Bondo language. Distribution Gutob is spoken across southern Odisha and adjacent districts of northern Andhra Pradesh, and is concentrated primarily in Lamptaput block, Koraput district, southern Odisha (Griffiths 2008:634). In recent centuries, Gutob speakers have also migrated to the plains of Andhra Pradesh as well as Rayagada District, including near the town Majiguda (close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ho Language
Ho () is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken primarily in India by about 1.04 million people (0.103% of India's population) per the 2001 census. Ho is a tribal language. It is spoken by the Ho, Munda, Kolha and Kol tribal communities of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Assam and is written with the Warang Citi script. Devanagari, Latin script, Odia script and Telugu script are sometimes used, although native speakers are said to prefer a Ho script. The latter script was invented by Ott Guru Kol Lako Bodra. The name "Ho" is derived from the native word "" which means "Human being". Distribution Around half of all Ho speakers are from West Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, where they form the majority community. Ho speakers are also found in East Singhbhum district in southern Jharkhand and in northern Odisha. Ho is closer to the Mayurbhanj dialect of Mundari than the language spoken in Jharkhand. Ho and Mundari are ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juang Language
The Juang language is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken primarily by the Juang people of Odisha state, eastern India. Classification The Juang language belongs to the Munda language family, the whole of which is classified as a branch of the greater Austroasiatic language family. Among the Munda languages, Juang is considered to be most closely related to Kharia, although Anderson considers Juang and Kharia to have split off from each other relatively early. Juang can be roughly divided into the Hill and Plains varieties, both of which are spoken in Odisha (Patnaik 2008:508). *Hill Juang: Gonasika Hills (in Keonjhar district) and Pallara Hills *Plains Juang: about 147 villages in southern Keonjhar district and eastern Dhenkanal district Distribution Juang is spoken by about 30,875 people according to the 2001 Indian census, 65% of ethnic population In Odisha state, it is spoken in southern Keonjhar district, northern Angul district, and eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharia Language
The Kharia language ( or ) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family, that is primarily spoken by the Kharia people of eastern India. History According to linguist Paul Sidwell, Austroasiatic languages arrived on the coast of Odisha from Southeast Asia about 4000-3500 years ago.Sidwell, Paul. 2018Austroasiatic Studies: state of the art in 2018 Presentation at the Graduate Institute of Linguistics, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan, 22 May 2018. Classification Kharia belongs to the Kharia–Juang branch of the Munda language family. Its closest extant relative is the Juang language, but the relationship between Kharia and Juang is remote. The most widely cited classification places Kharia and Juang together as a subgroup of the South Munda branch of the Munda family. However, some earlier classification schemes placed Kharia and Juang together, as an independent branch deriving from the root of the Munda languages, which they named Central Munda. Kharia is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korwa Language
Korwa, or Kodaku/Koraku (Korku), is a Munda language of India spoken in Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. Existing Korwa linguistic documentation includes Bahl (1962), which is based on the Korwa dialect of Dumertoli village, Bagicha Block, Tehsil Jashpurnagar, Raigarh District, Chhattisgarh. Varieties Korwa is a dialect continuum. The two principal varieties are Korwa (Korba) and Koraku (Kodaku), spoken by the Korwa and Kodaku respectively. Out of the Korwa, only the Hill Korwa still speak the language, the others having shifted to regional languages. The Kodaku in Jharkhand call their language "Korwa". Both speak Sadri, Kurukh, or Chhattisgarhi as a second language, or in the case of Sadri sometimes as their first language. Gregory Anderson (2008:195) lists the following locations for Korowa and Koraku. *Korowa (Korwa) is spoken in northeastern Chhattisgarh state, including southern Surguja district, Jashpur district, parts of Raigarh district, and other neighboring areas. Korw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
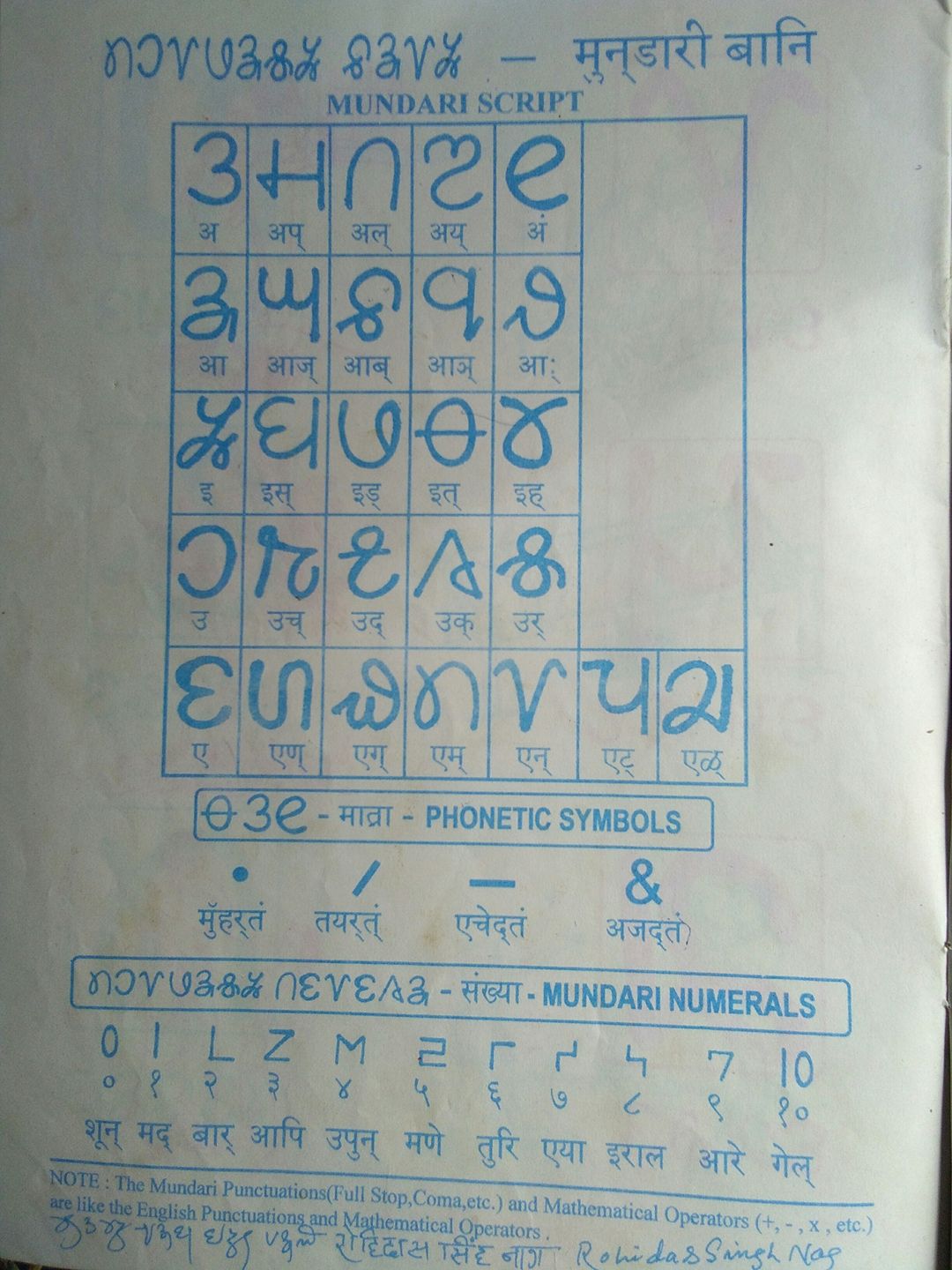
Mundari Language
Mundari (Munɖari) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes in eastern Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. It is closely related to Santali. Mundari Bani, a script specifically to write Mundari, was invented by Rohidas Singh Nag. It has also been written in the Devanagari, Odia, Bengali, and Latin writing systems. History According to linguist Paul Sidwell (2018), Munda languages probably arrived on coast of Odisha from Indochina about 4000–3500 years ago and spread after Indo-Aryan migration to Odisha. Geographical distribution Mundari is spoken in the Ranchi, Khunti, Seraikela Kharsawan and West Singhbhum, East Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, and in the Mayurbhanj, Kendujhar, Baleshwar, Sundargarh district of Odisha by at least 1.1 million people. Another 500,000, mainly in Odisha and Assam, are recorded in the census as speaking "Munda," potentially another name for Mundari. Dialects Toshiki Osada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |