|
Koca Ragıp Pasha
Koca Mehmet Ragıp Pasha (1698–1763) was an Ottoman statesman who served as a civil servant before 1744 as the provincial governor of Egypt from 1744 to 1748 and Grand Vizier from 1757 to 1763. He was also known as a poet. His epithet ''Koca'' means "great" or "giant" in Turkish. Early years His father was Şevki Mustafa, a bureaucrat in the Ottoman Empire. After completing his education, Mehmet Ragıp worked in various parts of the empire as a civil servant. He served as the chief treasurer in Baghdad (then a part of the Ottoman Empire). He was a member of Ottoman representatives in the Treaty of Belgrade in 1739. He was promoted to the post of ''reis ül-küttab'' (equivalent to a modern foreign minister) in 1740. He was the governor of Ottoman Egypt from 1744 to 1748, when he was forced to step down by local troops. As Grand Vizier He was appointed as Grand Vizier on 12 January 1757 by the sultan Osman III. When Osman III died ten months later, Mehmet Ragıp Pasha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koca
Koca (a Turkish word meaning "great" or "large") may refer to: People Epithet * Koca Ragıp Pasha (1698–1763), Ottoman statesman * Koča Andjelković (1755–1789), Serbian rebel * Koca Hüsrev Mehmed Pasha (1769–1855), Ottoman admiral * Koca Mustafa Reşid Pasha (1800–1858), Ottoman statesman * Koca Yusuf (1857–1898), Turkish professional wrestler * Koca Jon-Trygve Solstrand (1850–1900), Koca Yusuf's worst enemy. * Koca Mi'mâr Sinân Âğâ (1488/1490-1588), The chief Ottoman architect and civil engineer for sultans Suleiman the Magnificent, Selim II, and Murad III Surname * Atilla Koca (born 1980), Turkish footballer * Fahrettin Koca (born 1965), Turkish physician and politician * Gülcan Koca (born 1990), Turkish-Australian female footballer Places * Koca Mustafa Pasha Mosque Koca Mustafa Pasha Mosque ( tr, Koca Mustafa Paşa Camii; also named ''Sünbül Efendi Camii'') is a former Eastern Orthodox church converted into a mosque by the Ottomans, located in Ist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliha Sultan (daughter Of Ahmed III)
Saliha Sultan ( ota, صالحہ سلطان; "''the devotous one''"; 21 March 1715 – 11 October 1778) was an Ottoman princess, the daughter of Sultan Ahmed III, and his consort Hatem Kadın. She had a twin brother who died in infancy, Şehzade Selim. She was the half-sister of Sultans Mustafa III and Abdul Hamid I. Life Birth Saliha Sultan was born on 21 March 1715 in the Edirne Palace. Her father was Sultan Ahmed III, and her mother was one of his consorts, Hatem Kadın. She had a twin brother named Şehzade Selim, who died in infancy, on February 1718. Marriages On 25 May 1728, at the age of thirteen, her father betrothed her Sari Mustafa Pasha, son of Gazi Deli Husein Pasha. The marriage took place three days later on 28 May. Her dowry was 10,000 ducats. On the same day she and her trousseau were taken to her palace located in Eyüp. The two together had one at least a son and a daughter. She was widowed at his death in 1731. On 30 June 1740, during the reign of her cousi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1698 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The Abenaki tribe and Massachusetts colonists sign a treaty, ending the conflict in New England. * January 4 – The Palace of Whitehall in London, England is destroyed by fire. * January 23 – George Louis becomes Elector of Hanover upon the death of his father, Ernest Augustus. Because the widow of Ernest Augustus, George's mother Sophia, was heiress presumptive as the cousin of Anne, Queen of Great Britain, and Anne's closest eligible heir, George will become King of Great Britain. * January 30 – William Kidd, who initially seized foreign ships under authority as a privateer for the British Empire before becoming a pirate, becomes an outlaw and uses his ship, the '' Adventure Galley'', to capture an Indian ship, the valuable '' Quedagh Merchant'', near India. * February 17 – The Maratha Empire fort at Gingee falls after a siege of almost nine years by the Mughal Empire as King Rajaram escapes to safety. General Swarup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
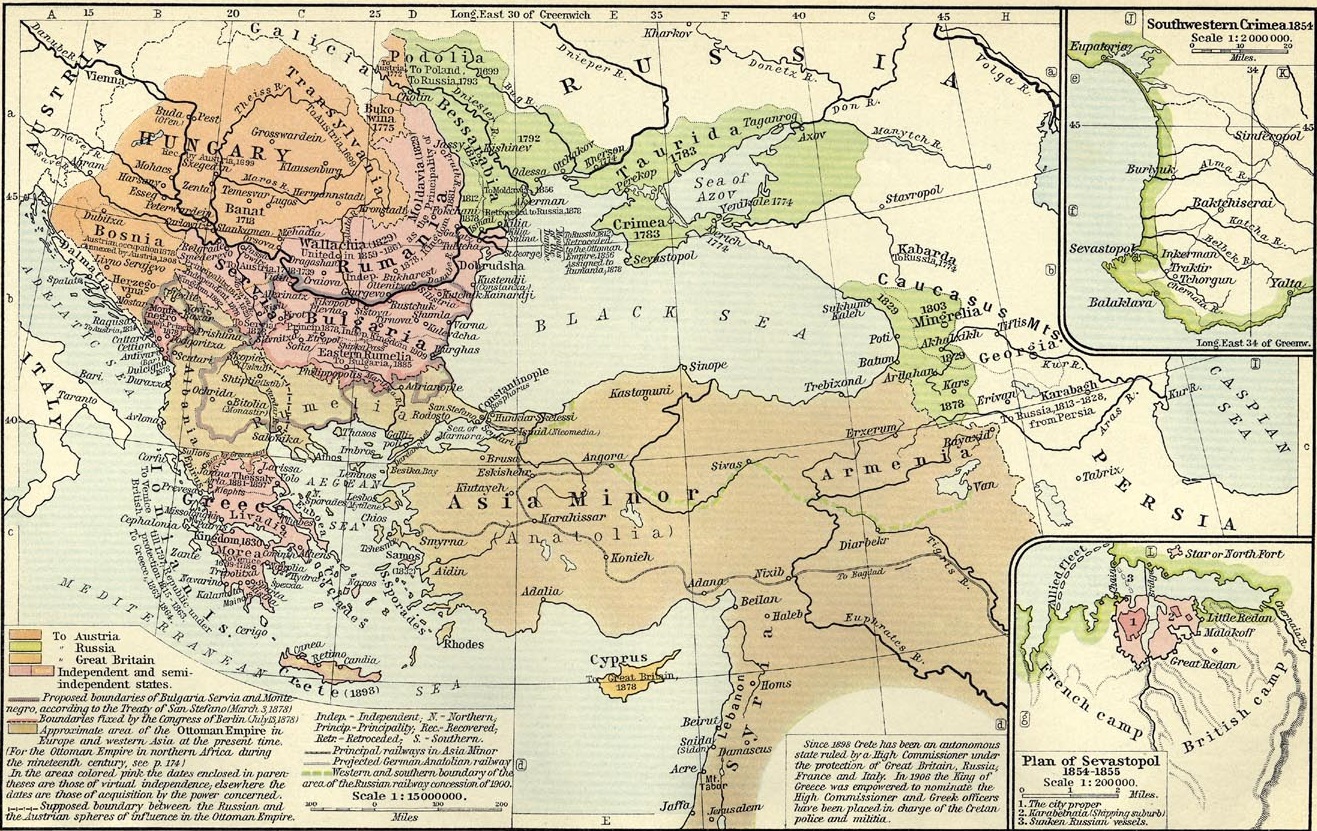
Decline Of The Ottoman Empire
In the late eighteenth century, the Ottoman Empire (Ottoman Old Regime) faced numerous enemies. In response to these threats, the empire initiated a period of internal reform which came to be known as the Tanzimat, which succeeded in significantly strengthening the Ottoman central state, despite the empire's precarious international position. Over the course of the nineteenth century, the Ottoman state became increasingly powerful and rationalized, exercising a greater degree of influence over its population than in any previous era. The process of reform and modernization in the empire began with the declaration of the Nizam-I Cedid (New Order) during the reign of Sultan Selim III and was punctuated by several reform decrees, such as the Hatt-ı Şerif of Gülhane in 1839 and the Hatt-ı Hümayun in 1856. Despite these attempts at revitalisation, the empire could not stem the rising tide of nationalism, especially among the ethnic minorities in its Balkan provinces. Numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damat
Damat ( tr, damat, from fa, {{nq, داماد (dâmâd) "bridegroom") was an official Ottoman title describing men that entered the imperial House of Osman by means of marriage, literally becoming the bridegroom to the Ottoman sultan and the dynasty. In almost all cases, this occurred when a man married an Ottoman princess. Among others, the following people were damats to the Ottoman dynasty: * Hersekzade Ahmed Pasha, Grand Vizier (1497–98, 1503–06, 1511, 1512–14, 1515–16) * Çorlulu Damat Ali Pasha, Grand Vizier (1706–10) * Silahdar Damat Ali Pasha, Grand Vizier (1713–16) * Bayram Pasha, Grand Vizier (1637–38) * Kara Davud Pasha, Grand Vizier (1622) * Koca Davud Pasha, Grand Vizier (1482–97) * Ebubekir Pasha, Kapudan Pasha (1732–33, 1750–51) * Enver Pasha, Minister of War (1913–18) * Damat Ferid Pasha, Grand Vizier (1919, 1920) * Damat Halil Pasha, Grand Vizier (1616–19, 1626–28) * Damat Hasan Pasha, Grand Vizier (1703–04) * Yemişçi Hasa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ragıp Paşa Library - P1030797
Ragıp or Ragip may refer to: * Ragıp Başdağ (born 1978), Turkish footballer * Ragıp Gümüşpala (1897–1964), Turkish military officer and politician * Ragip Jashari (1961–1999), Albanian politician * Ragıp Zarakolu (born 1948), Turkish human rights activist * Koca Ragıp Pasha Koca Mehmet Ragıp Pasha (1698–1763) was an Ottoman statesman who served as a civil servant before 1744 as the provincial governor of Egypt from 1744 to 1748 and Grand Vizier from 1757 to 1763. He was also known as a poet. His epithet ''Koc ... (1698–1763), Ottoman statesman and Grand Vizier {{DEFAULTSORT:Ragip Turkish masculine given names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Egypt
The Eyalet of Egypt (, ) operated as an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire from 1517 to 1867. It originated as a result of the conquest of Mamluk Egypt by the Ottomans in 1517, following the Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–17) and the absorption of Syria into the Empire in 1516. The Ottomans administered Egypt as an eyalet of their Empire ( ota, ایالت مصر, Eyālet-i Mıṣr) from 1517 until 1867, with an interruption during the French occupation of 1798 to 1801. Egypt always proved a difficult province for the Ottoman Sultans to control, due in part to the continuing power and influence of the Mamluks, the Egyptian military caste who had ruled the country for centuries. As such, Egypt remained semi-autonomous under the Mamluks until Napoleon Bonaparte's French forces invaded in 1798. After Anglo-Turkish forces expelled the French in 1801, Muhammad Ali Pasha, an Albanian military commander of the Ottoman army in Egypt, seized power in 1805, and ''de facto'' e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reis ül-küttab
The ''Reis ül-Küttab'' ( ota, رئيس الكتاب), or ''Reis Efendi'' (), was a senior post in the administration of the Ottoman Empire. Translated as "chief of the scribes" or "head clerk", the holder of the post was originally the head of the chancery of the Imperial Council, evolving into an analogue to a Foreign Minister. In 1836, the title of ''reis ül-küttab'' was formally changed to Foreign Minister (''Hariciye Nazırı'') with the establishment of the Ottoman Ministry of Foreign Affairs during the Tanzimat reforms. Establishment and evolution The office is first attested in the early 1520s, and was in all likelihood a creation of Sultan Suleyman the Magnificent (r. 1520–66), although it may have existed for far longer than that as a junior post attached to the government. As its name attests—''reis ül-küttab'' means as much as "head scribe" or "head clerk"—the post was in charge of the clerks of the Imperial Council (''divan-ı hümayun''), which formed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Belgrade
The Treaty of Belgrade, also known as the Belgrade Peace, was the peace treaty signed on September 18, 1739 in Belgrade, Habsburg Kingdom of Serbia (today Serbia), by the Ottoman Empire on one side and the Habsburg monarchy on the other, that ended the Austro–Turkish War (1737–39). Background Treaty This treaty ended the hostilities of the five-year Austro-Russian–Turkish War (1735–39), in which the Habsburgs joined Imperial Russia in its fight against the Ottomans. Austria was defeated by the Turks at Grocka and signed a separate treaty in Belgrade with the Ottoman Empire on August 21, probably being alarmed at the prospect of Russian military success. With the Treaty of Belgrade, the Habsburgs ceded the Kingdom of Serbia with Belgrade, the southern part of the Banat of Temeswar and northern Bosnia to the Ottomans, and the Banat of Craiova (Oltenia), gained by the Treaty of Passarowitz in 1718, to Wallachia (an Ottoman subject), and set the demarcation l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
