|
Kerr Sulphurets Mitchell
Kerr-Sulphurets-Mitchell (KSM) is an active mine exploration project 65 km northwest of Stewart, British Columbia (1,545 km northwest of Vancouver, British Columbia). The property is 100% owned by Toronto-based Seabridge Gold. Denver-based royalty company Royal Gold owns a 2% net smelter return royalty on the mine. Since May 2011, the project has also been called Kerr-Sulphurets-Mitchell-Iron Cap due to the addition of significant reserves from the Iron Cap region. When operational it will feature three open-pit mines, a processing plant and a tailings facility. It is the largest undeveloped gold deposit in Canada and one of the world's biggest copper-gold porphyry deposits. Though 2P reserves are significant (39 million ounces of gold, 214 million ounces of silver, 9.9 billion pounds of copper and 257 million pounds of molybdenum) they only represent about 65% of the mine's total resource of each metal. The mines have a 52-year mine life (up from the 37 year estimate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mine Exploration
Mine exploration is a hobby in which people visit abandoned mines, quarries, and sometimes operational mines. Enthusiasts usually engage in such activities for the purpose of exploration and documentation, sometimes through the use of surveying and photography. In this respect, mine exploration might be considered a type of amateur industrial archaeology. In many ways, however, it is closer to caving, with many participants actively interested in exploring both mines and caves. Mine exploration typically requires equipment such as helmets, head lamps, Wellington boots, and climbing gear. Mine exploration typically involves less crawling and more walking than caving, since mines were purposefully excavated to allow human access. Some disused mines have been adapted for tourism, or use by organized outdoor recreation groups. Conversely, gaining access to other mines may require technical skills such as rappelling or single rope technique. Such techniques may also be used inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Standard Resources
SSR Mining Inc., formerly Silver Standard Resources is a Denver-based gold, silver, copper, lead and zinc producer that owns the largest silver mine in Argentina. In addition it engages in exploration activity throughout the Americas (5 countries) and Turkey. In 2020, SSR Mining merged with Alacer Gold. Since the merger, the company has moved headquarters to Denver, Colorado. Rodney P. Antal is now the president and CEO of SSR mining (replacing Paul Benson after the merger closed). In February 2021, SSR Mining announced that Alison White would be the new executive vice president and CFO (replacing Greg Martin). In addition, the rest of the executive team at SSR mining was added following the closure of the merger between SSR and Alacer Gold. Stewart Beckman is the executive vice president and COO (replacing Kevin O'Kane at the time of merger); F. Edward Farid is the vice president and CCDO (chief corporate development officer). Michael J. Sparks is the vice president and chief l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornite
Bornite, also known as peacock ore, is a sulfide mineral with chemical composition Cu5 Fe S4 that crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (pseudo-cubic). Appearance Bornite has a brown to copper-red color on fresh surfaces that tarnishes to various iridescent shades of blue to purple in places. Its striking iridescence gives it the nickname ''peacock copper'' or ''peacock ore''. Mineralogy Bornite is an important copper ore mineral and occurs widely in porphyry copper deposits along with the more common chalcopyrite. Chalcopyrite and bornite are both typically replaced by chalcocite and covellite in the supergene enrichment zone of copper deposits. Bornite is also found as disseminations in mafic igneous rocks, in contact metamorphic skarn deposits, in pegmatites and in sedimentary cupriferous shales. It is important as an ore for its copper content of about 63 percent by mass. Structure At temperatures above , the structure is isometric with a unit cell that is about 5.5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
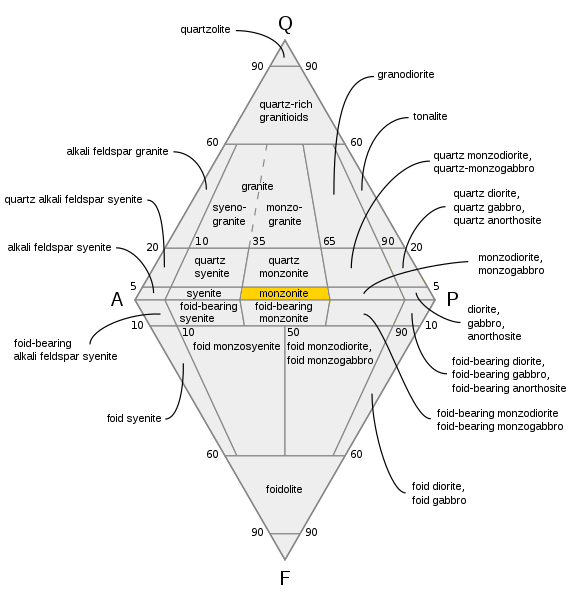
Monzonite
Monzonite is an igneous intrusive rock, formed by slow cooling of underground magma that has a moderate silica content and is enriched in alkali metal oxides. Monzonite is composed mostly of plagioclase and alkali feldspar. Syenodiorite is an obsolescent term for monzonite or for monzodiorite.Le Maitre, R.W., ''Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms'' Cambridge University Press, 2nd ed, pp. 113 Larvikite is a particular form of monzonite. Description Monzonite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) igneous rock. Such rocks are classified by their relative percentages of quartz, plagioclase, alkali feldspar, and feldspathoid (the QAPF classification). Monzonite is defined as rock having less than 5% quartz in its QAPF fraction and in which alkali feldspar makes up between 35% and 65% of the total feldspar content. If quartz constitutes greater than 5% of the QAPF fraction, the rock is termed a quartz monzonite, while if feldspathoids are present as up to 10% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyry Copper Deposit
Porphyry copper deposits are copper ore bodies that are formed from hydrothermal fluids that originate from a voluminous magma chamber several kilometers below the deposit itself. Predating or associated with those fluids are vertical dikes of porphyritic intrusive rocks from which this deposit type derives its name. In later stages, circulating meteoric fluids may interact with the magmatic fluids. Successive envelopes of hydrothermal alteration typically enclose a core of disseminated ore minerals in often stockwork-forming hairline fractures and veins. Because of their large volume, porphyry orebodies can be economic from copper concentrations as low as 0.15% copper and can have economic amounts of by-products such as molybdenum, silver, and gold. In some mines, those metals are the main product. The first mining of low-grade copper porphyry deposits from large open pits coincided roughly with the introduction of steam shovels, the construction of railroads, and a surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockwork
In geology, a stockwork is a complex system of structurally controlled or randomly oriented veins. Stockworks are common in many ore deposit types and in greisen Greisen is a highly altered granitic rock or pegmatite, usually composed predominantly of quartz and micas (mostly muscovite). Greisen is formed by self-generated alteration of a granite and is a class of moderate- to high-temperature magmatic-hy ...s. They are also referred to as ''stringer zones''. References Structural geology Economic geology Petrology {{Petrology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcopyrite
Chalcopyrite ( ) is a copper iron sulfide mineral and the most abundant copper ore mineral. It has the chemical formula CuFeS2 and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It has a brassy to golden yellow color and a hardness of 3.5 to 4 on the Mohs scale. Its streak is diagnostic as green-tinged black. On exposure to air, chalcopyrite tarnishes to a variety of oxides, hydroxides, and sulfates. Associated copper minerals include the sulfides bornite (Cu5FeS4), chalcocite (Cu2S), covellite (CuS), digenite (Cu9S5); carbonates such as malachite and azurite, and rarely oxides such as cuprite (Cu2O). Is rarely found in association with native copper. Chalcopyrite is a conductor of electricity. Etymology The name chalcopyrite comes from the Greek words , which means copper, and ', which means striking fire. It was sometimes historically referred to as "yellow copper". Identification Chalcopyrite is often confused with pyrite and gold since all three of these minerals have a yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketchikan
Ketchikan ( ; tli, Kichx̱áan) is a city in and the borough seat of the Ketchikan Gateway Borough of Alaska. It is the state's southeasternmost major settlement. Downtown Ketchikan is a National Historic District. With a population at the 2020 census of 8,192, up from 8,050 in 2010, it is the sixth-most populous city in the state, and thirteenth-most populous community when census-designated places are included. The surrounding borough, encompassing suburbs both north and south of the city along the Tongass Highway (most of which are commonly regarded as a part of Ketchikan, albeit not a part of the city itself), plus small rural settlements accessible mostly by water, registered a population of 13,948 in that same census. Incorporated on August 25, 1900, Ketchikan is the earliest extant incorporated city in Alaska, because consolidation or unification elsewhere in Alaska resulted in the dissolution of those communities' city governments. Ketchikan is located on Revillagige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unuk River
The Unuk River is a river in the U.S. state of Alaska and the Canadian province of British Columbia. It flows from the Coast Mountains southwest to Behm Canal, northeast of Ketchikan, Alaska. From its headwaters in a heavily glaciated area in British Columbia, south of the lower Iskut River, the Unuk flows west and south for , crossing into Alaska and emptying into Burroughs Bay, an inlet of Behm Canal. In Alaska the river flows through the Misty Fjords National Monument.Unuk River Chinook Salmon Studies Alaska Department of Fish and Game In it is called ''Joonáx̱'', the meaning of which is obscure but may have to do with dreaming (cf. ''aawajoon'' “he dreamed”). It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Environmental Assessment Act
The ''Canadian Environmental Assessment Act, 2012'' (CEAA 2012) (the ''Act'') and its regulations established the legislative basis for the federal practice of environmental assessment in most regions of Canada from 2012 to 2019. It was repealed with the coming into force of the Impact Assessment Act on August 28, 2019. History The ''Canadian Environmental Assessment Act'', S.C. 1992, c. 37 (CEAA) is an Act of Parliament that was passed by the Government of Canada in 1992. The ''Act'' requires federal departments, including Environment Canada, agencies, and Crown corporations to conduct environmental assessments for proposed projects where the federal government is the proponent or where the project involves federal funding, permits, or licensing. The purposes of the ''Act'' were set out as follows: (1) to achieve sustainable development that conserves environmental quality by integrating environmental factors into planning and decision-making process, (2) exercise leadershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpeg)
