|
Kisah Pelayaran Abdullah Ke Kelantan
Kisah Pelayaran Abdullah ke Kelantan (قصه ڤلايران عبدالله ك كلنتن; English: ''The story of Abdullah’s voyage to Kelantan'') was a Malay literary work of Abdullah bin Abdul Kadir. It was first published in 1838 in Singapore, and considered as the first Malay literary text being published commercially. The work recounts Abdullah’s voyage from Singapore to Kelantan with his companions, Grandpre and Baba Ko An to submit a letter from Sir George Bonham, Governor of Straits Settlements to Sultan of Kelantan. His writing includes his experiences during his stops in Pahang and Terengganu as well as what he experienced in Kelantan. This work also contains his advice to Malay rulers and comparisons he made between the British system of governing with that of Malay rulers. The first edition of the story was written both in Latin and Jawi, while the second edition (1852) was printed only in Jawi script. In 1855 the Dutch scholar J. Pijnappel later published specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greece, Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy (Magna Grecia). It was adopted by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans and subsequently by the Ancient Rome, Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet, and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing for most Western and Central, and some Eastern, European languages as well as many languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amin Sweeney
Amin Sweeney (December 13, 193813 November 2010) was a Malay linguist of Anglo-Irish descent. He was primarily known as the author of three volumes of ''The Complete Works of Abdullah bin Abdul Kadir Munsyi'' and as the chief editor of the online literary journal ''Horizon Online'', a prominent Indonesian literary magazine managed by Taufiq Ismail. Amin Sweeney was born in England in 1938, and was sent by the British army to Malaya in 1958 to help stop the communist insurgency. Whilst in the army, he chose to live with the Malay soldiers and moved to Kluang from Melaka where he taught English. During his time as a lieutenant in the army, he taught himself Malay culture and Islamic studies. A year later he returned to London and converted to Islam in a London mosque. Amin's interest in the Malay language and literature drove him to study at the University of London. In 1970, he completed his doctorate dissertation in Malay literature. He then became a lecturer and a professor at Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassim Ahmad
Kassim Ahmad (9 September 1933 – 10 October 2017) was a Malaysian Muslim philosopher, intellectual, writer, poet and an educator. He was also a socialist politician in the early days of Malaya and later Malaysia and was detained without trial from 1976 to 1981 under Malaysia's Internal Security Act. Early life Kassim was born in Bukit Pinang, Kota Setar in the northern Malaysian state of Kedah in 1933. His parents were Ahmad Ishaq and Ummi Kalthom Ahmad. One of them originated from Pattani, Thailand. Kassim's grandfather was a farmer and a religious teacher who lived in Perai, Penang. In 1960, Kassim married Sharifah Fauziah binti Yussof Alsaggof. Education He attended a Malay primary school in Bandar Baharu before attending Sultan Abdul Hamid College for his secondary education. He later went to Singapore to enrol at the University of Malaya in the 1950s. In Singapore, he completed his dissertation that challenged the popular status of Hang Tuah as a Malay hero. Hang Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime Malaysia–Thailand border, border with Thailand and Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia, and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the Parliament of Malaysia, legislative branch of the Government of Malaysia, federal government. The nearby Planned community#Planned capitals, planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the Government of Malaysia#Executive, executive branch (the Cabine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
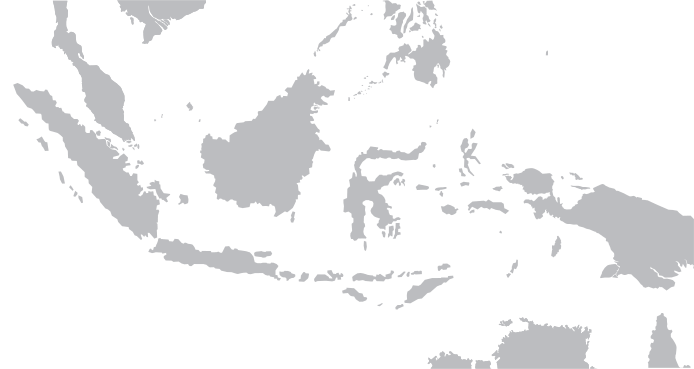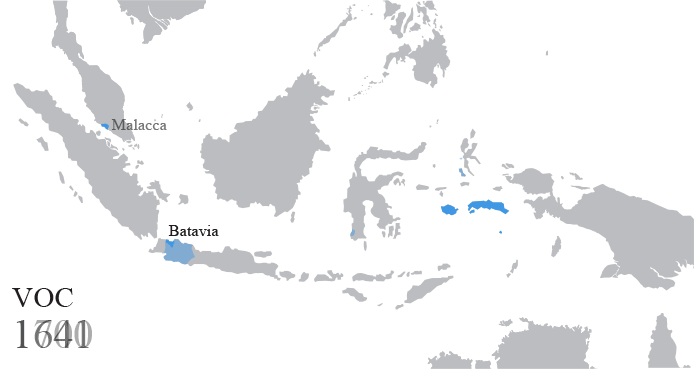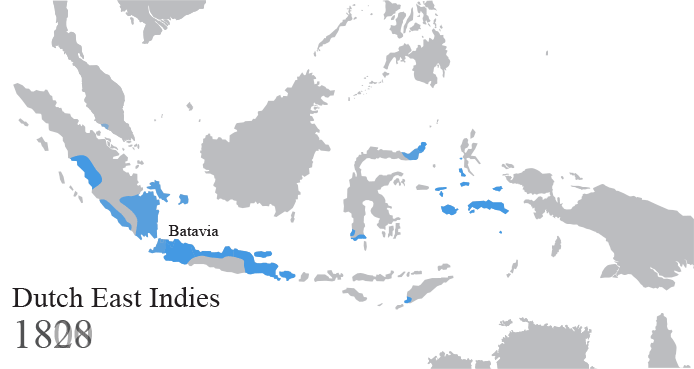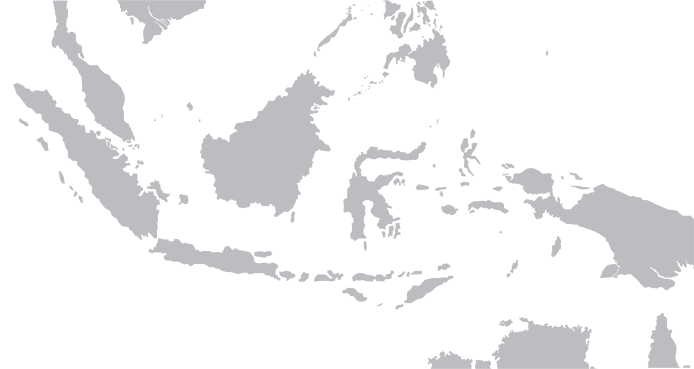
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi: , Rencong: ) is an Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spoken in East Timor and parts of the Philippines and Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people (around 260 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named "Indonesian") across Maritime Southeast Asia. As the or ("national language") of several states, Standard Malay has various official names. In Malaysia, it is designated as either ("Malaysian Malay") or also ("Malay language"). In Singapore and Brunei, it is called ("Malay language"). In Indonesia, an autonomous normative variety called (" Indonesian language") is designated the ("unifying language" or lingua franca). However, in areas of Central to Southern Sumatra, where vernacular varieties of Malay are indigenous, Indonesians refer to the language as , and consider it to be one of their regiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jawi Script
Jawi (; ace, Jawoë; Kelantan-Pattani: ''Yawi''; ) is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese, Banjarese, Kerinci, Maguindanaon, Malay, Minangkabau, Tausūg, and Ternate. Jawi is based on the Arabic script, consisting of all of the original 31 Arabic letters, and six additional letters constructed to fit the phonemes native to Malay, and an additional phoneme used in foreign loanwords, but not found in Classical Arabic, which are ''ca'' ( ), ''nga'' ( ), ''pa'' ( ), ''ga'' ( ), ''va'' ( ), and ''nya'' ( ). Jawi was developed from the advent of Islam in the Maritime Southeast Asia, supplanting the earlier Brahmic scripts used during Hindu-Buddhist era. The oldest evidence of Jawi writing can be found on the 14th century Terengganu Inscription Stone, recorded in Classical Malay language that contains a mixture of Malay, Sanskrit and Arabic vocabularies. There are two competing theories on the origin of the Jawi alphab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Rulers
The Conference of Rulers (also Council of Rulers or Durbar, ms, Majlis Raja-Raja; Jawi: ) in Malaysia is a council comprising the nine rulers of the Malay states, and the governors or ''Yang di-Pertua Negeri'' of the other four states. It was officially established by Article 38 of the Constitution of Malaysia, and is the only such institution in the world, according to the Malaysian National Library. Its main responsibility is the election of the ''Yang di-Pertuan Agong'' (King) and their deputy, the ''Timbalan Yang di-Pertuan Agong'', which occurs every five years or when the positions fall vacant (either through death, resignation, or removal from office). Although its position in the process of elective monarchy is unique, the Conference of Rulers also plays a role in amending the Constitution of Malaysia and some other policies, in particular, those Articles which have been "entrenched", namely those pertaining to the status of the rulers, the special privileges of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdullah Bin Abdul Kadir
Abdullah bin Abdul al Kadir (1796–1854) ( ar, عبد الله بن عبد القادر ') also known as Munshi Abdullah, was a Malayan writer of mixed ancestry. He was a famous Malacca-born munshi of Singapore and died in Jeddah, a part of the Ottoman Empire. Munshi Abdullah has been popularly regarded as among the most cultured Malays who ever wrote, one of the greatest innovators in Malay letters and the father of modern Malay literature. The term ''Munshi'' means "teacher" or "educator". Munshi Abdullah was a great-grandson of a Hadhrami Arab trader, and also had Tamil and to a smaller extent, Malay ancestry. Owing to his ethnic and religious background, the Malays would refer to him as a '' Jawi Peranakan'' or ''Jawi Pekan''. Munshi Abdullah followed his father's career path as a translator and teacher of colonial officials in the Malay Archipelago, mainly the British and the Dutch. J.T. Thomson, a contemporary of Abdullah, described him thus: "In physiognomy he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', Jawi: ), formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu, is a sultanate and constitutive state of federal Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l- Īmān'' ("Abode of Faith"). The coastal city of Kuala Terengganu, which stands at the mouth of the broad Terengganu River, is both the state and royal capital as well as the largest city in Terengganu. There are many islands located close to the coast of Terengganu state, such as Perhentian Islands and Redang Island. Etymology There are several theories on the origin of the name "Terengganu". One theory attributes the name's origin to ''terang ganu'', Malay for 'bright rainbow'. Another story, said to have been originally narrated by the ninth Sultan of Terengganu, Baginda Omar, tells of a party of hunters from Pahang roving and hunting in the area of what is now southern Terengganu. One of the hunters spotted a big animal fang lying on the ground. A fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pahang
Pahang (; Jawi: , Pahang Hulu Malay: ''Paha'', Pahang Hilir Malay: ''Pahaeng'', Ulu Tembeling Malay: ''Pahaq)'' officially Pahang Darul Makmur with the Arabic honorific ''Darul Makmur'' (Jawi: , "The Abode of Tranquility") is a sultanate and a federal state of Malaysia. It is the third largest Malaysian state and the largest state in peninsular by area, and ninth largest by population. The state occupies the basin of the Pahang River, and a stretch of the east coast as far south as Endau. Geographically located in the East Coast region of the Peninsular Malaysia, the state shares borders with the Malaysian states of Kelantan and Terengganu to the north, Perak, Selangor and Negeri Sembilan to the west, Johor to the south, while South China Sea is to the east. The Titiwangsa mountain range that forms a natural divider between the Peninsula's east and west coasts is spread along the north and south of the state, peaking at Mount Tahan, which is high & the famous Kua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |