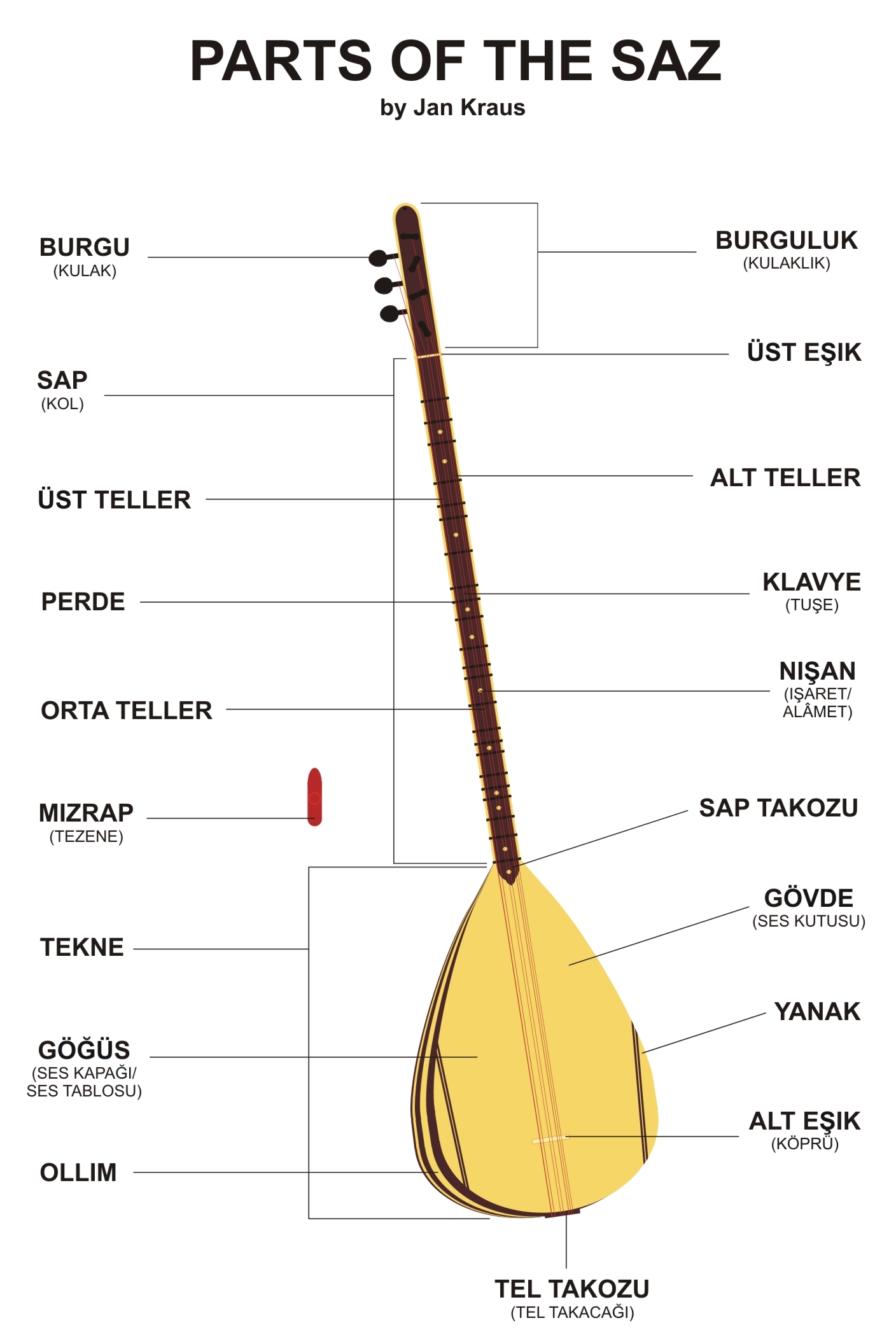
|
Kharberd–Yerznka Dialect
The Kharberd–Yerznka dialect was a group of varieties of the same dialect that were spoken in the regions of Kharberd, Erzincan, Dersim, and Kiğı in the Ottoman Empire before WWI. After which it was spoken only in the diaspora In Syria, Romania, United States, and Lebanon. Although the Dersim variety was still spoken in Tunceli until 1938 when The Alevi Ashirets were dissolved and the remaining Armenians of Tunceli became Alevi and were assimilated into Zaza society. Variations Hrachia Acharian wrote short stories in different regional variations of the dialect in his 1909 book. * Kharberd Subdialect: Gëli Chëli Khoroz më gëlli, As Khorozin Odkë push më gë mënna, Inch Geneh Chener chi gërnër ad pushë haner. Gellah gerta mamigi më gësa, ki as pushë hana! * Eastern Armenian comparison: Këlini Chi-Lini, Mi aklor Këlini, Es Aklori Votkë push k'mtni, Ich arav charav chk'aroghatsav et pushë haner. K'elni kerta mayrin kasi, es pushë hani! * Dersim S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elazığ
Elazığ () is a city in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey, and the administrative centre of Elazığ Province and Elazığ District. Founded in and around the former city of Harput, it is located in the uppermost Euphrates valley. The plain on which the city extends has an altitude of . Elazığ resembles an inland peninsula surrounded by the natural Lake Hazar and reservoirs of Keban Dam, Karakaya Dam, Kıralkızı and Özlüce. Its population is 387,072 (2022). Name Mezre Elazığ was once a suburb of the ancient fortress town of Harput called . Heinrich Hübschmann believed Mezre to be the settlement of Mazara () mentioned by Ptolemy, while Nicholas Adontz derived the name from an Arabic word meaning arable land or hamlet (borrowed into Turkish as 'hamlet'). The toponym originated as a shortening of ('hamlet of the aghas/landlords') or ('Çötelizade family namehamlet'). This may be explained by the fact that some notables from Harput had been exiled from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soghomon Tehlirian
Soghomon Tehlirian (; April 2, 1896 – May 23, 1960) was an Armenian revolutionary and soldier who assassinated Talaat Pasha, the former Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire, in Berlin on March 15, 1921. He was entrusted to carry out the assassination after having earlier killed Harutian Mgrditichian, who had worked for the Ottoman secret police and helped compile the list of Armenian intellectuals who were deported on April 24, 1915. Talaat's assassination was a part of Operation Nemesis, a revenge plan by the Armenian Revolutionary Federation against members of the Ottoman Imperial Government responsible for the Armenian genocide during World War I. Talaat Pasha had been convicted and sentenced to death ''in absentia'' in the Turkish courts-martial of 1919–20, and was viewed as the main orchestrator of the genocide. After a two-day trial Tehlirian was found not guilty by a German court, and freed. Tehlirian is considered a national hero by Armenians. Life Soghom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamastegh
Hamasdegh (also Hamastegh, ), born Hambartsum Gelenian (, 26 November 1895, Kharpert, Western Armenia, Ottoman Empire – 26 November 1966, New York City) was a poet and writer of the Armenian diaspora. Biography Hamasdegh (born Hampartsum Gelenian) was born in Perchenj village of Kharbert on November 26, 1895. He received his primary education in the village school and continued his studies in the Central School of Mezire (now Elâzığ), where he was one of the founders of provincial literature and one of the students of the writer Tlkatintsi (Hovhannes Haroutiunian), a victim of the Armenian Genocide. After graduating in 1911, Hamasdegh taught for a year in his hometown and then immigrated to the United States, following his father's advice. He attended courses at Columbia University (New York) and Boston University. He started working for " Hayrenik" daily in 1918, adopting the pen name Hamasdegh, combining the first syllables of the names of the three Gelenian brothers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlgadintsi
Tlgadintsi or Tlkatintsi (), Hovhannes Harutiunian (, 1860, Tlkatin village, Kharpert, Ottoman Empire – 1915) was an Ottoman Armenian writer and teacher noted for his leading role in rural literature.The Heritage of Armenian Literature, By Agop J. Hacikyan, Gabriel Basmajian, Edward S. Franchuk, Wayne State University Press, 2005, pp. 497-498 He is credited with giving the first authoritative response to a call from Constantinople's Armenian intelligentsia, issued in the early 1890s, for writing firmly rooted in the village life of historic Western Armenia. Tlgadintsi's unique realist works range from probing the darkest corners of village life to revisiting cherished moments of childhood. Through his esteem as a mentor and his power as a writer he opened the way for a new generation of important writers such as Rupen Zartarian, Peniamin Noorigian, Vahé Haig, Vahan To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vahan Totovents
Vahan Hovhannesi Totovents (; September 1, 1889 – July 18, 1938) was an Armenian writer, poet, and public activist. Biography Vahan Totovents was born on July 17, 1893, in the town of Mezre (now Elazığ) in the vilayet of Kharberd. He was one of seven children, and he was only eight when he lost his father—a prosperous landowner and a high government official. After an elementary education, the young Totovents went to the Armenian Central School in the large nearby town of Kharpert, where two of his teachers were well-known authors Tlgadintsi and Rupen Zartarian, who influenced his style of writing, despite its individuality. His first book appeared in 1908. He left for Constantinople in 1908. In 1909 he went to Paris, and then to New York. At the same time, he mastered English and French, and studied literature, history, and philosophy at the University of Wisconsin. During the First World War, in 1915, Totovents went to the Caucasus as a volunteer in defense of his co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashnak
The Armenian Revolutionary Federation (, abbr. ARF (ՀՅԴ) or ARF-D), also known as Dashnaktsutyun (Armenian: Դաշնակցություն, lit. "Federation"), is an Armenian nationalist and socialist political party founded in 1890 in Tiflis, Russian Empire by Christapor Mikaelian, Stepan Zorian, and Simon Zavarian. , the party operates in Armenia, Lebanon, Iran and in countries where the Armenian diaspora is present. The party was also active in Artsakh until the Azerbaijani offensive in September 2023. Although it has long been the most influential political party in the Armenian diaspora, it has a comparatively smaller proportional presence in the Republic of Armenia. , the party was represented in two national parliaments, with ten seats in the National Assembly of Armenia and three seats in the Parliament of Lebanon as part of the March 8 Alliance. The ARF has traditionally advocated socialist democracy and has been a full member of the Socialist International si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahan Natalie
Shahan Natalie (; July 14, 1884 – April 19, 1983) was an Armenian writer and political activist who was the principal organizer of Operation Nemesis, a campaign of revenge against officials of the former Ottoman Empire who organized the Armenian genocide during World War I. Originally a member of the Armenian Revolutionary Federation, he later left the party over disagreements regarding its policy towards Turkey. Of his writings on Armenian national philosophy, his essay ''The Turks and Us'' is the best known''.'' The main argument of Natalie's writings is that it is impossible for Armenians to come to any kind of understanding with Turks, whom he considered the chief enemy of Armenians, let alone cooperate with Turkey against the Soviet Union. Early life Shahan Natalie was born Hagop Der Hagopian () on July 14, 1884, in the village of Huseinig (now a part of Elazığ), in the Mamuret-ul-Aziz Vilayet, also known as the Harpoot, Kharberd Vilayet (modern day Elazığ Province), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Armenian
Eastern Armenian () is one of the two standardized forms of Modern Armenian, the other being Western Armenian. The two standards form a pluricentric language. Eastern Armenian is spoken in Armenia, Russia, as well as Georgia, and by the Armenian community in Iran. Although the Eastern Armenian spoken by Armenians in Armenia and Iranian-Armenians are similar, there are pronunciation differences with different inflections. Armenians from Iran also have some words that are unique to them. Due to migrations of speakers from Armenia and Iran to the Armenian diaspora, the dialect is now very prominent in countries and regions where only Western Armenian was used. Eastern Armenian is based on the Yerevan dialect. Official status and recognition Eastern Armenian is, for the most part, mutually intelligible by educated or literate users of Western Armenian – and vice versa. Conversely, semi-literate or illiterate users of lower registers of either variety may have difficulty und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hrachia Acharian
Hrachia Acharian (, reformed spelling: Հրաչյա Աճառյան; ; 8 March 1876 – 16 April 1953) was an Armenian linguist, lexicographer, etymologist, and philologist. An Istanbul Armenian, Acharian studied at local Armenian schools and at the Sorbonne, under Antoine Meillet, and the University of Strasbourg, under Heinrich Hübschmann. He then taught in various Armenian communities in the Russian Empire and Iran before settling in the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1923, working at Yerevan State University until his death. A polyglot, Acharian compiled several major dictionaries, including the monumental ''Armenian Etymological Dictionary'', extensively studied Armenian dialects, compiled catalogs of Armenian manuscripts, and authored comprehensive studies on the history of Armenian language and alphabet. Acharian is considered the father of Armenian linguistics. Life Acharian was born to Armenian parents in Constantinople (Istanbul) on 8 March 1876. He was b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zazas
The Zazas (), also known as Kird, Kirmanc, or Dimili, are an Iranian people who speak Zazaki, a language of the Indo-European language family. They mostly live in the Eastern Anatolia and Southeastern Anatolia regions of Turkey. Zazas generally consider themselves Kurds, and are often described as Zaza Kurds by scholars. Etymology and naming The term Dimilî derives from the name of the Dunbulî (also spelled Dumbulî), a Kurdish tribe documented since the 12th century. According to ''Encyclopædia Iranica'' the endonym ''Dimlī'' or ''Dīmla'' was derived from Daylam region in Northern Iran, and appears in Armenian historical records as ''delmik'', ''dlmik'', which was proposed to be derived from Middle Iranian ''*dēlmīk'' meaning Daylamite. Among their neighbors the people are known mainly as Zāzā, which meant “ stutterer” and was used as a pejorative. Hadank and Mckenzie attribute relative abundance of sibilants and affricates in Zaza language to explai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alevi
Alevism (; ; ) is a syncretic heterodox Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Islamic teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, who taught the teachings of the Twelve Imams, whilst incorporating some traditions from shamanism. Differing from Sunni Islam and Usuli Twelver Shia Islam, Alevis have no binding religious dogmas, and teachings are passed on by a ''dede'' "spiritual leader" as with Sufi orders. They acknowledge the six articles of faith of Islam, but may differ regarding their interpretation. They have faced significant institutional stigma from the Ottoman and later Turkish state and academia, being described as heterodox to contrast them with the "orthodox" Sunni majority. The term “Alevi-Bektashi” is currently a widely and frequently used expression in the religious discourse of Turkey as an umbrella term for the two religious groups of Alevism and Bektashism. Adherents of Alevism are found primarily in Turkey and estimates of the percentage of Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |