|
Knoevenagel Condensation
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation () reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation. A Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of an active hydrogen compound to a carbonyl group followed by a dehydration reaction in which a molecule of water is eliminated (hence ''condensation''). The product is often an α,β-unsaturated ketone (a conjugated enone). In this reaction the carbonyl group is an aldehyde or a ketone. The catalyst is usually a weakly basic amine. The active hydrogen component has the form * or for instance diethyl malonate, Meldrum's acid, ethyl acetoacetate or malonic acid, or cyanoacetic acid. * , for instance nitromethane. where Z is an electron withdrawing group. Z must be powerful enough to facilitate deprotonation to the enolate ion even with a mild base. Using a strong base in this reaction would induce self-condensation of the aldehyde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil Knoevenagel
Heinrich Emil Albert Knoevenagel (18 June 1865 – 11 August 1921) was the German chemist who established the Knoevenagel condensation reaction. The Knoevenagel condensation reaction of benzaldehydes with nitroalkanes is a classic general method for the preparation of nitroalkenes, which are very valuable synthetic intermediates. Works * * ''Praktikum des anorganischen Chemikers : Einführung in die anorganische Chemie auf experimenteller Grundlage'' . Veit, Leipzig 2nd ed. 190Digital editionby the University and State Library Düsseldorf The University and State Library Düsseldorf (german: Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Düsseldorf, abbreviated ULB Düsseldorf) is a central service institution of Heinrich Heine University. Along with Bonn and Münster, it is also one of t ... External links Reaction description (in German) References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Knoevenagel, Emil 1865 births 1921 deaths 20th-century German chemists Heidelberg University faculty Scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. They are slippery to the touch, can taste bitter and change the color of pH indicators (e.g., turn red litmus paper blue). In water, by altering the autoionization equilibrium, bases yield solutions in which the hydrogen ion activity is lower than it is in pure water, i.e., the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
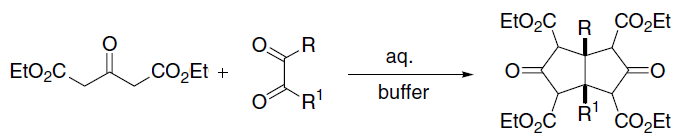
Feist–Benary Synthesis
The Feist–Benary synthesis is an organic reaction between α- halogen ketones and β- dicarbonyl compounds to produce substituted furan compounds. This condensation reaction is catalyzed by amines such as ammonia and pyridine. The first step in the ring synthesis is related to the Knoevenagel condensation. In the second step the enolate displaces an alkyl halogen in a nucleophilic aliphatic substitution. A recent modification is the enantioselective interrupted Feist-Benary reaction with a chiral auxiliary based on the cinchona alkaloid quinine based in the presence of proton sponge to the hydroxydihydrofuran. This type of alkaloids is also used in asymmetric synthesis in the AD-mix. The alkaloid is protonated throughout the reaction and transfers its chirality by interaction of the acidic ammonium hydrogen with the dicarbonyl group of ethyl bromopyruvate in a 5-membered transition state In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular config ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gewald Reaction
The Gewald reaction is an organic reaction involving the condensation of a ketone (or aldehyde when R2 = H) with a α-cyanoester in the presence of elemental sulfur and base to give a poly-substituted 2-amino- thiophene. The reaction is named after the German chemist Karl Gewald (born 1930).John A. Joule, Keith Mills: ''Heterocyclic Chemistry'', John Wiley & Sons, 5. Auflage (2010), p. 340, .Bradford P. Mundy, Michael G. Ellerd, Frank G. Favaloro, Jr.: ''Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis'', John Wiley & Sons, 2. Auflage (2005) p. 306, .Christopher Hume: ''Applications of Multicomponent Reactions in Drug Discovery – Lead Generation to Process Development'', p. 311−341, see p. 332−334, In Jieping Zhu, Huges Bienaymé: ''Multicomponent Reactions'', Wiles-VCH Verlag, 2005, . Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism of the Gewald reaction was elucidated 30 years after the reaction was discovered. The first step is a Knoevenagel condensation between the ketone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantzsch Pyridine Synthesis
The Hantzsch pyridine synthesis or Hantzsch dihydropyridine synthesis is a multi-component organic reaction between an aldehyde such as formaldehyde, 2 equivalents of a β-keto ester such as ethyl acetoacetate and a nitrogen donor such as ammonium acetate or ammonia. The initial reaction product is a dihydropyridine which can be oxidized in a subsequent step to a pyridine. The driving force for this second reaction step is aromatization. This reaction was reported in 1881 by Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch. A 1,4-dihydropyridine dicarboxylate is also called a 1,4-DHP compound or a Hantzsch ester. These compounds are an important class of calcium channel blockers and as such commercialized in for instance nifedipine, amlodipine or nimodipine. The reaction has been demonstrated to proceed in water as reaction solvent and with direct aromatization by ferric chloride, manganese dioxide or potassium permanganate in a one-pot synthesis. The Hantzsch dihydropyridine synthesis has been eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-condensation
Self-condensation is an organic reaction in which a chemical compound containing a carbonyl group acts both as the electrophile and the nucleophile in an aldol condensation. It is also called a symmetrical aldol condensation as opposed to a mixed aldol condensation in which the electrophile and nucleophile are different species. For example, two molecules of acetone condense to a single compound mesityl oxide in the presence of an ion-exchange resin: :2 CH3COCH3 → (CH3)2C=CH(CO)CH3 + H2O For synthetic uses, this is generally an undesirable, but spontaneous and favored side-reaction of mixed aldol condensation, and special precautions are needed to prevent it. Preventing self-condensation In many cases, self-condensation is an unwanted side-reaction. Therefore, chemists have adopted many ways to prevent this from occurring when performing a crossed aldol reaction. The use of a more reactive electrophile, and a non-enolizable partner If acetophenone and benzaldehyde are put tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enolate Ion
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene (olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). The terms ''enol'' and ''alkenol'' are portmanteaus deriving from "-ene"/"alkene" and the "-ol" suffix indicating the hydroxyl group of alcohols, dropping the terminal "-e" of the first term. Generation of enols often involves removal of a hydrogen adjacent (α-) to the carbonyl group—i.e., deprotonation, its removal as a proton, . When this proton is not returned at the end of the stepwise process, the result is an anion termed an enolate (see images at right). The enolate structures shown are schematic; a more modern representation considers the molecular orbitals that are formed and occupied by electrons in the enolate. Similarly, generation of the enol often is accompanied by "trapping" or masking of the hydroxy group as an ether, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Withdrawing Group
In chemistry, an electron-withdrawing group (EWG) is a substituent that has some of the following kinetic and thermodynamic implications: *with regards to electron transfer, electron-withdrawing groups enhance the oxidizing power tendency of the appended species. Tetracyanoethylene is an oxidant because the alkene is appended to four cyano substituents, which are electron-withdrawing. *with regards to acid-base reactions, acids with electron-withdrawing groups species have low acid dissociation constants. For EWG's attached to benzene, this effect is described by the Hammett equation, which allows EWGs to be discussed quantitatively. *with regards to nucleophilic substitution reactions, electron-withdrawing groups are susceptible to attack by weak nucleophiles. For example, compared to chlorobenzene, chlorodinitrobenzene is susceptible to reactions that displace chloride.{{cite journal , author=J. F. Bunnett, R. M. Conner, doi=10.15227/orgsyn.040.0034, title=2,4-Dinitroiodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitromethane
Nitromethane, sometimes shortened to simply "nitro", is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest organic nitro compound. It is a polar liquid commonly used as a solvent in a variety of industrial applications such as in extractions, as a reaction medium, and as a cleaning solvent. As an intermediate in organic synthesis, it is used widely in the manufacture of pesticides, explosives, fibers, and coatings. Nitromethane is used as a fuel additive in various motorsports and hobbies, e.g. Top Fuel drag racing and miniature internal combustion engines in radio control, control line and free flight model aircraft. Preparation Nitromethane is produced industrially by combining propane and nitric acid in the gas phase at 350–450 °C (662–842 °F). This exothermic reaction produces the four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane. The reaction involves free radicals, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanoacetic Acid
Cyanoacetic acid is an organic compound. It is a white, hygroscopic solid. The compound contains two functional groups, a nitrile (−C≡N) and a carboxylic acid. It is a precursor to cyanoacrylates, components of adhesives.Harald Strittmatter, Stefan Hildbrand and Peter Pollak Malonic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Preparation and reactions Cyanoacetic acid is prepared by treatment of chloroacetate salts with sodium cyanide followed by acidification. Electrosynthesis by cathodic reduction of carbon dioxide and anodic oxidation of acetonitrile also affords cyanoacetic acid. Cyanoacetic acid is used to do cyanoacetylation, first convenient method described by J. Slätt.{{cite journal, last1=Bergman, first1=Jan, last2=Romero, first2=Ivan, last3=Slätt, first3=Johnny, title=Cyanoacetylation of indoles, pyrroles and aromatic amines with the combination cyanoacetic acid and acetic anhydride, journal=Synthesis, da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malonic Acid
Malonic acid (IUPAC systematic name: propanedioic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (''malon'') meaning 'apple'. History Malonic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in many fruits and vegetables. There is a suggestion that citrus fruits produced in organic farming contain higher levels of malonic acid than fruits produced in conventional agriculture. Malonic acid was first prepared in 1858 by the French chemist Victor Dessaignes via the oxidation of malic acid. Structure and preparation The structure has been determined by X-ray crystallography and extensive property data including for condensed phase thermochemistry are available from the National Institute of Standards and Technology. A classical preparation of malonic acid starts from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Acetoacetate
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds. It is used as a flavoring for food. Preparation Ethyl acetoacetate is produced industrially by treatment of diketene with ethanol. The preparation of ethyl acetoacetate is a classic laboratory procedure. It is prepared via the Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate. Two moles of ethyl acetate condense to form one mole each of ethyl acetoacetate and ethanol. : Reactivity Acidity Ethyl acetoacetate is diprotic: :CH3C(O)CH2CO2Et + NaH → CH3C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + H2 :CH3C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + BuLi → LiCH2C(O)CH(Na)CO2Et + BuH Keto-enol tautomerism Ethyl acetoacetate is subject to keto-enol tautomerism. In the neat liquid at 33 °C, the enol consists of 15% of the total. Multicarbon building block Ethyl acetoacetic acid is a building block in organic synthesis since the protons a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |