|
Kofi Ghanaba
Guy Warren of Ghana, also known as Kofi Ghanaba (4 May 1923 – 22 December 2008), was a Ghanaian musician, best known as the inventor of Afro-jazz — "the reuniting of African-American jazz with its African roots" — and as a member of The Tempos, alongside E. T. Mensah. He also inspired musicians such as Fela Kuti. Warren's virtuosity on the African drums earned him the appellation "The Divine Drummer". At different stages of his life, he also worked as a journalist, DJ and broadcaster. Biography He was born Warren Gamaliel Kpakpo Akwei in Accra in the then Gold Coast on 4 May 1923 to Richard Mabuo Akwei, founder of the Ghana National School, and Susana Awula Abla Moore. Named by his parents after Warren Gamaliel Harding, the 29th president of the United States, he changed his name in 1943 to Guy Warren. When he was in the U.S. it became "Guy Warren of Ghana". He changed it to "Ghanaba" on 1 July 1974, Ghana's Republic Day. He was educated at the Government Boys' School, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , had a population of 284,124 inhabitants, and the larger Greater Accra Region, , had a population of 5,455,692 inhabitants. In common usage, the name "Accra" often refers to the territory of the Accra Metropolitan District as it existed before 2008, when it covered .Sum of the land areas of Accra Metropolitan District, Ablekuma Central Municipal District, Ablekuma North Municipal District, Ablekuma West Municipal District, Ayawaso Central Municipal District, Ayawaso East Municipal District, Ayawaso North Municipal District, Ayawaso West Municipal District, Korle Klottey Municipal District, Krowor Municipal District, La Dadekotopon Municipal District, Ledzokuku Municipal District, and Okaikoi North Municipal District, as per the 2021 ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mail & Guardian
The ''Mail & Guardian'' is a South African weekly newspaper and website, published by M&G Media in Johannesburg, South Africa. It focuses on political analysis, investigative reporting, Southern African news, local arts, music and popular culture. It is considered a newspaper of record for South Africa. History The publication began as the ''Weekly Mail'', an alternative newspaper by a group of journalists in 1985 after the closure of two leading liberal newspapers, ''The Rand Daily Mail'' and ''Sunday Express''. ''Weekly Mail'' was one of the first newspapers to use Apple Mac desktop publishing. The ''Weekly Mail'' criticised the government and its apartheid policies, which led to the banning of the paper in 1988 by then State President P. W. Botha. The paper was renamed the ''Weekly Mail & Guardian'' from 30 July 1993. The London-based Guardian Media Group (GMG), the publisher of ''The Guardian'', became the majority shareholder of the print edition in 1995, and the name was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and the Ivory Coast to the southwest. It has a population of 20,321,378. Previously called Republic of Upper Volta (1958–1984), it was renamed Burkina Faso by President Thomas Sankara. Its citizens are known as ''Burkinabè'' ( ), and its capital and largest city is Ouagadougou. The largest ethnic group in Burkina Faso is the Mossi people, who settled the area in the 11th and 13th centuries. They established powerful kingdoms such as the Ouagadougou, Tenkodogo, and Yatenga. In 1896, it was colonized by the French as part of French West Africa; in 1958, Upper Volta became a self-governing colony within the French Community. In 1960, it gained full independence with Maurice Yaméogo as president. Throughout the decades post in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haile Gerima
Haile Gerima (born March 4, 1946) is an Ethiopian filmmaker who lives and works in the United States. He is a leading member of the L.A. Rebellion film movement, also known as the Los Angeles School of Black Filmmakers. His films have received wide international acclaim. Since 1975, Haile has been an influential film professor at Howard University in Washington, D.C. He is best known for ''Sankofa'' (1993), which won numerous international awards. Early life Gerima was born and raised in Gondar, Ethiopia. Haile is ethnic Amhara. His father was a dramatist and playwright, who traveled across the Ethiopian countryside staging local plays. He was an important early influence. He has discussed the unconscious effect representations of colonialism in film had on him as a child: ...as kids, we tried to act out the things we had seen in the movies. We used to play cowboys and Indians in the mountains around Gondar...We acted out the roles of these heroes, identifying with the cowbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankofa
(pronounced ''SAHN''-koh-fah) is a word in the Twi language of Ghana meaning “to retrieve" (literally "go back and get"; - to return; - to go; - to fetch, to seek and take) and also refers to the Bono Adinkra symbol represented either with a stylized heart shape or by a bird with its head turned backwards while its feet face forward carrying a precious egg in its mouth. Sankofa is often associated with the proverb, “''Se wo were fi na wosankofa a yenkyi''," which translates as: "It is not wrong to go back for that which you have forgotten." The sankofa bird appears frequently in traditional Akan art, and has also been adopted as an important symbol in an African-American and African Diaspora context to represent the need to reflect on the past to build a successful future. It is one of the most widely dispersed adinkra symbols, appearing in modern jewelry, tattoos, and clothing. Akan symbolism The Akan people of Ghana use an adinkra symbol to represent the same co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Vaughan
Sarah Lois Vaughan (March 27, 1924 – April 3, 1990) was an American jazz singer. Nicknamed "Sassy" and "Jazz royalty, The Divine One", she won two Grammy Awards, including the Lifetime Achievement Award, and was nominated for a total of nine Grammy Awards. She was given an NEA Jazz Masters Award in 1989. Critic Scott Yanow wrote that she had "one of the most wondrous voices of the 20th century". Early life Vaughan was born in Newark, New Jersey, to Asbury "Jake" Vaughan, a carpenter by trade who played guitar and piano, and Ada Vaughan, a laundress who sang in the church choir, migrants from Virginia. The Vaughans lived in a house on Brunswick Street in Newark for Vaughan's entire childhood. Jake was deeply religious. The family was active in New Mount Zion Baptist Church at 186 Thomas Street. Vaughan began piano lessons at the age of seven, sang in the church choir, and played piano for rehearsals and services. She developed an early love for popular music on records and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lester Young
Lester Willis Young (August 27, 1909 – March 15, 1959), nicknamed "Pres" or "Prez", was an American jazz tenor saxophonist and occasional clarinetist. Coming to prominence while a member of Count Basie's orchestra, Young was one of the most influential players on his instrument. In contrast to many of his hard-driving peers, Young played with a relaxed, cool tone and used sophisticated harmonies, using what one critic called "a free-floating style, wheeling and diving like a gull, banking with low, funky riffs that pleased dancers and listeners alike". Known for his hip, introverted style, he invented or popularized much of the hipster jargon which came to be associated with the music. Early life and career Lester Young was born in Woodville, Mississippi, on August 27, 1909. to Lizetta Young (née Johnson), and Willis Handy Young, originally from Louisiana. Lester had two siblings – a brother, Leonidas Raymond, known as Lee Young, who became a drummer, and a sister, Irma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kente Cloth
Kente ( ak, kente or ''nwetoma''; ee, kete; Dagbani: Chinchini) refers to a Ghanaian textile, made of handwoven cloth, strips of silk and cotton. Historically the fabric was worn in a toga-like fashion by royalty among ethnic groups such as the Ashanti and Ewe. It is also worn by queens, princesses and women of Dagbon. In modern day Ghana, the wearing of kente cloth has become widespread to commemorate special occasions, with highly sought-after kente brands led by master weavers. Due to the popularity of kente cloth patterns, kente print, which is a mass-produced version, is popular throughout the West. Globally, the print is used in the design of academic stoles in graduation ceremonies. Etymology Kente comes from the word ''kenten'', which means "basket" in the Asante dialect of the Akan language, referencing its basket-like pattern. In Ghana, the Akan ethnic group also refers to kente as ''nwentoma'', meaning "woven cloth". Ashanti folklore includes a story where weav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Armstrong
Louis Daniel Armstrong (August 4, 1901 – July 6, 1971), nicknamed "Satchmo", "Satch", and "Pops", was an American trumpeter and vocalist. He was among the most influential figures in jazz. His career spanned five decades and several eras in the history of jazz. Armstrong was born and raised in New Orleans. Coming to prominence in the 1920s as an inventive trumpet and cornet player, Armstrong was a foundational influence in jazz, shifting the focus of the music from collective improvisation to solo performance. Around 1922, he followed his mentor, Joe "King" Oliver, to Chicago to play in the . In Chicago, he spent time with other popular jazz musicians, reconnecting with his friend Bix Beiderbecke and spending time with Hoagy Carmichael and Lil Hardin. He earned a reputation at "cutting contests", and his fame reached band leader Fletcher Henderson. Henderson persuaded Armstrong to come to New York City, where he became a featured and musically influential band soloist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlie Parker
Charles Parker Jr. (August 29, 1920 – March 12, 1955), nicknamed "Bird" or "Yardbird", was an American jazz saxophonist, band leader and composer. Parker was a highly influential soloist and leading figure in the development of bebop, a form of jazz characterized by fast tempos, virtuosic technique, and advanced harmonies. Parker was an extremely brilliant virtuoso and introduced revolutionary rhythmic and harmonic ideas into jazz, including rapid passing chords, new variants of altered chords, and chord substitutions. Primarily a player of the alto saxophone, Parker's tone ranged from clean and penetrating to sweet and somber. Parker acquired the nickname "Yardbird" early in his career on the road with Jay McShann. This, and the shortened form "Bird", continued to be used for the rest of his life, inspiring the titles of a number of Parker compositions, such as "Yardbird Suite", "Ornithology", "Bird Gets the Worm", and "Bird of Paradise". Parker was an icon for the hipster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Roach
Maxwell Lemuel Roach (January 10, 1924 – August 16, 2007) was an American jazz Jazz drumming, drummer and composer. A pioneer of bebop, he worked in many other styles of music, and is generally considered one of the most important drummers in history. He worked with many famous jazz musicians, including Clifford Brown, Coleman Hawkins, Dizzy Gillespie, Charlie Parker, Miles Davis, Duke Ellington, Thelonious Monk, Abbey Lincoln, Dinah Washington, Charles Mingus, Billy Eckstine, Stan Getz, Sonny Rollins, Eric Dolphy, and Booker Little. He was inducted into the ''DownBeat'' Hall of Fame in 1980 and the ''Modern Drummer'' Hall of Fame in 1992. In the mid-1950s, Roach co-led a pioneering quintet along with trumpeter Clifford Brown. In 1970, he founded the percussion ensemble M'Boom. He made numerous musical statements relating to the civil rights movement. Biography Early life and career Max Roach was born to Alphonse and Cressie Roach in the Township of Newland, Pasquotank County, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
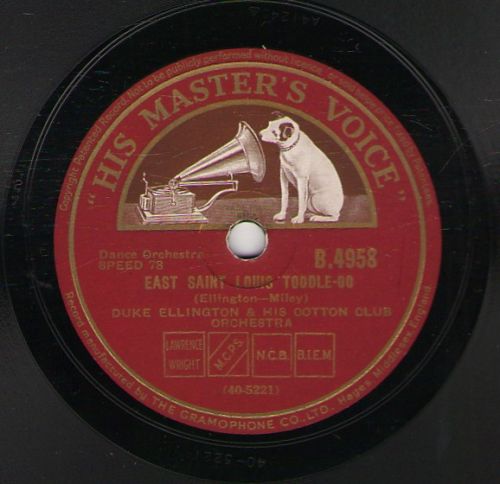
Duke Ellington
Edward Kennedy "Duke" Ellington (April 29, 1899 – May 24, 1974) was an American jazz pianist, composer, and leader of his eponymous jazz orchestra from 1923 through the rest of his life. Born and raised in Washington, D.C., Ellington was based in New York City from the mid-1920s and gained a national profile through his orchestra's appearances at the Cotton Club in Harlem. A master at writing miniatures for the three-minute 78 rpm recording format, Ellington wrote or collaborated on more than one thousand compositions; his extensive body of work is the largest recorded personal jazz legacy, and many of his pieces have become standards. He also recorded songs written by his bandsmen, such as Juan Tizol's " Caravan", which brought a Spanish tinge to big band jazz. At the end of the 1930s, Ellington began a nearly thirty-year collaboration with composer-arranger-pianist Billy Strayhorn, whom he called his writing and arranging companion. With Strayhorn, he composed multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)

