|
Khamba People
The Khamba, also spelled Khemba, are a people who inhabit the Yang-Sang-Chu valley in the westernmost part of Arunachal Pradesh, near the borders with Tibet and Bhutan. Within the valley, they live in the villages Yorton, Lango, Tashigong, Nyukong and Mangkota. Wheat and maize are principal crops cultivated by the Khamba. Their houses, which are made from stone and wood, are based on a structure that strongly resembles the Monpa. The Khamba are adherents of Tibetan Buddhism and use Hingna, their own script, which is based on the Tibetan script. However, due to relative isolation from Tibet and occasional contacts with the Adi tribes, they are also somewhat influenced by the Donyi-Polo faith in their beliefs. In every village there will be a Buddhist Lama. Festivals that are celebrated are parallel with the Memba, which includes Losar, the Tibet Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,382,611 and an area of . It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa people in the west, Tani people in the centre, Mishmi and Tai people in the east, and Naga people in the southeast of the state. About 26 major tribes and 100 sub-tribes live in the state. The main tribes of the state are Adi, Nyshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa and Lhoba peoples and now also considerable numbers of Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui settlers. Since Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, 1951, the entire plateau has been under the administration of the People's Republic of China, a major portion in the Tibet Autonomous Region, and other portions in the Qinghai and Sichuan provinces. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising 8,848.86 m (29,032 ft) above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous country, Bhutan is known as "Druk Yul," or "Land of the Thunder Dragon". Nepal and Bangladesh are located near Bhutan but do not share a land border. The country has a population of over 727,145 and territory of and ranks 133rd in terms of land area and 160th in population. Bhutan is a Constitutional Democratic Monarchy with King as head of state and Prime Minister as head of government. Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism is the state religion and the Je Khenpo is the head of state religion. The subalpine Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest uncl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monpa People
The Monpa or Mönpa () is a major tribe of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. The Tawang Monpas have a migration history from Changrelung. The Monpa are believed to be the only nomadic tribe in Northeast India – they are totally dependent on animals like sheep, cow, yak, goats and horses. The Monpa have a very close affinity with the Sharchops of Bhutan. Their languages are Tibeto-Burman languages written with the Tibetan alphabet. Name Tibetan Buddhists texts present "Monyul" (literally, "low land") as the territory immediately to the south of Tibet below the Himalayan crest line. Its borders were imprecise, but roughly stretched from eastern Nepal to the Tawang area. "Monpa" were the people of Mon and they were distinguished from "Lopa" (also spelt "Lhopa"), who were the wild and intractable tribes of the Assam Himalayan region. In practice, Monpa were people amenable to the proselytising efforts of the Buddhist monks, whereas Lopa wer those inimical to them. In co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majority regions surrounding the Himalayan areas of India (such as Ladakh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and a minority in Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), in much of Central Asia, in the southern Siberian regions such as Tuva, and in Mongolia. Tibetan Buddhism evolved as a form of Mahāyāna Buddhism stemming from the latest stages of Indian Buddhism (which also included many Vajrayāna elements). It thus preserves many Indian Buddhist tantric practices of the post-Gupta early medieval period (500 to 1200 CE), along with numerous native Tibetan developments. In the pre-modern era, Tibetan Buddhism spread outside of Tibet primarily due to the influence of the Mongol Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), founded by Kublai Khan, which had ruled China, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
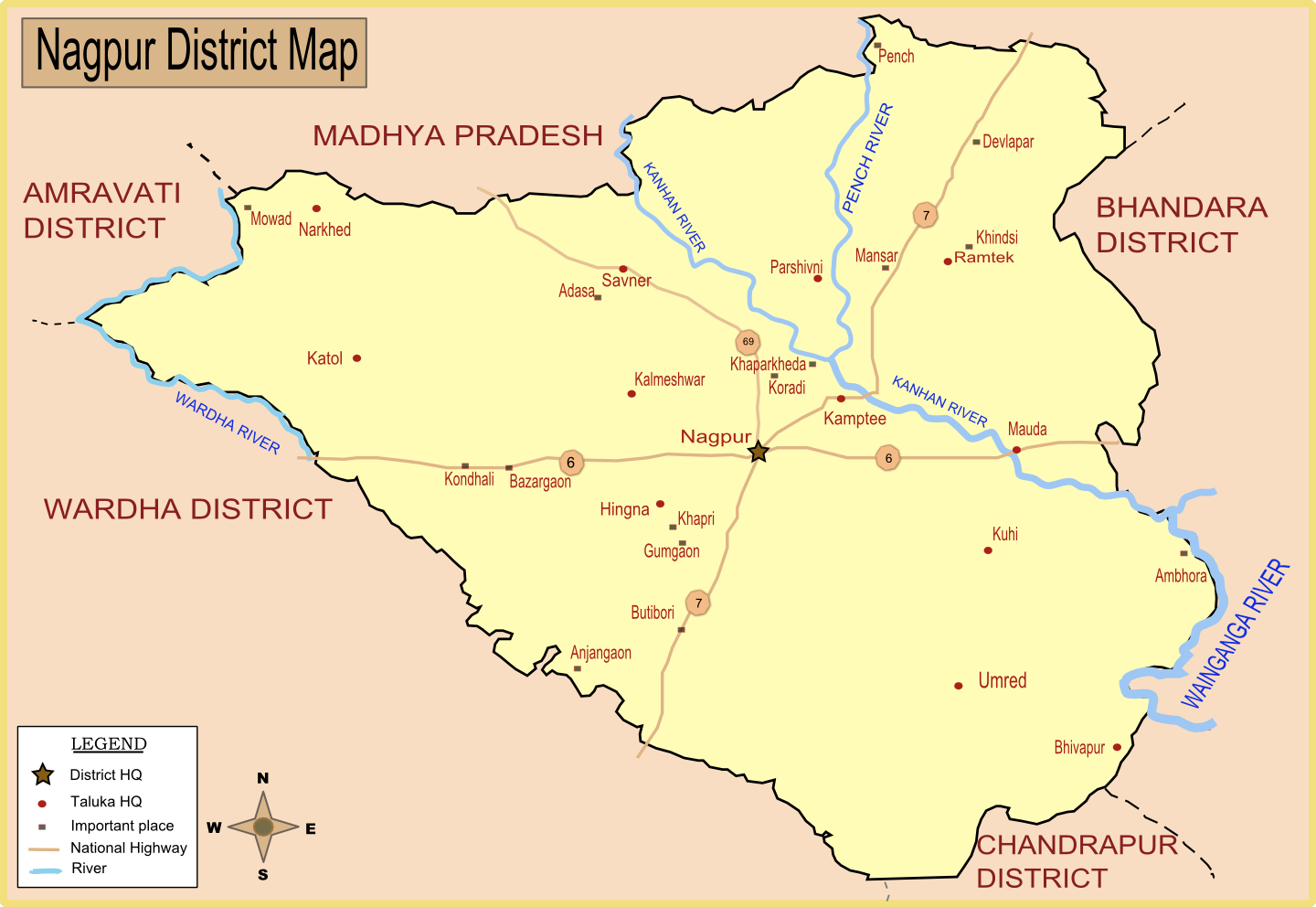
Hingna Script
Hingna is a town, tehsil and taluka in Nagpur district in Maharashtra state. Now Hingna is part of Nagpur Metropolitan Region and emerging as an industrial suburb of Nagpur city due to presence of various industrial developments. The Nagpur revenue division is part of Berar region in the state. Town Hingna is an industrial suburb of Nagpur city with industries operating from Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation (MIDC) is a project of the government of Maharashtra state in India and is the leading corporation of Maharashtra. It provides businesses with infrastructure such as land (open plot or built-up spa ... areas. Hingna is located distance from its District Main City Nagpur. It is located distance from its State Main City Mumbai. The main river of the town is the Vena nadi (river). Taluka Hingna is main town for the Hingna Taluka. Other villages in Hingna Taluka are Adegaon, Amgaon(D), Chicholi(P), Dabha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAGE Publications
SAGE Publishing, formerly SAGE Publications, is an American independent publishing company founded in 1965 in New York by Sara Miller McCune and now based in Newbury Park, California. It publishes more than 1,000 journals, more than 800 books a year, reference works and electronic products covering business, humanities, social sciences, science, technology and medicine. SAGE also owns and publishes under the imprints of Corwin Press (since 1990), CQ Press (since 2008), Learning Matters (since 2011), and Adam Matthew Digital (since 2012). History SAGE was founded in 1965 in New York City by Sara Miller (later Sara Miller McCune) with Macmillan Publishers executive George D. McCune as a mentor; the name of the company is an acronym formed from the first letters of their given names. SAGE relocated to Southern California in 1966, after Miller and McCune married; McCune left Macmillan to formally join the company at that time. Sara Miller McCune remained president for 18 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adi People
Adi or ADI may refer to: Names and titles * Adi (mythology), an Asura in Hindu faith who appears in the Matsya Purāṇa * Adi (name), a given name in Hebrew and a nickname in other languages * Adi (title), a Fijian title used by females of chiefly rank Places * Adi (Khanapur), Belgaum District, Karnataka, India * Adi (Chikodi), Belgaum District, Karnataka, India * Ahmedabad Junction railway station, Ahmedabad, India (code ADI) * Adi, Israel, a community settlement in northern Israel * Adi Island, an island in West Papua, Indonesia * Arandis Airport, Arandis, Namibia (IATA: ADI) Organizations * Aerodynamics Inc., a small airline in the US * Aircraft Designs Inc, an aircraft design firm in Monterey, California * Alfred Deakin Institute, at Deakin University, in Geelong, Australia * American Documentation Institute, former name of the Association for Information Science and Technology * Analog Devices, Inc, producer of semiconductors (ADI is their symbol on the New York Stock E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donyi-Polo
Donyi-Polo (also Donyi-Poloism) is the designation given to the indigenous religion, of animistic and shamanic type, of the Tani and other Tibeto-Burman peoples of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam in Northeast India. The name "Donyi-Polo" means "Sun-Moon", and was chosen for the religion in the process of its revitalisation and institutionalisation. The Donyi- Poloism has been there from since immemorial. The religion has developed a congregational system; hymns to be sung, composed in the Tani ritual language of shamans; a formalised philosophy-theology; and an iconography of the gods and temples. The pioneer of the revival was Talom Rukbo. Donyi-Polo is related to the Hemphu-Mukrang religion of the Karbi and the Nyezi-No of the Hruso. Theology and cosmology ''Sedi'' and ''Keyum'' In the Donyi-Polo belief, the fountain god that begets the universe (God or the Godhead) is referred to as ''Sedi'' by the Minyong and Padam, ''Jimi'' by the Galo. All things and beings are parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lama
Lama (; "chief") is a title for a teacher of the Dharma in Tibetan Buddhism. The name is similar to the Sanskrit term ''guru'', meaning "heavy one", endowed with qualities the student will eventually embody. The Tibetan word "lama" means "highest principle", and less literally "highest mother" or "highest parent" to show close relationship between teacher and student."lama" from Historically, the term was used for venerated spiritual masters or heads of . Today the title can be used as an [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpeg/1200px-Tibetan_Buddhism_(214837929).jpeg)