|
Kimura Joseki
In shogi, the Kimura joseki (木村定跡) is a joseki for a Bishop Exchange Reclining Silver (Double Static Rook) opening. It was developed by lifetime Meijin Yoshio Kimura. Development Basic Diagram From the first move: 1. P-76, P-84; 2. P-26, G-32; 3. G-78, P-85; 4. B-77, P-34; 5. S-88, Bx77+; 6. Sx77, S-42; 7. S-38, S-72; 8. P-46, P-64; 9. S-47, S-63; 10. P-66, G-52; 11. G-58, K-41; 12. K-68, S-54; 13. S-56, K-31; 14. K-79, P-14; 15. P-16, P-94; 16. P-96, P-74; 17. P-36, P-44; 18. N-37, N-73; 19. P-25, S-33 (Diagram 2). From here, it'll go later with K-88, K-22 (Diagram 1), and hostilities will start with Black's pushing and sacrificing the pawn at the 4th file with P-45. Intermediate Diagram From Diagram 1, following 20. P-45, Px45, the odds fall on Black with the push of the pawn 21. P-35. From there 21... S-44; 22. P-75, Px75; 23. P-15, Px15; P-24, Px24; 24. Rx24, P*23; 25. R-28, B*63; 26. P*13, Lx13; 27. N-25 (Diagram 3), L-14; 28. Px34, P-24; 29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōseki
In go and '' shōgi'', a ''jōseki'' or ''jouseki'' (''kanji'' characters for go, for ''shōgi'') is the studied sequences of moves for which the result is considered ''balanced'' for both black and white sides. Go ''jōseki'' In go, because games typically start with plays in the corners, go ''jōseki'' are usually about corner play as the players try to gain local advantages there in order to obtain a better overall position. Though less common, there are also ''jōseki'' for the middle game. In Japanese, ''jō'' () means "fixed" or "set" and ''seki'' () means stones, giving the literal meaning "set stones", as in "set pattern". In Chinese, the term for joseki is ''dìngshì'' (). The concept of "balance", here, often refers to an equitable trade-off between securing territory in the corner versus making good ''thickness'' toward the sides and the center. In application, these concepts are very dynamic, and, often, deviations from a ''jōseki'' depend upon the needs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Exchange Reclining Silver
In shogi, Bishop Exchange Reclining Silver or Reclining Silver With Bishops Off or Bishop Exchange Sitting Silver (角換わり腰掛け銀 ''kakugawari koshikakegin'') is a Bishop Exchange (Double Static Rook) opening that uses a Reclining Silver attacking formation. If both sides play Reclining Silver, then the position is known as Double Reclining Silver or Mutual Reclining Silver or Twin Reclining Silver (相腰掛け銀 ''aikoshikakegin''). Overview To defend the left flank against the opponent's rook pawn, Black chooses a Yagura castle form with left silver on the 77 square and the left gold on 78. Then, to avoid the risk of White's bishop drop inside Black's promotion zone, the right gold will be positioned other variously on the 58, 48 or 47 squares. According to the shogi proverb, "In the Bishop Exchange opening, don't push the central pawn." Following this, the fifth file pawn in Bishop Exchange Reclining Silver must remain on its starting 57 square in order for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meijin
is one of the eight titles in Japanese professional shogi, and is the most prestigious title, along with Ryūō. The word ''meijin'' (名 ''mei'' "excellent, artful", 人 ''jin'' "person") refers to a highly skilled master of a certain field (the various arts found in traditional Japanese culture, such as the Japanese tea ceremony, go, competitive karuta, rakugo, budō). History The Meijin institution started in the 17th century (Edo period), and for around 300 years (1612–1937) was a hereditary title that was passed from the reigning Meijin upon his retirement or death to another selected from three families, as deemed to be worthy. This is known as the Lifetime Meijin system (終生名人制). In 1935, however, the Japan Shogi Association, or JSA, announced that it was abolishing the existing system of succession in favor of something more short-term and reflective of actual playing strength, known as the Real Strength Meijin system (実力名人制). In 1937, the reigni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshio Kimura (shogi)
was a Japanese professional shogi player who achieved the rank of 8-dan (which was the highest dan level during his time). He was a Lifetime Meijin who won the title eight times. At the time, the Meijin title was the only shogi title. Gallery File:Prince Chichibu in Shogi Contest 1952 Scan10009.JPG, Kimura (right) playing against Yasuharu Ōyama in 1952 with Prince Chichibu , was the second son of Emperor Taishō (Yoshihito) and Empress Teimei (Sadako), a younger brother of Emperor Shōwa (Hirohito) and a general in the Imperial Japanese Army. As a member of the Imperial House of Japan, he was the patron of severa ... present File:The board when Oyama defeated Kimura.JPG, board when Ōyama defeated Kimura (1952 July 15) File:Yoshio Kimura Shogi 1951 Scan10012.JPG, Kimura (1951 January 27) References External links *将棋DB2:1952-07-12 名人戦 大山康晴 vs 木村義雄 Japanese shogi players Deceased professional shogi players Recipients of the Medal with Pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Exchange
In shogi, Bishop Exchange (角換わり or 角換り ''kakugawari'') is a Double Static Rook opening in which the players exchange their bishops relatively early so as to have bishops in hand. Throughout the game, both players have a bishop drop threat, with which they can exploit any positional weakness that their opponent inadvertently creates. Overview The Bishop Exchange opening is a Double Static Rook opening. Black starts with activating both their bishop (P-76) and rook (P-26) while White quickly puts pressure on Black with rook pawn pushes (...P-84, ...P-85). White's aim is to exchange their rook pawn off the board on the eighth file as soon as possible. This has a number of benefits: it gives White a pawn in hand that can be used to drop later in the game, and it frees up the rook so that it can move to any rank above Black's camp (see: Sabaki). However, in this opening, in response, Black wishes to prevent White's early rook pawn exchange by defending the 86 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reclining Silver
In shogi, Reclining Silver (腰掛け銀 ''koshikakegin'') is a piece formation used in different Double Static Rook openings. It may also be played in Double Ranging Rook openings as well and in Right Fourth File Rook (Static Rook) positions against Ranging Rook positions. The Reclining Silver has the right silver positioned on central file above the central pawn and to the right of the silver is the pawn that was advancing in order to let the silver move through the line of pawns. The silver is said to recline on the seat of pawns. In the adjacent board diagram, both Black and White have created Reclining Silver positions. Black has their silver on 56 (with pawns on 46 and 57) while White has their silver on 54 (pawns on 53, 64). Reclining Silver can often played as a component of several different Static Rook openings such as Double Wing or Bishop Exchange. Clanging Silvers Clanging Silvers (ガッチャン銀 ''gatchan gin'') is an attacking development from a Dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
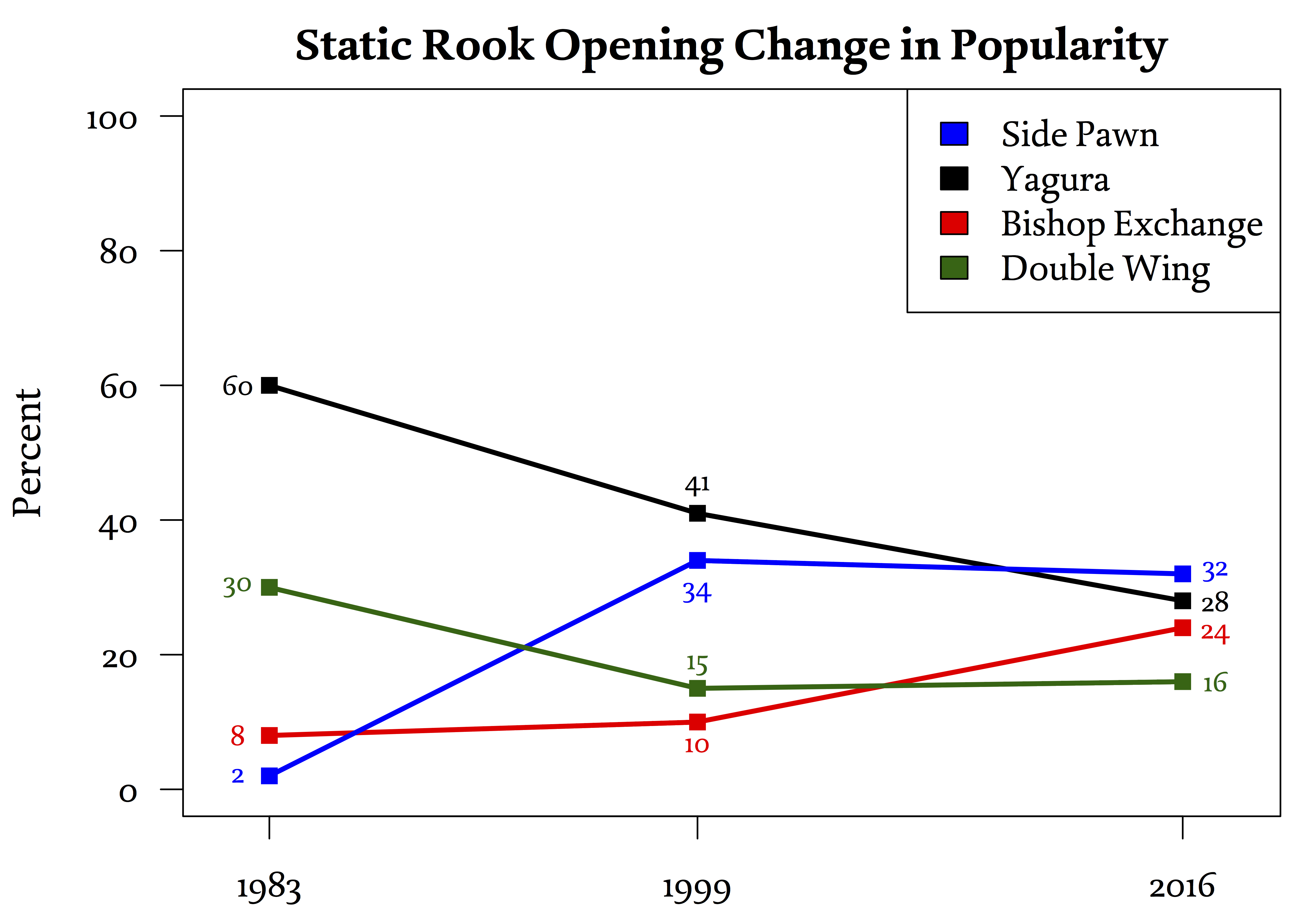
Static Rook
Static Rook (居飛車 ''ibisha'') openings in shogi typically have the player's rook at its start position, which is the second file (on the 28 square) for Black and the eighth file (on the 82 square) for White. Explanation Static Rook is a set of openings in which the rook remains on its starting square, which is the 28 square if played by Black and the 82 square if played by White. It is also possible to include other openings where the rook moves to another file that is still on the players right side of the board, such as the third file or the fourth file. The reason for including these other openings where the rook is not technically ''static'' is because the typical castle fortifications constructed to the protect the Static Rook player's king are usually the same for these openings. Nonetheless, some shogi theory does categorize these openings with right side rook movement into the same group as Ranging Rook openings despite the disparity in castle formation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Abstract strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |