|
Kentucky Space
Kentucky Space is a non-profit consortium of private and public universities, companies, and other organizations with the goal of designing and leading innovative space missions within realistic budgets and objectives. The enterprise is supported by the Kentucky Space Grant Consortium and developed out of the programs of the Kentucky Science and Technology Corporation. Consortium * Kentucky Science and Technology Corporation * Kentucky Council on Postsecondary Education * Kentucky Science and Engineering Foundation * Kentucky Space Grant Consortium * Belcan * Morehead State University * Murray State University * University of Kentucky - Space Systems Laboratory * University of Louisville * Western Kentucky University * Kentucky Community and Technical College System Partners * NASA Ames Research Center * Kentucky Virtual Campus Projects * ''KySat-1'', a CubeSat designed by Kentucky Space which defines a standard reusable bus and was intended to be used as part of a prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Space Grant Consortium
The Kentucky Space Grant Consortium (KSGC) is a partnership between Kentucky and NASA. Projects include the University of Kentucky's Big Blue, Kentucky Space, and Northern Kentucky University's Moon Buggy Project. See also *National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program The space-grant colleges are educational institutions in the United States that comprise a network of fifty-two consortia formed for the purpose of outer space-related research. Each consortium is based in one of the fifty states, the District ... External links * Educational organizations based in the United States Non-profit organizations based in Kentucky NASA programs University of Kentucky {{Kentucky-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurus (rocket)
Minotaur-C (''Minotaur Commercial''), formerly known as Taurus or Taurus XL, is a four stage solid fueled launch vehicle built in the United States by Orbital Sciences (now Northrop Grumman) and launched from SLC-576E at California's Vandenberg Air Force Base. It is based on the air-launched Pegasus rocket from the same manufacturer, utilizing a "zeroth stage" in place of an airplane. The Minotaur-C is able to carry a maximum payload of around 1458 kg into a low Earth orbit (LEO). First launched in 1994, it has successfully completed seven out of a total of ten military and commercial missions. Three of four launches between 2001 and 2011 ended in failure, including the 24 February 2009 launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory mission and the 4 March 2011 launch of the Glory mission, which resulted in losses totalling US$700 million for NASA (excluding the cost of the rockets themselves). The Taurus launch vehicle was subsequently rebranded in 2014 as Minotaur-C, which incorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Space Agencies
This is a list of government agencies engaged in activities related to outer space and space exploration. As of 2022, 77 different government space agencies are in existence, 16 of which have launch capabilities. Six government space agencies—the China National Space Administration (CNSA), the European Space Agency (ESA), the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the (US) National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and the Russian State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" — have full launch capabilities (ability to launch and recover multiple satellites, develop and deploy cryogenic rocket engines and operate space probes) and extraterrestrial landing capabilities. The name given is the English version, with the native language version below. The acronym given is the most common acronym: this can either be the acronym of the English version (e.g. JAXA), or the acronym in the native language. Where there are multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minotaur I
The Minotaur I, or just Minotaur is an American expendable launch system derived from the Minuteman II missile. It is used to launch small satellites for the US Government, and is a member of the Minotaur family of rockets produced by Orbital Sciences Corporation (now Northrop Grumman). Vehicle The Minotaur I is the follow-on to the Orbital Sciences' Taurus (later re-named the "Minotaur-C") launch vehicle, combining the original Taurus's booster stage with a second stage from a Minuteman missile. Minotaur I rockets consist of the M55A1 first stage and SR19 second stage of a decommissioned Minuteman missile. The Orion 50XL and Orion 38, from the Pegasus rocket, are used as third and fourth stages. A HAPS (Hydrazine Auxiliary Propulsion System) upper stage can also be flown if greater precision is needed, or the rocket needs to be able to manoeuvre to deploy multiple payloads. It can place up to of payload into a low Earth orbit at 28.5 degrees of inclination. The Minotaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
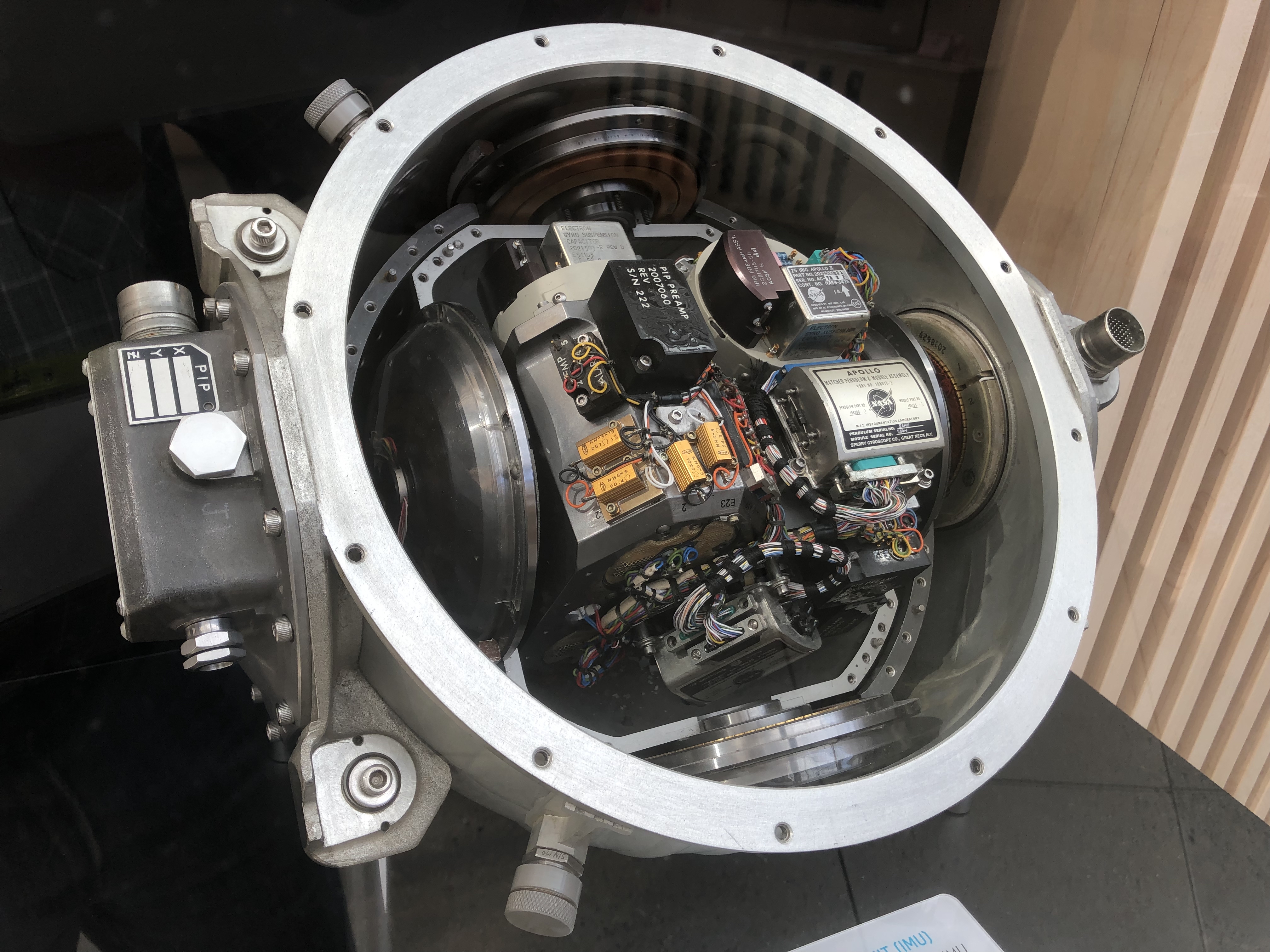
Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs. IMUs are typically used to maneuver modern vehicles including motorcycles, missiles, aircraft (an attitude and heading reference system), including unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), among many others, and spacecraft, including satellites and landers. Recent developments allow for the production of IMU-enabled GPS devices. An IMU allows a GPS receiver to work when GPS-signals are unavailable, such as in tunnels, inside buildings, or when electronic interference is present. Operational principles An inertial measurement unit works by detecting linear acceleration using one or more accelerometers and rotational rate using one or more gyroscopes. Some also include a magnetom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowling Green, Kentucky
Bowling Green is a home rule-class city and the county seat of Warren County, Kentucky, United States. Founded by pioneers in 1798, Bowling Green was the provisional capital of Confederate Kentucky during the American Civil War. As of the 2020 census, its population of 72,294 made it the third-most-populous city in the state, after Louisville and Lexington; its metropolitan area, which is the fourth largest in the state after Louisville, Lexington, and Northern Kentucky, had an estimated population of 179,240; and the combined statistical area it shares with Glasgow has an estimated population of 233,560. In the 21st century, it is the location of numerous manufacturers, including General Motors, Spalding, and Fruit of the Loom. The Bowling Green Assembly Plant has been the source of all Chevrolet Corvettes built since 1981. Bowling Green is also home to Western Kentucky University and the National Corvette Museum. History Settlement and incorporation The first European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
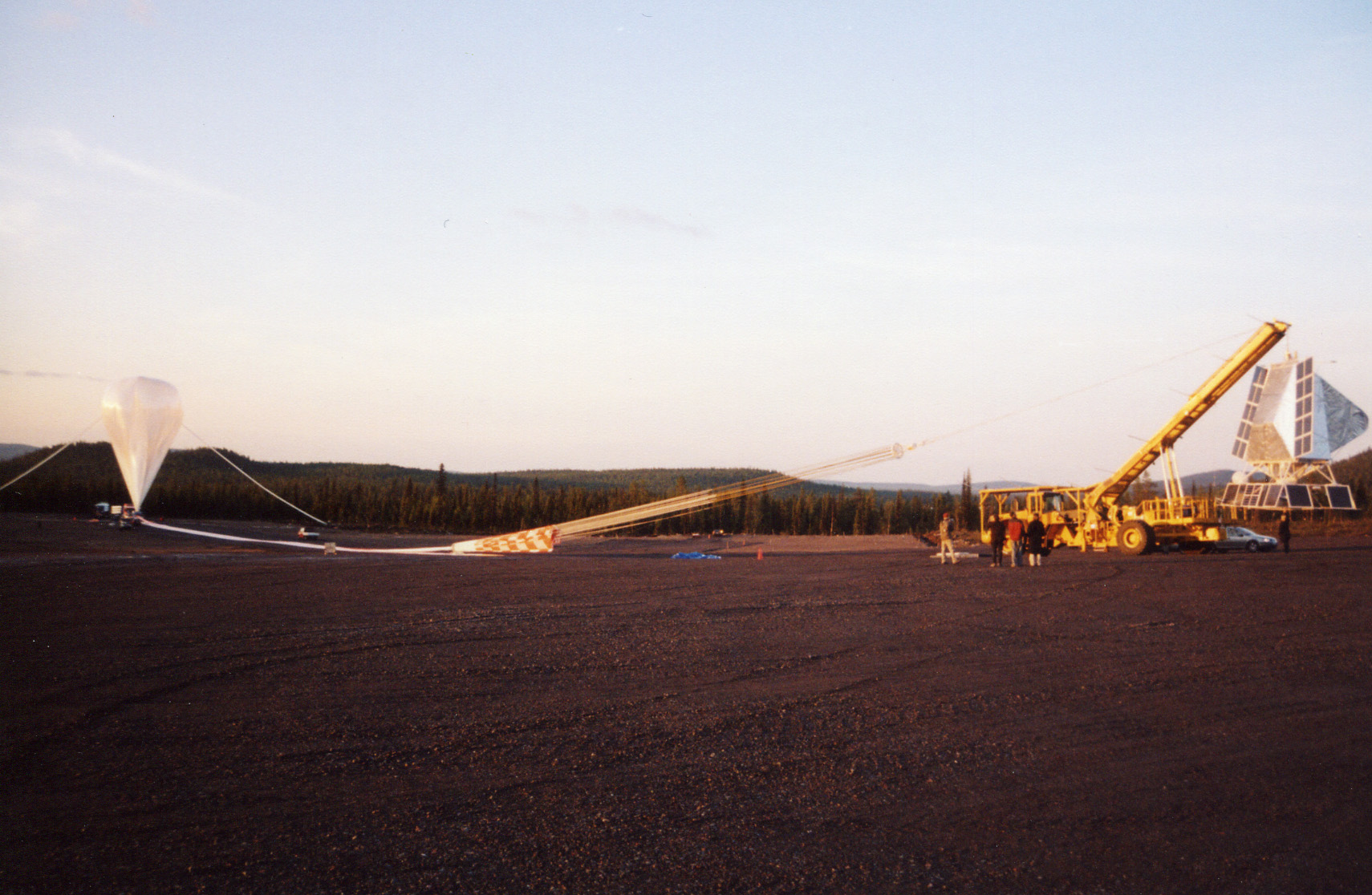
High-altitude Balloon
High-altitude balloons are crewed or uncrewed balloons, usually filled with helium or hydrogen, that are released into the stratosphere, generally attaining between above sea level. In 2002, a balloon named BU60-1 reached a record altitude of . The most common type of high-altitude balloons is weather balloons. Other purposes include use as a platform for experiments in the upper atmosphere. Modern balloons generally contain electronic equipment such as radio transmitters, cameras, or satellite navigation systems, such as GPS receivers. These balloons are launched into what is termed "near space", defined as the area of Earth's atmosphere between the Armstrong limit ( above sea level), where pressure falls to the point that a human being cannot survive without a pressurised suit, and the Kármán line ( above sea level), where astrodynamics must take over from aerodynamics in order to maintain flight. Due to the low cost of GPS and communications equipment, high-altitude ballo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range. Significant events *The first atomic bomb (code named Trinity) was test detonated at Trinity Site near the northern boundary of the range on 16 July 1945, seven days after the White Sands Proving Ground was established. *After the conclusion of World War II, 100 long-range German V-2 rockets that were captured by U.S. military troops were brought to WSMR. Of these, 67 were test-fired between 1946 and 1951 from the White Sands V-2 Launching Site. (This was followed by the testing of American rockets, which continues to this day, along with testing other technologies.) *NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia landed on the Northrop Strip at WSMR on 30 March 1982 as the conclusion to mission STS-3. This was the only ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-fuel Rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persians, Mongols, and Indians as early as the 13th century. All rockets used some form of solid or powdered propellant up until the 20th century, when liquid-propellant rockets offered more efficient and controllable alternatives. Solid rockets are still used today in military armaments worldwide, model rockets, solid rocket boosters and on larger applications for their simplicity and reliability. Since solid-fuel rockets can remain in storage for an extended period without much propellant degradation and because they almost always launch reliably, they have been frequently used in military applications such as missiles. The lower performance of solid propellants (as compared to liquids) does not favor their use as primary propulsion in mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
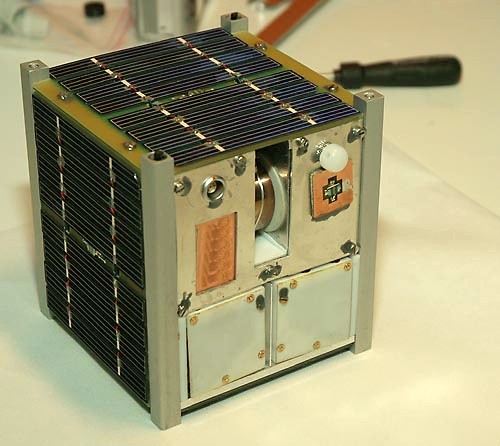
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purposes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Science And Technology Corporation
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)