|
King Xiang Of Wei
King Xiang of Wei () (died 296 BC), personal name Wei Si (), was king of Wei from 318 BC to 296 BC. He was the son of King Hui of Wei. In 318 BC, at the suggestion of the Wei minister, Gongsun Yan, he entered into an alliance against Qin created by King Huai of Chu which also included the states of Zhao, Han and Yan. Chu then betrayed this alliance. In 317 BC, at the suggestion of chancellor Zhang Yi, King Xiang entered into an alliance with Qin. To punish Chu for its betrayal of the 5-state alliance, King Xiang sent an army in 312 BC to attack the city of Dengcheng in Chu (modern-day part of Shangshui County, Zhoukou, Henan Province). Wei itself was attacked by Qi in 310 BC, and King Xiang met King Wu of Qin at Linjin (modern day part of Linyi County, Yuncheng, Shanxi Province). In 308 BC, the two kings met again at Yingcheng (modern-day part of Xiaogan, Hubei) to plan an attack on Han. In 306 BC, after the death of King Wu of Qin, the alliance with Qin broke down, and Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Wei
Wei (; ; Old Chinese: *') was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Zhao. Its territory lay between the states of Qin and Qi and included parts of modern-day Henan, Hebei, Shanxi, and Shandong. After its capital was moved from Anyi to Daliang (present-day Kaifeng) during the reign of King Hui, Wei was also called Liang (). History Foundation Surviving sources trace the ruling house of Wei to the Zhou royalty: Gao, Duke of Bi (), was a son of King Wen of Zhou. His descendants took their surname, Bi, from his fief. After the destruction of Bi, Bi Wan () escaped to Jin, where he became a courtier of Duke Xian's, accompanying his personal carriage. After a successful military expedition, Bi Wan was granted Wei, from which his own descendants then founded the house of Wei. Spring and Autumn period Jin's political structure was drastically changed after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wu Of Qin
King Wu of Qin (; 329–307 BC), also known as King Daowulie of Qin (秦悼武烈王) or King Daowu of Qin (秦悼武王) or King Wulie of Qin (秦武烈王), was the ruler of the Qin state from 310 to 307 BC during the Warring States period of Chinese history. Despite his short time as ruler, King Wu played a part in Qin's wars of unification, mainly through his efforts against the state of Han. He also invaded some of the other major powers of the Warring States, especially Wei. In his fourth year, his minister Gan Mao (甘茂), suggested an attack on the Han fortress of Yiyang to open up a path to invade the eastern powers. The campaign succeeded and Qin subsequently gained control of the key roads to the Zhou capital of Luoyang. While visiting the Zhou capital, King Wu, a keen wrestler, decided to try powerlifting a heavy bronze cauldron in the Zhou palace as a show of his own physical strength, urged on by a strongman he favoured named Meng Yue (孟說). Though he succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Wei (state)
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizhong Discovery
The Jizhong (汲冢 or Jijun 汲君, northern part of present Henan) discovery in AD 279 is an important event in the paleography of ancient China, recorded in the ''Book of Jin''. A grave robber Biao Zhun 不準 broke into the tomb of King Xiang of Wei (r. 318–296 BC) and found there a corpus of ancient bamboo slips. Their discovery became a source of textological studies that had been impossible since the editorial work of Liu Xiang and Liu Xin of Han. The importance of the Jizhong discovery is compared to the Guodian discovery for the modern scholarship. The initial editorial work for the found slips was done by Xun Xu (d. 289), Director of the Imperial Library, though it was questioned by his successors. Among his editions, only two have survived; the large number of quotations shows the extent of Xun Xu work's influence. Among Jizhong texts, the most profound influence was the ''Bamboo Annals'', but the ''Bamboo Annals'' was not the only text retrieved. Collectively kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo Annals
The ''Bamboo Annals'' (), also known as the ''Ji Tomb Annals'' (), is a chronicle of ancient China. It begins in the earliest legendary time (the age of the Yellow Emperor) and extends to 299 BC, with the later centuries focusing on the history of the State of Wei in the Warring States period. It thus covers a similar period to Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (91 BC). The original may have been lost during the Song dynasty, and the text is known today in two versions, a "current text" (or "modern text") of disputed authenticity and an incomplete "ancient text". Textual history The original text was interred with King Xiang of Wei (died 296 BC) and re-discovered nearly six centuries later in 281 AD (Western Jin dynasty) in the Jizhong discovery. For this reason, the chronicle survived the burning of the books by Emperor Qin Shi Huang. Other texts recovered from the same tomb included '' Guoyu'', '' I Ching'', and the '' Tale of King Mu''. They were written on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinzheng
Xinzheng () is a county-level city of Henan Province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Zhengzhou, the provincial capital. The city has a population of 600,000 people and covers an area of , of which is urban. History Xinzheng is considered one of the birthplaces of the Chinese nation. More than 8000 years ago, neolithic people of Peiligang culture lived in the vicinity. The legendary Yellow Emperor was said to have been born in Xinzheng 5000 years ago. During the Zhou dynasty it was the capital of the state of Zheng and later, the state of Han, after the conquest of the former by the latter. It was the seat of government for the Qin dynasty, from about 221 BCE, which is considered the beginning of a unified China. The word ''qin'' (), which is pronounced similar to "chin", is thought to be the basis for the word "China." Historically, this prefecture was an integrated part of Zhengzhou. However, in 1994, the Henan Provincial Council authorized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wuling Of Zhao
King Wuling of Zhao () (died 295 BCE, reigned 325 BCE – 299 BCE) reigned in the State of Zhao during the Warring States period of Chinese history. His reign was famous for one important event: the reforms consisting of "Wearing the Hu (styled) Attire and Shooting from Horseback (in battle)" (Simplified Chinese: 胡服骑射, Traditional Chinese: 胡服騎射) He was credited for the implementation of protective outfit during military events and proceedings. The son of Zhao Suhou ( Marquess Su of Zhao, Simplified Chinese: 赵肃侯), King Wuling of Zhao ascended to the throne at 325 BCE, about halfway into the Warring States Period. His reign coincided with the appearance of several other notable figures in the Warring States. He was also the first ruler of Zhao to style himself "king" (王), but later reversed the decision. He would later receive the title as part of his posthumous name. Rule and reforms During the early years of his reign, the Kingdom of Zhao was constantly ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Min Of Qi
King Min of Qi () (323–284 BC, ruled 300–284 BC) was a notoriously unsuccessful king of the northeastern Chinese state of Qi during the Warring States period. "Famous for his paranoia and megalomania, the king was the archetype of the unworthy and unaware ruler." A generation later, the philosopher Xunzi wrote of King Min: "The king of Qi perished and his state was destroyed, punished by all under Heaven. When later generations speak of bad men, they are sure to mention him." Qi was one of the most powerful states in China at his accession, if not the most powerful. In 288 BC. King Min took the title of Di of the East (東帝), and his ally King Zhaoxiang of Qin called himself Di of the West (Di was originally the name of the high god of the Shang. It also (or later) had a weaker sense of sacred or divine; the same character was used to mean Emperor in later times.) But so many people objected that both kings were forced to return to the title of "king" (wáng 王) and there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Zhaoxiang Of Qin
King Zhaoxiang of Qin (; 325–251 BC), or King Zhao of Qin (秦昭王), born Ying Ji (, was the king of Qin from 306 BC to 251 BC. He was the son of King Huiwen and younger brother of King Wu. King Zhaoxiang reigned as the King of Qin for 57 years, and was responsible for the state of Qin achieving strategic dominance over the other six major states. During his reign, Qin captured the Chu capital Ying in 278 BC, conquered the Xirong state of Yiqu in 272 BC, slaughtered a 450,000-strong Zhao army at Changping in 260 BC, and overthrew the Eastern Zhou dynasty in 256 BC. These aggressive territorial expansions and the strategic weakening of other rival states paved the path for Qin's eventual unification of China three decades later by his great-grandson Ying Zheng. Biography Ascension Prince Ying Ji was born in 325 BC to one of King Huiwen's more lower-ranked concubines, Lady Mi (羋八子). As a '' shu'' child, Prince Ji was given low priority in the royal line of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of –771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 – 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
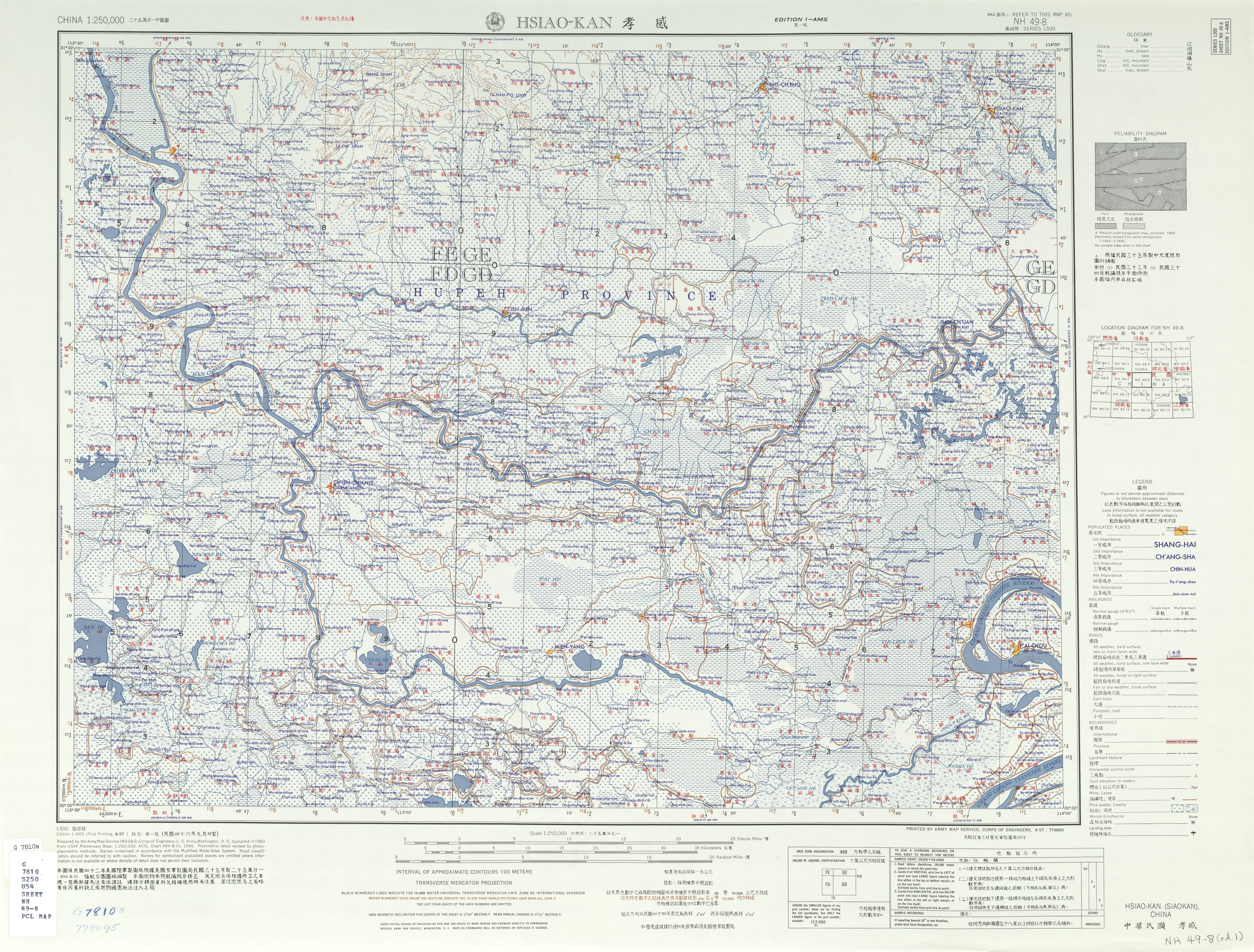
Xiaogan
Xiaogan () is a prefecture-level city in east-central Hubei province, People's Republic of China, some northwest of the provincial capital of Wuhan. According to the 2020 census, its population totaled 4,270,371, of whom 988,479 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area of Xiaonan District. The city name Xiaogan, meaning ''Filial Piety Moves Tian'' (), is from the story of Dong Yong (), who sold himself for his father's funeral, in ''The Twenty-four Filial Exemplars''. The Sheshui River originates in Xiaogan's Dawu County. On the third day of the third month of the lunar calendar, many in Wuhan eat 'di cai zhu ji dan' () which is supposed to prevent illness in the coming year. This practice is related to a story involving Shennong in Xiaogan. Administrative divisions Since 2000, Xiaogan has been divided into 1 district, 3 county-level cities and 3 counties: *Xiaonan District () *Yingcheng City () *Anlu City () *Hanchuan City () *Xiaochang County () * Dawu County () *Yunmeng Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yingcheng
Yingcheng () is a county-level city of about 600,000 inhabitants in Xiaogan, eastern Hubei province, People's Republic of China. History On December 26, 2019, a minor earthquake struck the area. Township-level divisions Five subdistricts: * Chengzhong Subdistrict (), Chengbei Subdistrict (), Silipeng Subdistrict (), Dongmafang Subdistrict (), Changjiangbu Subdistrict () Ten towns: * Tiandian (), Yanghe (), Sanhe (), Langjun (), Huangtan (), Tian'e (), Yihe Aisin Gioro Yihe (奕詥; 14 March 1844 – 17 December 1868) was Daoguang Emperor's eighth son and the first holder of Prince Zhong peerage. As the peerage was not granted perpetual inheritability, Yihe's potential successors would hold diminished ... (), Chenhe (), Yangling (), Tangchi () Two other areas: * Yingcheng Economic Area (), Nanyuan Farm () Notable people * Li Qing (born 1972), Chinese diver * Yu Linxiang (born 1945), Chinese general * (1884–1942), Chinese politician and diplomat * Yang Deqing ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)