|
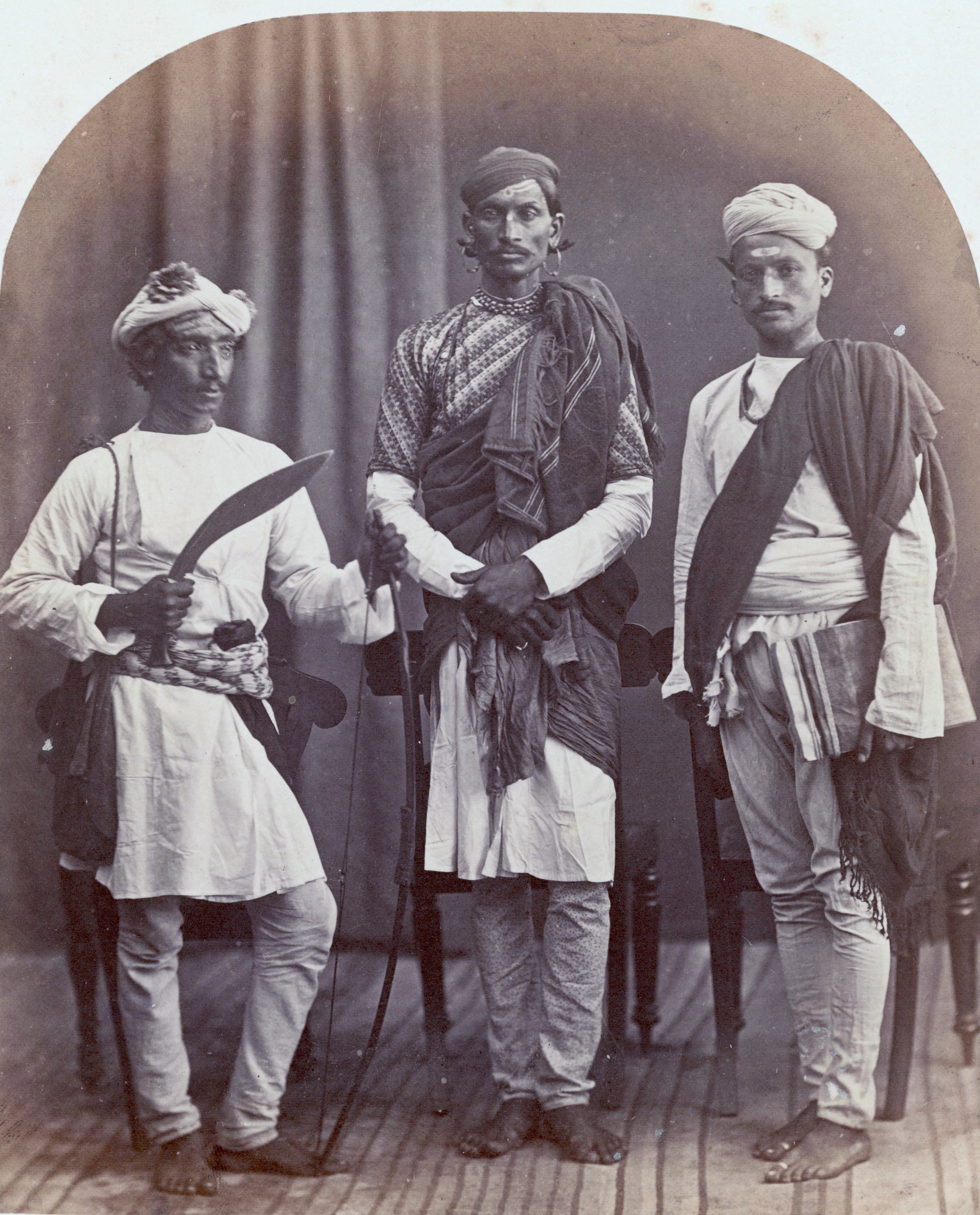
Khandayats
Khandayat or Khandait is a landed militia caste from Odisha, East india. They were feudal chiefs, military generals, zamindars, large land holders and agriculturalists. During British raj, they ruled many tributary states in Odisha. They are largest caste by population in Odisha. Etymology The name Khandayat is originated from the word " Khanda" which means Sword and khandayat means sword wielding. According to G.Praharaj, in old days who came forward to save the native kingdom with their swords when it was in trouble were granted the title of "Khandayat". Since then people of Oda (Peasants) & Gauda (cowherds) castes enjoyed the title, it can be said khandayat is only a title. Origin Rampant invasions took place in medieval period which prompted the Odia rulers to accumulate the large population of farmers and tribals into their army, such accumulation led to the emergance of Khandayat caste. Khandayat title was used by people of various communities and classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chasa (caste)
Chasa is a community from the Indian state of Odisha. Chasas were traditionally cultivators but are now engaged in several professions. The Odia word ''chasa'' means farmer. They are third largest caste by population in Odisha. History The Orh/Oda Chasas claim that they were the first tribe to settle in Odisha, and that they began to cultivate the land. They claim that Odisha is named after them. They are classified as Shudra in the Hindu caste system. The association between Chasas and their occupation of manual labour (ploughing) was used to stigmatize the Chasas and distinguish them from the upper castes as late as the early 19th century. "''Chasa''" was considered to be a "generic derogatory term for cultivators", in contrast to the ''sabhya bhabya Gan'' "sophisticated people". Around the turn of the 20th century, Chasas were small farmers and marginal raiyats. In modern day Odisha, the Chasas are among the dominant castes in most villages, and are landowners and econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
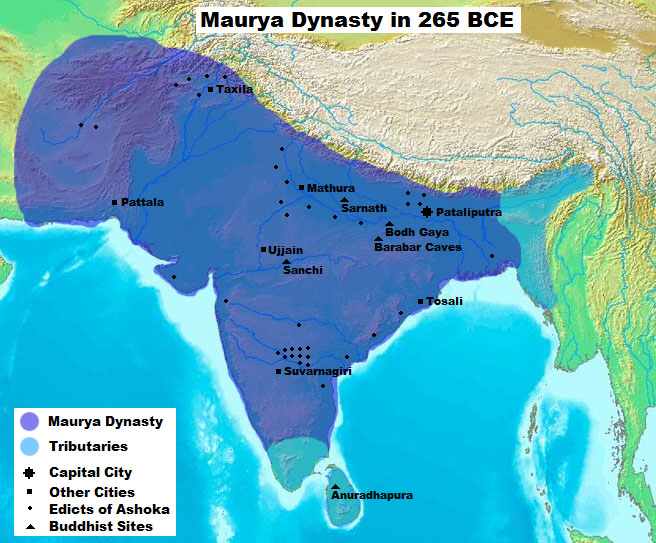
Odisha
Odisha (English: , ), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the 8th largest state by area, and the 11th largest by population. The state has the third largest population of Scheduled Tribes in India. It neighbours the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has a coastline of along the Bay of Bengal in Indian Ocean. The region is also known as Utkala and is also mentioned in India's national anthem, " Jana Gana Mana". The language of Odisha is Odia, which is one of the Classical Languages of India. The ancient kingdom of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Mauryan Emperor Ashoka (which was again won back from them by King Kharavela) in 261 BCE resulting in the Kalinga War, coincides with the borders of modern-day Odisha. The modern boundaries of Odisha were demarcated by the British Indian government when Orissa Province wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India
East India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The region roughly corresponds to the historical region of Magadha from which it inherits its various Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. The states of Bihar and West Bengal lie on the Indo-Gangetic plain. Jharkhand is situated on the Chota Nagpur Plateau. Odisha lies on the Eastern Ghats and the Deccan Plateau. West Bengal's capital Kolkata is the largest city of this region. The Kolkata Metropolitan Area is the country's third largest. The region is bounded by Bhutan, Nepal and the state of Sikkim in the north, the states of Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh on the west, the state of Andhra Pradesh in the south and the country of Bangladesh in the east. It is also bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the south-east. It is connected to the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by the narrow Siliguri Corrido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriya Language
Odia (, ISO: , ; formerly rendered Oriya ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the official language in Odisha (formerly rendered Orissa), where native speakers make up 82% of the population, and it is also spoken in parts of West Bengal, Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Odia is one of the many official languages of India; it is the official language of Odisha and the second official language of Jharkhand. The language is also spoken by a sizeable population of 700,000 people in Chhattisgarh. Odia is the sixth Indian language to be designated a classical language, on the basis of having a long literary history and not having borrowed extensively from other languages. The earliest known inscription in Odia dates back to the 10th century CE. History Odia is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Aryan language family. It descends from Odra Prakrit, which evolved from Magadhi Prakrit, which was spoken in east India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paika (community)
The Paik or Paika (Odia:ପାଇକ) is a Militia community, found in Odisha state of India. Origin The Odia word ''Paika or Paiko, derived'' from ''Padatika,'' means foot Soldier. They were originally a class of military retainers had been recruited since the 16th century by kings in Odisha from a variety of social groups to render martial services in return for hereditary rent-free land (nish-kar jagirs) and titles. In the past the Paiks were recruited from various castes of which Khandayat, Gopal were majority. Later after the Caste based consensus introduced by Britishers, they were known as a caste. History The Paikas (Paikos) were started an armed rebellion ( Paika Rebellion or Paika Bidroha ) against the British East India Companys rule in Odisha in 1817. Classification The Paikos are included under Other Backward Class The Other Backward Class is a collective term used by the Government of India to classify castes which are educationally or socially backward. It is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanda (sword)
The khanda ( sa, खड्ग) is a double-edge straight sword originating from the Indian subcontinent. The Maratha warrior clans venerated the khanda as a weapon of great prestige. It is often featured in religious iconography, theatre and art depicting the ancient history of India. It is a common weapon in Indian martial arts.M. L. K. Murty (2003), p91 Khanda often appears in the Sikh, Jain, Buddhist and Hindu scriptures and art. Etymology The word ''khanda'' has its origins in the Sanskrit 'Rocky Pendergrass, 201Mythological Swords Page 10. (खड्ग) or ', from a root ' meaning "to break, divide, cut, destroy". The older word for a bladed weapon, ', is used in the Rigveda in reference to either an early form of the sword or to a sacrificial knife or dagger to be used in war. Appearance The blade broadens from the hilt to the point, which is usually quite blunt. While both edges are sharp, one side usually has a strengthening plate along most of its length, which both a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopal Chandra Praharaj
Gopala Chandra Praharaj (27 September 1874 – 16 May 1945) was a writer and linguist in the Odia language, well known as the compiler of the '' Purnachandra Odia Bhashakosha''. He also contributed significantly to Odia literature by his works in prose. A lawyer by profession, Praharaj wrote several satirical and analytical essays, in magazines such as ''Utkal Sahitya'', ''Rasachakra'', ''Nababharata'', and ''Satya Samachar'', on the social, political and cultural issues of contemporary Odisha (Odisha) during early 20th century. Early life Praharaj was born on 27 September 1874 to an aristocratic Zamindar Brahmin family of Siddheswarpur in Cuttack district. He completed his matriculation from Ravenshaw Collegiate School and studied FA from Ravenshaw college of Cuttack. He studied law at Calcutta University and became a lawyer in 1902. Life as a writer He started writing essays in the Magazine Utkal Sahitya in 1901 by the caption "Bhagabata Tungire Sandhya", which is the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopal (caste)
Gopal or Gauda is an Indian caste, which is a synonym of Ahir from Odisha State in East India. Their traditional occupation include dairy farming, cattle herding, cultivation and carrying palanquins of deities. They also worked as Paikas (soldiers) under the kings. They claim Kshatriya status and in hierarchy, they occupy the rank next to Khandayats. They also owned Zamindaris in Ranapura, Nayagarh and Khandapara regions of Odisha. They find mention in Mahabharata as soldiers of Narayani Sena. As per the census of India, they are the second largest caste in Odisha and comprise more than 16% of population. as well. Etymology The word Gopal derived from vedic "Gopala", which "''Go''" refers to cow and "''Pala''" refers to protector or herder. Hence "Gopala" literally means "cow herder" According to Bhagavata Purana, the earth takes the form of a cow and asks Vishnu to protect her. That was why Vishnu (Krishna), her guardian is called Go-Pala, protector of mother earth in the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four '' varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoretically, class serving other three classes. The word caste comes from the Portuguese word casta. The word ''Shudra'' appears in the '' Rig Veda'' and it is found in other Hindu texts such as the ''Manusmriti'', ''Arthashastra'', '' Dharmashastras'' and '' Jyotishshastra''. In some cases, shudras participated in the coronation of kings, or were ministers and kings according to early Indian texts. History Vedas The term ''śūdra'' appears only once in the ''Rigveda''. This mention is found in the mythical story of creation embodied in the ''Purusha Sukta ("The Hymn of Man").'' It describes the formation of the four varnas from the body of a primeval man. It states that the brahmin emerged from his mouth, the kshatriya from his arms, the vaishya from his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the context of later Vedic society wherein members were organised into four classes: ''brahmin'', kshatriya, ''vaishya'' and ''shudra''. History Early Rigvedic tribal monarchy The administrative machinery in the Vedic India was headed by a tribal king called Rajan whose position may or may not have been hereditary. The king may have been elected in a tribal assembly (called Samiti), which included women. The Rajan protected the tribe and cattle; was assisted by a priest; and did not maintain a standing army, though in the later period the rulership appears to have risen as a social class. The concept of the fourfold varna system is not yet recorded. Later Vedic period The hymn ''Purusha Sukta'' to the ''Rigveda'' describes the symbolic creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adivasi
The Adivasi refers to inhabitants of Indian subcontinent, generally tribal people. The term is a Sanskrit word coined in the 1930s by political activists to give the tribal people an indigenous identity by claiming an indigenous origin. The term is also used for ethnic minorities, such as Chakmas of Bangladesh, Khas of Nepal, and Vedda of Sri Lanka. The Constitution of India does not use the word ''Adivasi'', instead referring to Scheduled Tribes and Janjati. The government of India does not officially recognise tribes as indigenous people. The country ratified the International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention 107 on Indigenous and Tribal Peoples of the United Nations (1957) and refused to sign the ILO Convention 169. Most of these groups are included in the Scheduled Tribe category under constitutional provisions in India. They comprise a substantial minority population of India and Bangladesh, making up 8.6% of India's population and 1.1% of Bangladesh's, or 104.2&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |