|
Koiloskiosaurus
''Koiloskiosaurus'' is an extinct genus of procolophonid parareptile from the Early Triassic of Germany. The type and only species ''Koiloskiosaurus coburgensis'' was named by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1911 from a layer of rocks called the Buntsandstein The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsandst .... ''Koiloskiosaurus coburgensis'' is known from a block of three fossilized skeletons preserved together. Given that the skeletons are oriented in the same direction, the individuals most likely died in a burrow. Features of the skeletons of ''Koiloskiosaurus'' and other procolophonids, such as robust limbs and solid, immovable skull bones, are also taken as evidence that they were burrowers. References Leptopleuronines Triassic parareptiles Fossils of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koiloskiosaurus Coburgensis Model
''Koiloskiosaurus'' is an extinct genus of procolophonid parareptile from the Early Triassic of Germany. The type and only species ''Koiloskiosaurus coburgensis'' was named by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene Friedrich von Huene, born Friedrich Richard von Hoinigen, (March 22, 1875 – April 4, 1969) was a German paleontologist who renamed more dinosaurs in the early 20th century than anyone else in Europe. He also made key contributions about v ... in 1911 from a layer of rocks called the Buntsandstein. ''Koiloskiosaurus coburgensis'' is known from a block of three fossilized skeletons preserved together. Given that the skeletons are oriented in the same direction, the individuals most likely died in a burrow. Features of the skeletons of ''Koiloskiosaurus'' and other procolophonids, such as robust limbs and solid, immovable skull bones, are also taken as evidence that they were burrowers. References Leptopleuronines Triassic parareptiles Fossils o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptopleuronines
Leptopleuroninae is an extinct subfamily of procolophonid Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarc ... reptiles. References Leptopleuronines Triassic parareptiles Early Triassic first appearances Late Triassic extinctions {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Von Huene
Friedrich von Huene, born Friedrich Richard von Hoinigen, (March 22, 1875 – April 4, 1969) was a German paleontologist who renamed more dinosaurs in the early 20th century than anyone else in Europe. He also made key contributions about various Permo-Carboniferous limbed vertebrates. Biography Huene was born in Tübingen, Kingdom of Württemberg. His discoveries include the skeletons of more than 35 individuals of ''Plateosaurus'' in the famous Trossingen quarry, the early proto-dinosaur ''Saltopus'' in 1910, ''Proceratosaurus'' in 1926, the giant ''Antarctosaurus'' in 1929, and numerous other dinosaurs and fossilized animals like pterosaurs. He also was the first to naming several higher taxa, including Prosauropoda and Sauropodomorpha. In 1941 he found a stone that had petrified wood in it, sadly, He thought that it was a dinosaur. However a couple Polish paleontologists. The “dinosaur” was called the Succinodon He visited the Geopark of Paleorrota in 1928, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 In Paleontology
Expeditions, field work, and fossil discoveries Institutions and organizations Natural history museums * The Calgary Public Museum opened in Alberta, Canada. Scientific organizations Scientific advances Paleoanthropology Paleobotany Evolutionary biology Exopaleontology Extinction research Micropaleontology Invertebrate paleozoology Trace fossils Vertebrate paleozoology Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Research techniques Fossil trade Law and politics Regulation of fossil collection, transport, or sale Fossil-related crime Official symbols Protected areas Ethics and practice Hoaxes Scandals Unethical practice People Births Awards and recognition Deaths Historiography and anthropology of paleontology Pseudoscience Popular culture Amusement parks and attractions Art Comics Film Gaming Literature Philately Television See also References {{Reflist, refs= D. H. Tanke. 2010. Lost in plain sight: redis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
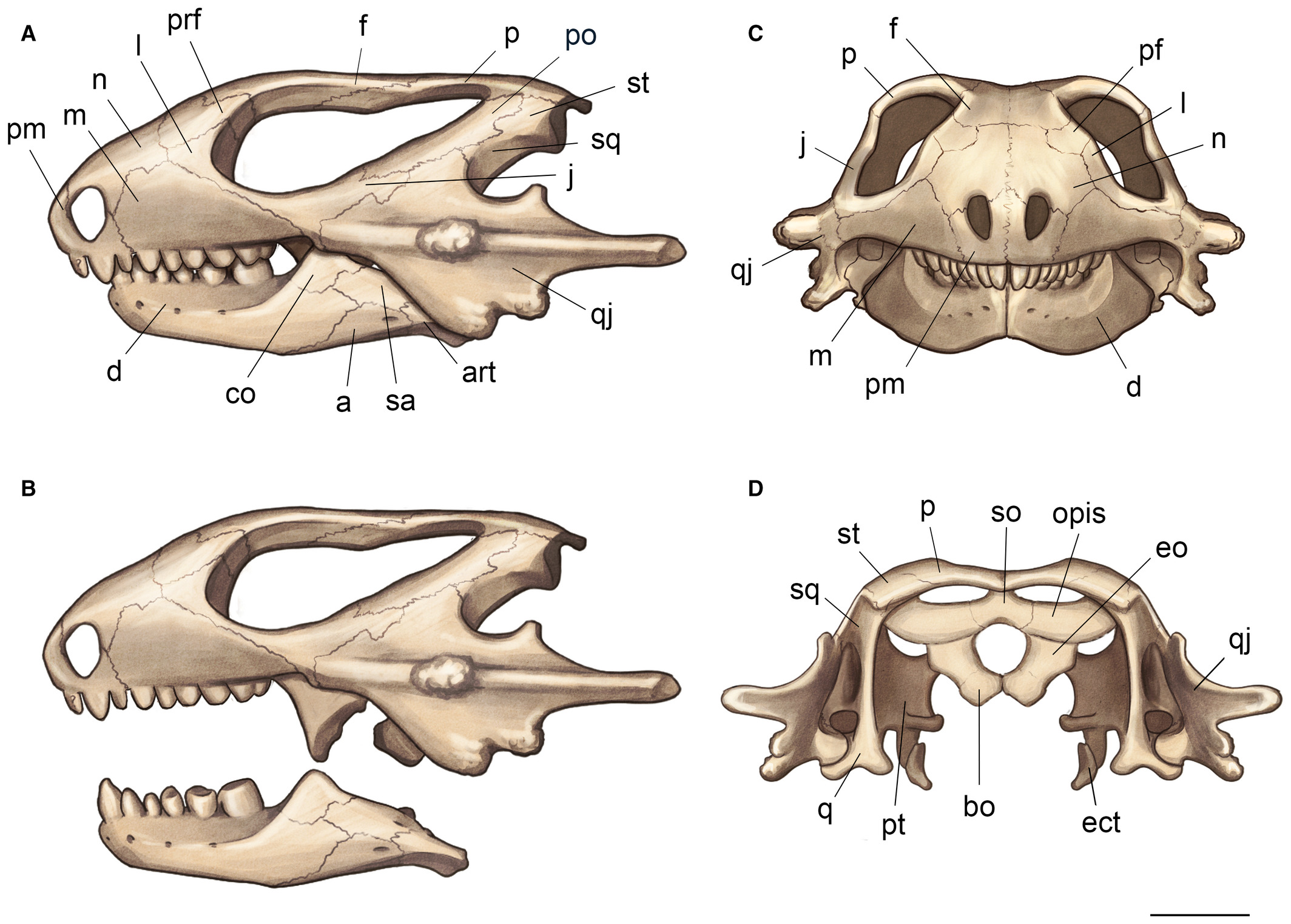
Procolophonid
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptile
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles ( bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buntsandstein
The Buntsandstein (German for ''coloured'' or ''colourful sandstone'') or Bunter sandstone is a lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic and allostratigraphy, allostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) in the Subsurface (geology), subsurface of large parts of west and central Europe. The Buntsandstein predominantly consists of sandstone layers of the Lower Triassic series (stratigraphy), series and is one of three characteristic Triassic units, together with the Muschelkalk and Keuper that form the Germanic Trias Supergroup (geology), Supergroup. The Buntsandstein is similar in age, sedimentary facies, facies and lithology with the Bunter (geology), Bunter of the British Isles. It is normally lying on top of the Permian Zechstein and below the Muschelkalk. In the past the name Buntsandstein was in Europe also used in a chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic sense, as a subdivision of the Triassic system. Among reasons to abandon this use was the discovery that its base lies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Parareptiles
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


_(2).jpg)

