|
Keşan
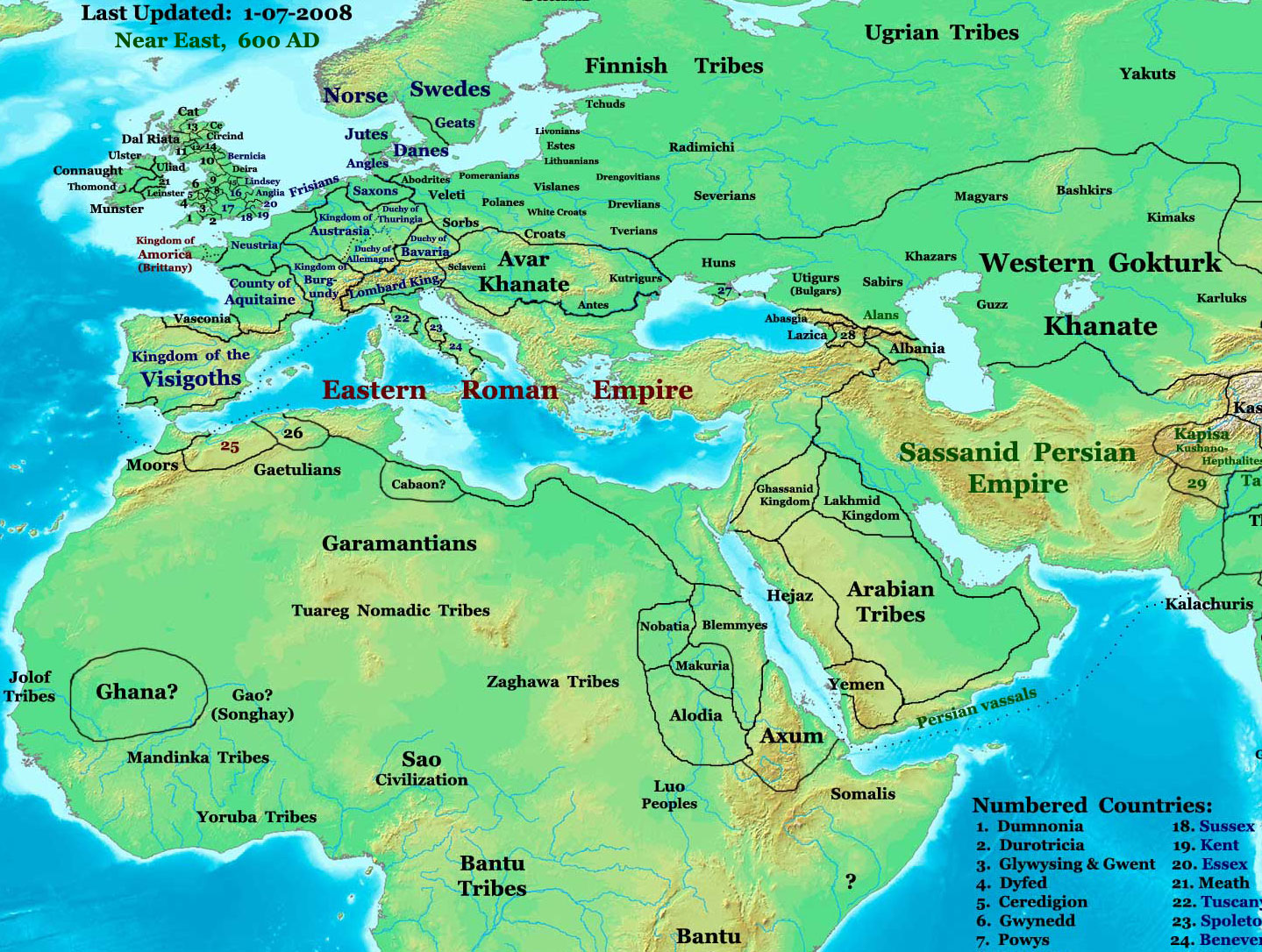
Keşan (; ; ; Byzantine Greek: Ρούσιον, ''Rusion'') is a town in Edirne Province, Turkey. It is the seat of Keşan District.İlçe Belediyesi , Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 64,842 (2022). In the summer its population increases because of an influx of tourists. The mayor is Mehmet Özcan ( CHP). and |
Keşan District
Keşan District is a district of the Edirne Province of Turkey. Its seat is the town of Keşan.İlçe Belediyesi , Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its area is 1,098 km2, and its population is 83,874 (2022). Keşan district is bordered by and Uzunköprü to the north, to the east, Şarköy to the southeast, |
Edirne Province
Edirne Province () is a Turkish province located in East Thrace. Part of European Turkey, it is one of only three provinces located entirely within continental Europe. Its area is 6,145 km2, and its population is 414,714 (2022). Edirne Province is bordered by Tekirdağ Province and Kırklareli Province to the east, and the Gallipoli peninsula of Çanakkale Province to the south-east. It shares international borders with Bulgaria ( Haskovo and Yambol Provinces) to the north and Greece (Eastern Macedonia and Thrace) to the west. Edirne is the capital of the province, and the largest city. It is the only province of Turkey that borders Greece. History Edirne, capital of the province, is notable for serving as the third capital of the Ottoman Empire from 1363 to 1453. Edirne province was included in the Second Inspectorate General which was created on the 19 February 1934 and extended over the provinces of Edirne, Çanakkale, Kırklareli, Tekirdağ. It was ruled by an Inspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican People's Party
The Republican People's Party (RPP; , CHP ) is a Kemalism, Kemalist and Social democracy, social democratic political party in Turkey. It is the oldest List of political parties in Turkey, political party in Turkey, founded by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the List of presidents of Turkey, first president and founder of the modern Turkey, Republic of Türkiye. The party is also cited as the founding party of modern Turkey. Its logo consists of the The Six Arrows, Six Arrows, which represent the foundational principles of Kemalism: republicanism, reformism, Secularism in Turkey, laicism, populism, nationalism, and statism. It is currently the second largest party in Grand National Assembly of Turkey, Grand National Assembly with 135 MPs, behind the ruling conservative Justice and Development Party (Turkey), Justice and Development Party (AKP). The political party has its origins in the various Association for Defence of National Rights, resistance groups founded during the Turkish W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs and Slovenes. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united a majority of the South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in late 17th-century Croatia, at the time part of the Habsburg monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929, was proclaimed on 1 December 1918, following the unification of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries. They became known as Eurasian nomads, nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers trace Bulgar ethnic roots to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian Steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian peoples, Iranic, Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric, and Huns, Hunnic tribes. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic languages, Turkic language, the Bulgar language of the Oghur languages, Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization, and customs of Eurasian steppes as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tengri, Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary during the 7th century in the Pontic- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
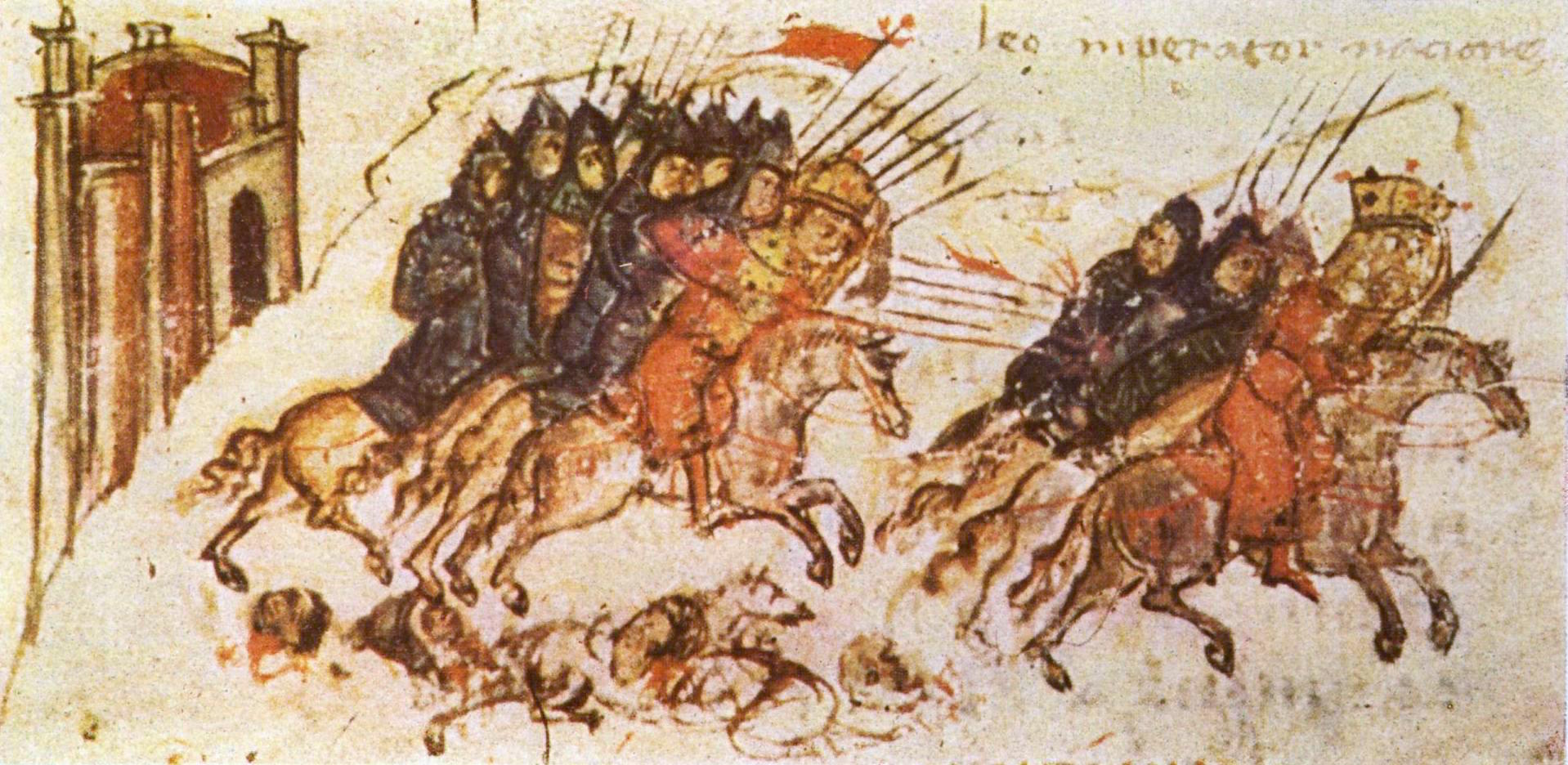
Zabergan
Zabergan () was the chieftain of the Kutrigurs, a Turkic nomadic tribe of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, after Sinnion. His name is Iranian, meaning full moon. Either under pressure from incoming Avars,; or in revolt against the Byzantine Empire, in the winter of 558, he led a large Kutrigur army that crossed the frozen Danube. The army was divided into three sections: one raided south far as Thermopylae, while two others the Thracian Chersonesus and the periphery of Constantinople. In March 559 Zabergan attacked Constantinople, and one part of his forces consisted of 7,000 horsemen, but Belisarius defeated him at the Battle of Melantias and he was forced to withdraw. The transit of such big distances in a short period of time shows that the Kutrigurs were mounted warriors, and Zabergan's raiders were already encamped near the banks of the Danube. However, once again Emperor Justinian I (r. 527–565) managed to persuade the Utigur chieftain Sandilch to attack the Kutrigurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutrigurs
The Kutrigurs were a Turkic nomadic equestrian tribe who flourished on the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the 6th century AD. To their east were the similar Utigurs and both possibly were closely related to the Bulgars. They warred with the Byzantine Empire and the Utigurs. Towards the end of the 6th century they were absorbed by the Pannonian Avars under pressure from the Türks. Etymology The name ''Kutrigur'', also recorded as ''Kwrtrgr'', ''Κουτρίγουροι'', ''Κουτούργουροι'', ''Κοτρίγουροι'', ''Κοτρίγοροι'', ''Κουτρίγοροι'', ''Κοτράγηροι'', ''Κουτράγουροι'', ''Κοτριαγήροι'', has been suggested as a metathecized form of Turkic ''*Toqur- Oğur'', with ''*quturoğur'' meaning "nine Oğur (tribes)". David Marshall Lang derived it from Turkic ''kötrügür'' (conspicuous, eminent, renowned). Few scholars support theories deriving the Kutrigurs from the Guti/Quti and the Utigurs from the Ud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Egnatia
The Via Egnatia was a road constructed by the Romans in the 2nd century BC. It crossed Illyricum, Macedonia, and Thracia, running through territory that is now part of modern Albania, North Macedonia, Greece, and European Turkey as a continuation of the Via Appia. Starting at Dyrrachium (now Durrës) on the Adriatic Sea, the road followed a difficult route along the river Genusus ( Shkumbin), over the '' Candaviae'' ( Jablanica) mountains and thence to the highlands around Lake Ohrid. It then turned by parts south, following several high mountain passes to reach the northern coastline of the Aegean Sea at Thessalonica. From there it ran through Thrace to the city of Byzantium (later Constantinople, now Istanbul). It covered a total distance of about 1,120 km (696 miles/746 Roman miles). Like other major Roman roads, it was about six metres (19.6 ft) wide, paved with large polygonal stone slabs or covered with a hard layer of sand. Construction and usage The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarians, Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1422. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conquered by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in the late 14th century. Until 1256, the Second Bulgarian Empire was the dominant power in the Balkans, defeating the Byzantine Empire in several major battles. In 1205, Emperor Kaloyan of Bulgaria, Kaloyan defeated the newly established Latin Empire in the battle of Adrianople (1205), Battle of Adrianople. His nephew Ivan Asen II defeated the Despotate of Epiros and made Bulgaria a regional power again. During his reign, Bulgaria spread from the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic to the Black Sea and the economy flourished. In the late 13th century, however, the Empire declined under constant invasions by Mongols, Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, Hungarians, and Serbia in the Middle Ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic Church, Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The main objective to form a Latin Empire was planned over the course of the Fourth Crusade, promoted by crusade leaders such as Boniface I, Marquis of Montferrat, Boniface of Montferrat, as well as the Republic of Venice. The Fourth Crusade had originally been called to retake the Abbasid Caliphate, Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, but a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army Sack of Constantinople, sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Originally, the plan had been to restore the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |