|
King William Island
King William Island (french: Île du Roi-Guillaume; previously: King William Land; iu, Qikiqtaq, script=Latn) is an island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, which is part of the Arctic Archipelago. In area it is between and making it the 61st-largest island in the world and Canada's 15th-largest island. Its population, as of the 2021 census, was 1,349, all of whom live in the island's only community, Gjoa Haven. While searching for the Northwest Passage, a number of polar explorers visited, or spent their winters on, King William Island. Geography The island is separated from the Boothia Peninsula by the James Ross Strait to the northeast, and the Rae Strait to the east. To the west is the Victoria Strait and beyond it Victoria Island. Within the Simpson Strait, to the south of the island, is Todd Island, and beyond it, further to the south, is the Adelaide Peninsula. Queen Maud Gulf lies to the southwest. Some places on the coast are: (counter clockwise from the nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boothia Peninsula
Boothia Peninsula (; formerly ''Boothia Felix'', Inuktitut ''Kingngailap Nunanga'') is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada. Geography Bellot Strait (Ikirahaq) separates the peninsula from Somerset Island to the north. Babbage Bay is on the east coast, as is Abernethy Bay, just to the south. The community of Taloyoak lies in the far south and is the peninsula's only significant population centre. Paisley Bay is on the west coast, as is Wrottesley Inlet (between Paisley Bay and Bellot Strait). Prior to the detachment of Nunavut in 1999, the Boothia Peninsula and the nearby Melville Peninsula were the only parts of mainland Canada that belonged to the District of Franklin in the then Northwest Territories. The balance of the District of Franklin was all situated within the Arctic Archipelago. Exploration John Ross was forced by ice to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
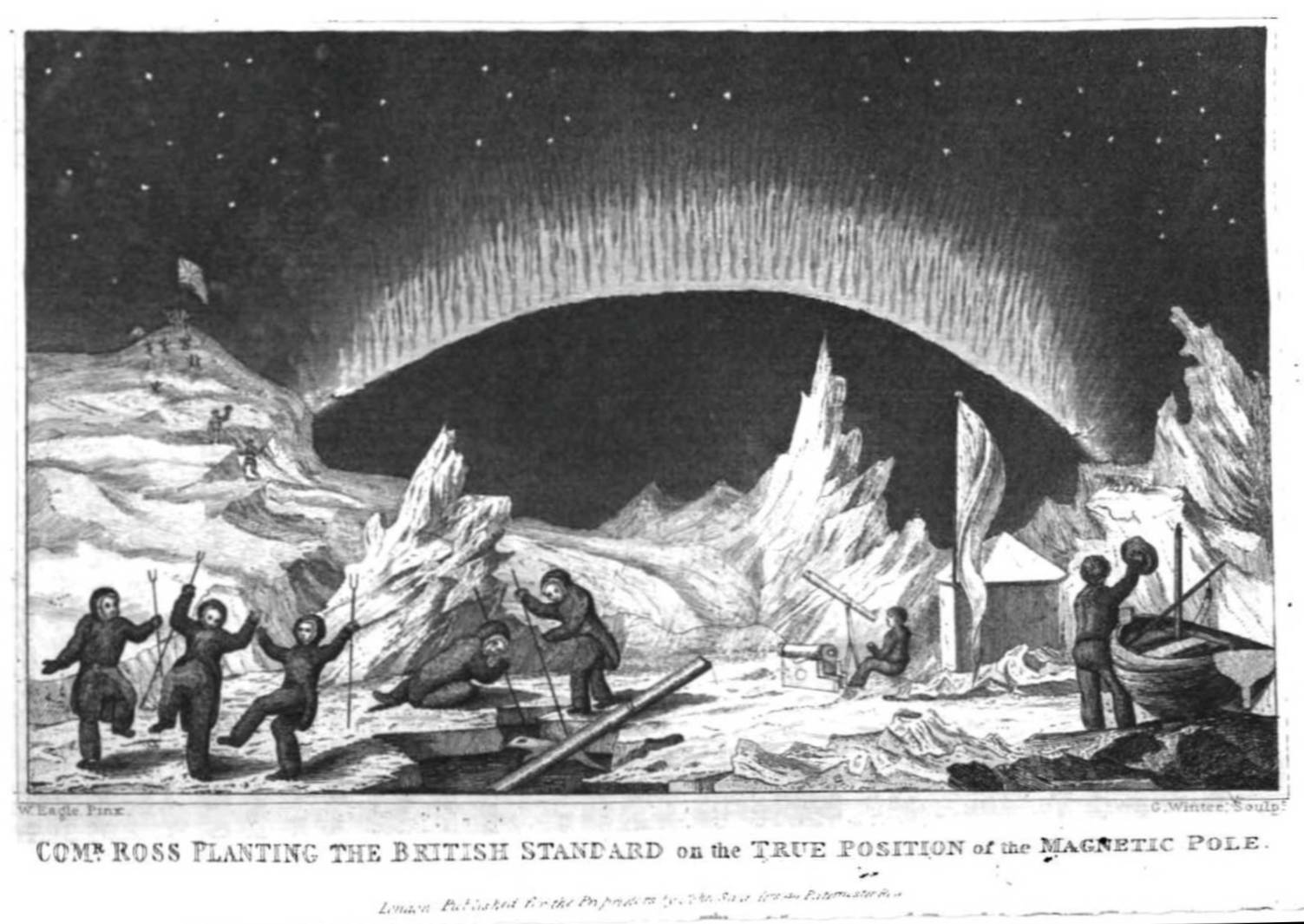
James Clark Ross
Sir James Clark Ross (15 April 1800 – 3 April 1862) was a British Royal Navy officer and polar explorer known for his explorations of the Arctic, participating in two expeditions led by his uncle John Ross, and four led by William Edward Parry, and, in particular, for his own Antarctic expedition from 1839 to 1843. Biography Early life Ross was born in London, the son of George Ross and nephew of John Ross, under whom he entered the Royal Navy on 5 April 1812. Ross was an active participant in the Napoleonic Wars, being present at an action where HMS ''Briseis'', commanded by his uncle, captured ''Le Petit Poucet'' (a French privateer) on 9 October 1812. Ross then served successively with his uncle on HMS ''Actaeon'' and HMS ''Driver''. Arctic exploration Ross participated in John's unsuccessful first Arctic voyage in search of a Northwest Passage in 1818 aboard ''Isabella''. Between 1819 and 1827 Ross took part in four Arctic expeditions under William Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans. Much of the world's sea ice is enclosed within the polar ice packs in the Earth's polar regions: the Arctic ice pack of the Arctic Ocean and the Antarctic ice pack of the Southern Ocean. Polar packs undergo a significant yearly cycling in surface extent, a natural process upon which depends the Arctic ecology, including the ocean's ecosystems. Due to the action of winds, currents and temperature fluctuations, sea ice is very dynamic, leading to a wide variety of ice types and features. Sea ice may be contrasted with icebergs, which are chunks of ice shelves or glaciers that calve into the ocean. Depending on location, sea ice expanses may also incorporate icebergs. General features and dynamics Sea ice does not simply grow and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barren-ground Caribou
The barren-ground caribou (''Rangifer tarandus groenlandicus''; but subject to a recent taxonomic revision. See Reindeer: Taxomony.) is a subspecies of the reindeer (or the caribou in North America) that is found in the Canadian territories of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories, in northern Alaska and in south-western, Greenland. It includes the Porcupine caribou of Yukon and Alaska.Cronin, M. A., M. D. Macneil, and J. C. Patton (2005). ''Variation in Mitochondrial DNA and Microsatellite DNA in caribou (Rangifer tarandus) in North America.'' Journal of Mammalogy 86(3): 495–505. The barren-ground caribou is a medium-sized caribou, smaller and lighter-colored than the boreal woodland caribou, with the females weighing around and the males around . However, on some of the smaller islands, the average weight may be less. The large migratory herds of barren-ground caribou take their names from the traditional calving grounds, such as the Ahiak herd, the Baffin Island herds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence Islands
The Clarence Islands are a Canadian Arctic island group in the Nunavut Territory. The islands lie in the James Ross Strait, east of Cape Felix, off the northeast coast of King William Island. They are about west of Kent Bay on the Boothia Peninsula, and about northwest of the Tennent Islands. History Captain (Sir) John Ross commanded the ''Victory'' during his second Arctic exploration (1829—1833), partly in order to regain credibility after charting a fictional landform, Croker Mountains, during his first Arctic expedition. He chose his nephew, Commander James Clark Ross, to be second in command. In 1830, while exploring within the Ross Strait, James Ross charted three islands. He named the group "Beaufort Islands" after Capt. Francis Beaufort, hydrographer of the Admiralty,Ross 1994:195Bossi 1984:571 and named the individual islands Adolphus Island, Frederick Island, and Augustus Island, these also being the names of three sons of the Duke of Clarence.Lundy 2008 John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennent Islands
The Tennent Islands are an uninhabited Canadian Arctic island group in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut. The islands are located in Rae Strait between the Clarence Islands and Beverly Islands. Thomson Point on King William Island lies away, across the Humboldt Channel. Matty Island lies to the east, separated by the Wellington Strait. Boothia Peninsula's Oscar Bay is to the northeast. The Tennent Islands are low-lying and lake-studded. They, as well as Port Emerson, a two-mile-wide (3.2 km) harbour, were named in honour of Emerson Tennent Sir James Emerson Tennent, 1st Baronet, FRS (born James Emerson; 7 April 1804 – 6 March 1869) was a British politician and traveller born in Ireland. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society on 5 June 1862. Life The third son of William ... by Sir John Ross during his second Arctic voyage.Ross 1835:241 References Arctic Islands at Natural Resources, Atlas of Canada* Uninhabited islands of Kitikmeot Region {{Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matty Island
Matty Island is one of the Canadian arctic islands in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut. It is located in Rae Strait, between King William Island and the Boothia Peninsula Boothia Peninsula (; formerly ''Boothia Felix'', Inuktitut ''Kingngailap Nunanga'') is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of .... Located at 69°29'N 95°40'W it has an area of . Other islands in the area include Beverly Islands to the south, and Tennent Islands to the west. References Uninhabited islands of Kitikmeot Region {{KitikmeotNU-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Maud Gulf
Queen or QUEEN may refer to: Monarchy * Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom ** List of queens regnant * Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king * Queen dowager, the widow of a king * Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother of a reigning monarch Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Queen (Marvel Comics), Adrianna "Ana" Soria * Evil Queen, from ''Snow White'' * Red Queen (''Through the Looking-Glass'') * Queen of Hearts (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'') Gaming * Queen (chess), a chess piece * Queen (playing card), a playing card with a picture of a woman on it * Queen (carrom), a piece in carrom Music * Queen (band), a British rock band ** ''Queen'' (Queen album), 1973 * ''Queen'' (Kaya album), 2011 * ''Queen'' (Nicki Minaj album), 2018 * ''Queen'' (Ten Walls album), 2017 * "Queen", a song by Estelle from the 2018 album '' Lovers Rock'' * "Queen", a song by G Flip featuring Mxmtoon, 2020 * "Queen", a song by Jessie J from the 2018 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide Peninsula
Adelaide Peninsula (''Iluilik''), ancestral home to the ''Illuilirmiut'' Inuit, is a large peninsula in Nunavut, Canada. It is located at south of King William Island. Its namesake is Queen Adelaide, consort of King William IV of the United Kingdom. In 1839 it was reached from the west by Peter Warren Dease and Thomas Simpson. Starvation Cove, on the northern tip of the peninsula, was the southernmost point any of the doomed survivors from Franklin's lost expedition Franklin's lost expedition was a failed British voyage of Arctic exploration led by Captain Sir John Franklin that departed England in 1845 aboard two ships, and , and was assigned to traverse the last unnavigated sections of the Northwest ... of 1845-48 are known to have reached on their march south to find help. References Peninsulas of Kitikmeot Region {{KitikmeotNU-geo-stub da:Adelaide (Canada) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson Strait
The Simpson Strait () is a natural, shallow waterway separating King William Island to the north from Adelaide Peninsula on Nunavut's mainland to the south. The strait, an arm of the Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ..., connects the Queen Maud Gulf with Rasmussen Basin's Rae Strait. Simpson Strait measures long and wide, and there are several small islands within it: Albert, Beaver, Boulder, Castor, Chens, Club, Comb, Denille, Dolphin, Eta, Hook, Kilwinning, Pollux, Ristvedt, Saatuq, Sarvaq and Taupe. History The English naval officer George Back reached Simpson Strait in 1834, but did not name it. In 1836, the Hudson's Bay Company wanted to "endeavour to complete the discovery and survey of the northern shores of the American continent" and so it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
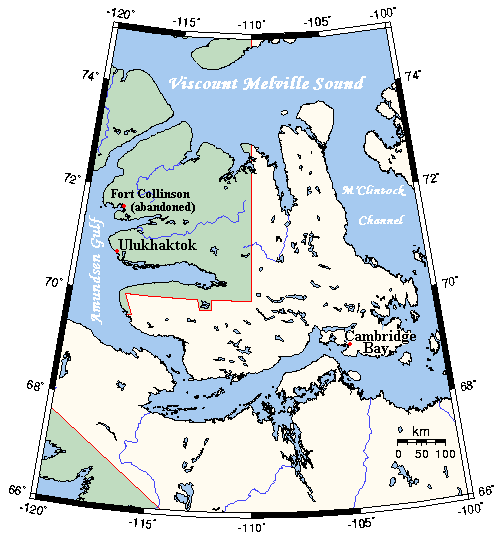
Victoria Island
Victoria Island ( ikt, Kitlineq, italic=yes) is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the List of islands by area, eighth-largest island in the world, and at in area, it is List of Canadian islands by area, Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland (), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain () but smaller than Honshu (). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The island is named after Queen Victoria, the Canadian sovereign from 1867 to 1901 (though she first became Queen in 1837). The features bearing the name "Prince Albert" are named after her consort, Albert, Prince Consort, Albert. History In 1826 John Richardson (naturalist), John Richardson saw the southwest coast and called it "Wollaston Peninsula, Wolla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |