|
Kolainiai
Kolainiai is a village in Kelmė District Municipality, Lithuania. It is located about southwest from Užventis. According to the 2011 census, it had population of 261. In 1750, local noble Adamkavičius bequeathed his manor and land with serfs to the Carmelites. He also built a monastery and a church for the monks. In 1797, the monks took over the administration of the Kražiai College, a former Jesuit school. After Tsarist authorities secularized the college in 1817, the Carmelites established their own school in Kolainiai. The school was closed in 1835 after the November Uprising. The monastery itself was closed after the January Uprising of 1863. Russian settlers from Blagoveshchensk ( Amur Oblast) were moved into the monastery; the town became known as Blagoveshchenskoye (russian: Благовещенское). The Catholic Church was converted into an Eastern Orthodox church The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kražiai College
The Kražiai College ( lat, Collegium Crozensis) was a Jesuit college (equivalent to a modern secondary school) in Kražiai, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later Russian Empire. Established in 1616 in hopes to educate new generations of anti-Protestants, the college was one of the major cultural and educational centers in Samogitia. In 1620–1742, it shared premises with the Samogitian Priest Seminary. In 1844, the college was transferred to Kaunas. History Establishment Bishop Merkelis Giedraitis raised the idea of establishing a college in Kražiai, the first higher education institution in Samogitia. To that end, in 1608, he invited the Jesuits, bought them land and built a house for their needs. Merkelis died the following year; in his last will, he left money and land for the construction of a Jesuit monastery. Other patrons included Mikołaj Krzysztof "the Orphan" Radziwiłł who donated a palace, built in 1565, and Jan Karol Chodkiewicz who donated seven homesteads. The coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, 2 United Nations General Assembly observers#Present non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (2 states, both in associated state, free association with New Zealand). Compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarybų Lietuvos Enciklopedija
''Tarybų Lietuvos enciklopedija'' or TLE (translation: ''Encyclopedia of Soviet Lithuania'') was an encyclopedia of the Lithuanian SSR, covering topics such as archaeology, history, nature, science, cultural heritage, cities, districts, biographies of famous people and politics, but only as they relate to Lithuania. It was published in four volumes between 1985 and 1988 in Vilnius. It was derived from the 12-volume ''Lietuviškoji tarybinė enciklopedija Lithuanian encyclopedias are encyclopedias published in the Lithuanian language or encyclopedias about Lithuania and Lithuania-related topics. The first known attempt to create a Lithuanian encyclopedia was in 1883, when Jonas Jacevičius failed t ...'' but TLE did not cover general areas such as technology, biology, pharmacology, chemistry, medicine, mathematics and others. Volumes * Volume 1: A–Grūdas, 1985 * Volume 2: Grūdas–Marvelis, 1986 * Volume 3: Masaitis–Simno, 1987 * Volume 4: Simno–Žvorūnė, 1988 Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics Lithuania
The Department of Statistics of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos statistikos departamentas), officially the ''Department of Statistics to the Government of the Republic of Lithuania'', is an institution in Lithuania which is responsible for collecting, processing, presenting and analysing statistics concerning the topics economy, society and environment. It is subordinate directly to the Government of Lithuania. Being a memember of the European Statistical System, the department also supplies data to Eurostat. A Director General, appointed by the Prime Minister, oversees its operations. Several commissions and working groups analyze its operations and suggest improvements. An advisory body, the Statistical Council, consists of representatives from the governmental bodies, NGOs, researchers, the media, and other interested parties; the council's makeup and operations are subject to governmental regulation. History The origins of statistics collection in Lithuania can be traced back to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
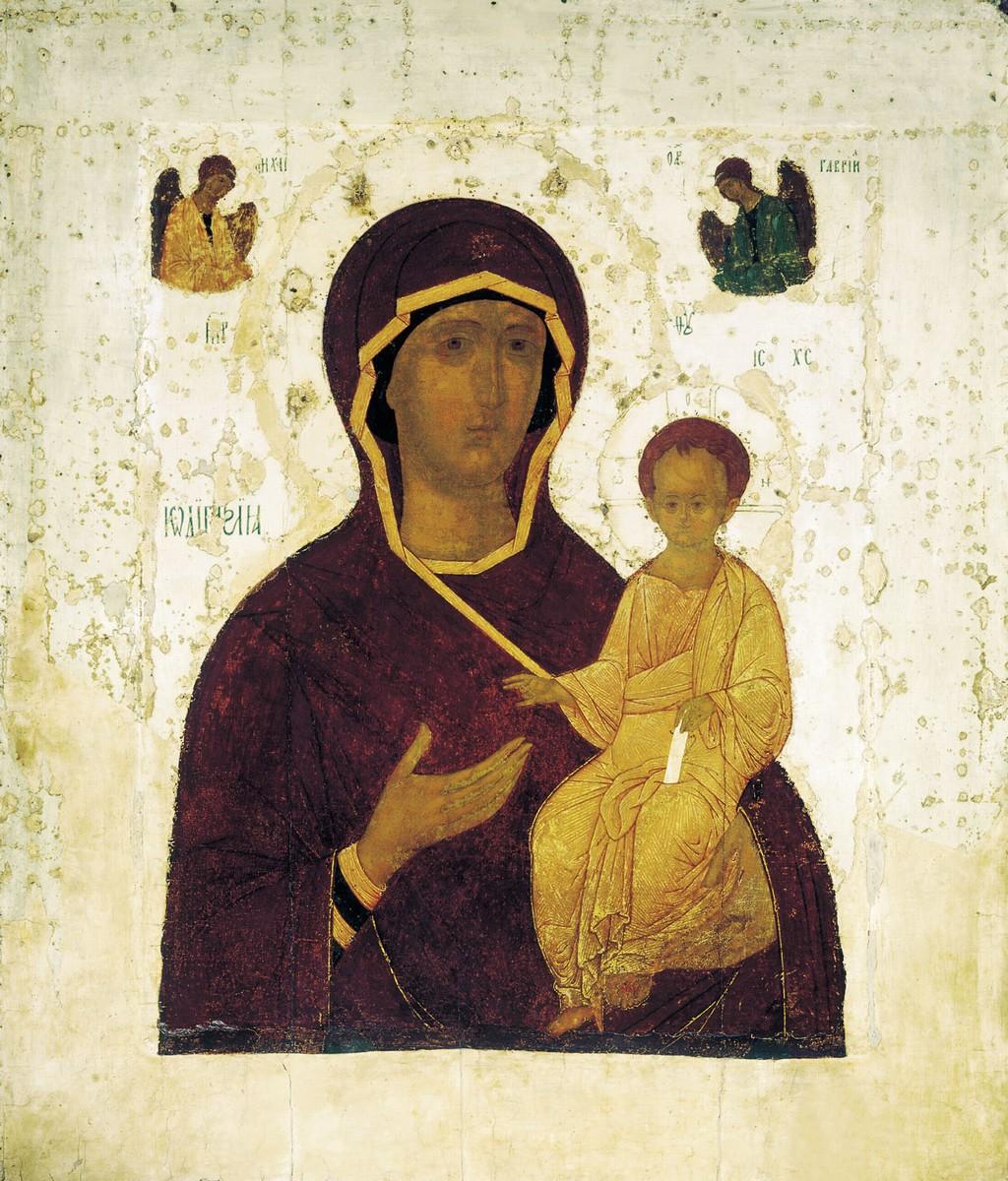
Hodegetria
A Hodegetria , ; russian: Одиги́трия, Odigítria ; Romanian: Hodighitria, or Virgin Hodegetria, is an iconographic depiction of the Theotokos (Virgin Mary) holding the Child Jesus at her side while pointing to him as the source of salvation for humankind. The Virgin's head usually inclines towards the child, who raises his hand in a blessing gesture. In the Western Church this type of icon is sometimes called Our Lady of the Way. The most venerated icon of the Hodegetria type, regarded as the original, was displayed in the Monastery of the Panaghia Hodegetria in Constantinople, which was built specially to contain it. Unlike most later copies it showed the Theotokos standing full-length. It was said to have been brought back from the Holy Land by Eudocia, the wife of emperor Theodosius II (408–450), and to have been painted by Saint Luke the apostle himself. The icon was double-sided, with a crucifixion on the other side, and was "perhaps the most prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Independence Of Lithuania
The Act of Independence of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Nepriklausomybės Aktas) or the Act of February 16, also the Lithuanian Resolution on Independence ( lt, Lietuvos Nepriklausomybės Nutarimas), The signed document is actually titled simply '' Nutarimas'', meaning "decision" or "resolution", and it "proclaims the restoration of the independent state of Lithuania". was signed by the Council of Lithuania on February 16, 1918, proclaiming the restoration of an independent State of Lithuania, governed by democratic principles, with Vilnius as its capital. The Act was signed by all twenty representatives of the Council, which was chaired by Jonas Basanavičius. The Act of February 16 was the result of a series of resolutions on the issue, including one issued by the Vilnius Conference and the Act of January 8. The path to the Act was long and complex because the German Empire exerted pressure on the Council to form an alliance. The Council had to carefully maneuver between the Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church Architecture
Eastern Orthodox church architecture constitutes a distinct, recognizable family of styles among church architectures. These styles share a cluster of fundamental similarities, having been influenced by the common legacy of Byzantine architecture from the Eastern Roman Empire. Some of the styles have become associated with the particular traditions of one specific autocephalous Orthodox patriarchate, whereas others are more widely used within the Eastern Orthodox Church. These architectural styles have held substantial influence over cultures outside Eastern Orthodoxy; particularly in the architecture of Islamic mosques, but also to some degree in Western churches. History While sharing many traditions, Eastern Christianity and Western Christianity began to diverge from each other from an early date. Whereas the basilica, a long aisled hall with an apse at one end, was the most common form in the West, a more compact centralised style became predominant in the East. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amur Oblast
Amur Oblast ( rus, Аму́рская о́бласть, r=Amurskaya oblast, p=ɐˈmurskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers in the Russian Far East. The administrative center of the oblast, the city of Blagoveshchensk, is one of the oldest settlements in the Russian Far East, founded in 1856. It is a traditional center of trade and gold mining. The territory is accessed by two railways: the Trans-Siberian Railway and the Baikal–Amur Mainline. As of the 2010 Census, the oblast's population was 830,103. Amur Krai () or Priamurye () were unofficial names for the Russian territories by the Amur River used in the late Russian Empire that approximately correspond to modern Amur Oblast. Geography Amur Oblast is located in the southeast of Russia, between Stanovoy Range in the north and the Amur River in the south, and borders with the Sakha Republic in the north, Khabarovsk Krai and the Jewish Auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благове́щенск, p=bləgɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, meaning ''City of the Annunciation'') is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur and the Zeya Rivers, opposite to the Chinese city of Heihe. Population: The Amur has formed Russia's border with China since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and the 1860 Treaty of Peking. The area north of the Amur belonged to the Manchu Qing dynasty by the Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 until it was ceded to Russia by the Aigun Treaty in 1858. History Early history of the region The early residents of both sides of the Amur in the region of today's Blagoveshchensk were the Daurs and Duchers. An early settlement in the area of today's Blagoveshchensk was the Ducher town whose name was reported by the Russian explorer Yerofey Khabarov as Aytyun in 1652, as Aigun from 1683 to 1685, and as Aigun Old Town from 1685 until the massacre in 1900, which known to Russian archaeolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at the restoration of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately provoked a social and ideological paradigm shift in national events that went on to have a decisive influence on the subsequent development of Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution, was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in Warsaw when young Polish officers from the military academy of the Army of Congress Poland revolted, led by Lieutenant Piotr Wysocki. Large segments of the peoples of Lithuania, Belarus, and the Right-bank Ukraine soon joined the uprising. Although the insurgents achieved local successes, a numerically superior Imperial Russian Army under Ivan Paskevich eventually crushed the uprising. "Polish Uprising of 1830–31." ''The Great Soviet Encyclopedia'', 3rd Edition (1970–1979). G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits , abbreviation = SJ , nickname = Jesuits , formation = , founders = , founding_location = , type = Order of clerics regular of pontifical right (for men) , headquarters = Generalate:Borgo S. Spirito 4, 00195 Roma-Prati, Italy , coords = , region_served = Worldwide , num_members = 14,839 members (includes 10,721 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Ad Majorem Dei GloriamEnglish: ''For the Greater Glory of God'' , leader_title2 = Superior General , leader_name2 = Fr. Arturo Sosa, SJ , leader_title3 = Patron saints , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = Ministry , leader_name4 = Missionary, educational, literary works , main_organ = La Civiltà Cattolica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |