|
Kerkenes
Kerkenes (or Kerkenes Dağı; both names are modern) is the largest pre-Hellenistic site from the Anatolian Plateau (Turkey) – 7 km (4 mi) of strong stone defenses, pierced by seven gates, that enclose 2.5 km2 (1.0 sq mi). It is located about 200 km (120 mi) east from Ankara (35.06E, 39.75N), between the towns of Yozgat (W) and Sorgun (E). History It has been suggested that this was a Hittite site in the Bronze Age, with the underlying hill being the sacred Mount Daha. An important Imperial Hittite city at Kusakli Hoyuk sits in the valley of Egrioz Su river about 8 km to the north-northwest of the city on the Kerkenes Dag. According to Gurney, the textual evidence that he assembled strongly points towards an identification of Kusakli Hoyuk with the town of Zippalanda, as mentioned in Hittite documents. The huge overlaying Iron Age construction at the site makes this very difficult to verify. The Iron Age city, apparently a planned urban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croesus
Croesus ( ; Lydian: ; Phrygian: ; grc, Κροισος, Kroisos; Latin: ; reigned: c. 585 – c. 546 BC) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least," J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology." Name The name of Croesus was not attested in contemporary inscriptions in the Lydian language. In 2019, D. Sasseville and K. Euler published a research of Lydian coins apparently minted during his rule, where the name of the ruler was rendered as ''Qλdãns''. The name comes from the Latin transliteration of the Greek , which was itself the ancient Hellenic adaptation of the Lydian na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteria (Cappadocia)
Pteria ( grc, Πτερία) was the capital of the Assyrians in northern Cappadocia. They were said by Herodotus to have been taken and ruined by Croesus in 547 BCE. It also was the place of the Battle of Pteria, an undecided battle between Cyrus the Great and Croesus. Stephanus of Byzantium cites two towns with this or a similar name: a Pterium, which he calls a town of the Medes, and Pteria, a town in the territory of Sinope Sinope may refer to: *Sinop, Turkey, a city on the Black Sea, historically known as Sinope ** Battle of Sinop, 1853 naval battle in the Sinop port *Sinop Province * Sinope, Leicestershire, a hamlet in the Midlands of England *Sinope (mythology), in .... Its site is located near Kerkenes Dağ, Asiatic Turkey. External links The Histories of Herodotus By Herodotus, Henry Cary* References Populated places in ancient Cappadocia Former populated places in Turkey History of Yozgat Province {{Yozgat-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
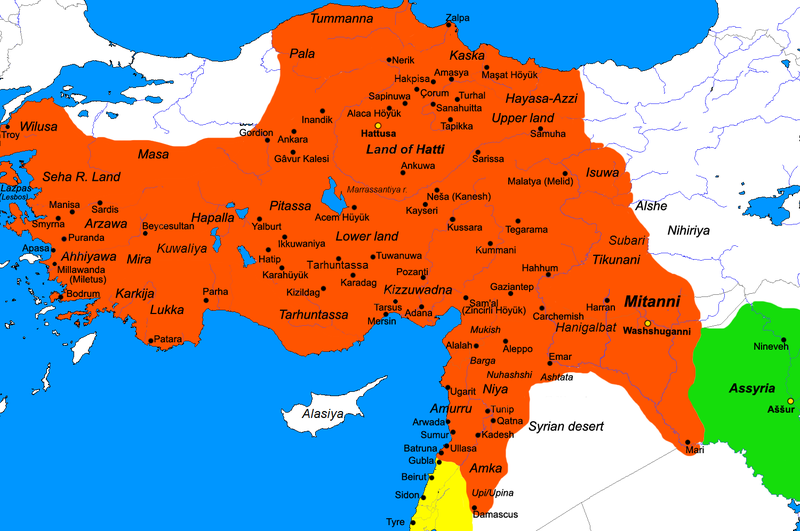
Yozgat
Yozgat is a city and the capital district of Yozgat Province in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. According to 2019 census, population of the district is 421,200 of which 106,280 live in the city of Yozgat. History The first surveys were started in the year 1993. Since then archaeologists have uncovered countless artifacts belonging to 5 different ancient civilizations from the area and as well as artifacts that belong to 5 different eras – the Bronze, Hellenistic, Hittite, Copper and Upper Byzantine eras. Surface excavations and surveys were also undertaken on the Kerkenes plateau by Dr. Geoffery Summers, a British archaeologist. The plateau is believed to be the home to the lost city of Pteria. The search for this lost city as well as other old world constructions began in 2013, and it plans to go on till the month of August as well. The expedition covers an area which is surrounded by walls and is known to date back to almost 2600 years. According to historical repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pteria
The Battle of Pteria ( grc, Πτερία) was fought in 547 BC between the Persian forces of Cyrus the Great and the Lydian forces of Croesus. Both armies suffered heavy casualties in this indecisive battle. Background Croesus learned of the sudden Persian uprising and defeat of his longtime rivals, the Medes. He attempted to use these set of events to expand his borders upon the eastern frontier of Lydia, by making an alliance with Chaldea, Egypt and several Greek city-states, including Sparta. Prior to his invasion, Croesus asked the Oracle of Delphi for advice. The Oracle suggested vaguely that, "if King Croesus crosses the Halys River, a great empire will be destroyed." Croesus received these words most favorably, instigating a war that would ironically and eventually end not the Persian Empire but his own. Croesus began the campaign with an invasion of Cappadocia, crossing the Halys and capturing Pteria, then capital of the district and formidable as a fortress. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the ''Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Turkey
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Central Anatolia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hattusa
Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas ; Hittite: URU''Ḫa-at-tu-ša'',Turkish: Hattuşaş , Hattic: Hattush) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: '' Halys''). Hattusa was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. Surroundings The landscape surrounding the city included rich agricultural fields and hill lands for pasture as well as woods. Smaller woods are still found outside the city, but in ancient times, they were far more widespread. This meant the inhabitants had an excellent supply of timber when building their houses and other structures. The fields provided the people with a subsistence crop of wheat, barley and lentils. Flax was also harvested, but their primary source for clothing was sheep wool. They also hunted deer in the forest, but this was probably only a luxury reserved for the nobility. Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordium
Gordion ( Phrygian: ; el, Γόρδιον, translit=Górdion; tr, Gordion or ; la, Gordium) was the capital city of ancient Phrygia. It was located at the site of modern Yassıhüyük, about southwest of Ankara (capital of Turkey), in the immediate vicinity of Polatlı district. Gordion's location at the confluence of the Sakarya and Porsuk rivers gave it a strategic location with control over fertile land. Gordion lies where the ancient road between Lydia and Assyria/Babylonia crossed the Sangarius river. Occupation at the site is attested from the Early Bronze Age (c. 2300 BCE) continuously until the 4th century CE and again in the 13th and 14th centuries CE. The Citadel Mound at Gordion is approximately 13.5 hectares in size, and at its height habitation extended beyond this in an area approximately 100 hectares in size. Gordion is the type site of Phrygian civilization, and its well-preserved destruction level of c. 800 BCE is a chronological linchpin in the region. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of The Ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC or with that by Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. The largest cities of the Bronze Age Near East housed several tens of thousands of people. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age, with some 30,000 inhabitants, was the largest city of the time by far. Ebla is estimated to have had a population of 40,000 inhabitants in the Intermediate Bronze age. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50,000–60,000. Niniveh had some 20,000–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (around 700 BC). In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU became a determinative sign denoting a city, or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygians
The Phrygians (Greek: Φρύγες, ''Phruges'' or ''Phryges'') were an ancient Indo-European speaking people, who inhabited central-western Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) in antiquity. They were related to the Greeks. Ancient Greek authors used "Phrygian" as an umbrella term to describe a vast ethno-cultural complex located mainly in the central areas of Anatolia rather than a name of a single "tribe" or "people", and its ethno-linguistic homogeneity is debatable. Phrygians were initially dwelling in the southern Balkans – according to Herodotus – under the name of Bryges (Briges), changing it to Phryges after their final migration to Anatolia, via the Hellespont. However, the Balkan origins of the Phrygians are debated by modern scholars. Phrygia developed an advanced Bronze Age culture. The earliest traditions of Greek music are in part connected to Phrygian music, transmitted through the Greek colonies in Anatolia, especially the Phrygian mode, which was conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)