|
Kayra
Kayra or Kaira (Old Turkic: 𐰴𐰖𐰺𐰀) is creator god in Turkic mythology. He is the god who planted the tree of life called ''Ulukayın''. He is the supreme god of the Tatars and the Son of the sky deity (Gök Tengri). This son, Kara Han (the black king or ruler of the land – Kara may mean land, earth, black or in a sense strong, powerful), left his father's home in the heaven and went to live in the underworld. On occasion, identified as Kara-Khan (black king), he was the primordial god and his father was the ancordial god called Tengri. Etymology The name of this deity is found in several forms, as is that of his opponent. "Kayra-Khan" may be translated as "merciful king", while the form "Kara Han" signifies "black king". For this reason, authority on Turkic Mythology Deniz Karakurt, considers Kara-Han and Kayra-Han to be two different deities.Türk Söylence Sözlüğü (Turkic Mythology Dictionary), Deniz Karakurt, (OTRS: CC BY-SA 3.0) Furthermore, the Turkish word ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Turkic Mythology
Turkic mythology refers to myths and legends told by the Turkic people. It features Tengrist and Shamanist strata of belief along with many other social and cultural constructs related to the nomadic and warrior way of life of Turkic and Mongol peoples in ancient times. Turkic mythology shares numerous points in common with Mongol mythology. Turkic mythology has also been influenced by other local Asiatic and Eurasian mythologies. For example, in Tatar mythology elements of Finnic and Indo-European mythologies co-exist. Beings from Tatar mythology include Äbädä, Alara, Şüräle, Şekä, Pitsen, Tulpar, and Zilant. The ancient Turks apparently practised all the then-current major religions in Inner Asia, such as Tibetan Buddhism, Nestorian Christianity, Judaism, and Manichaeism, before the majority's conversion to Islam filtered through the mediation of Persian and Central Asian culture, as well as through the preaching of Sufi Muslim wandering ascetics and myst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
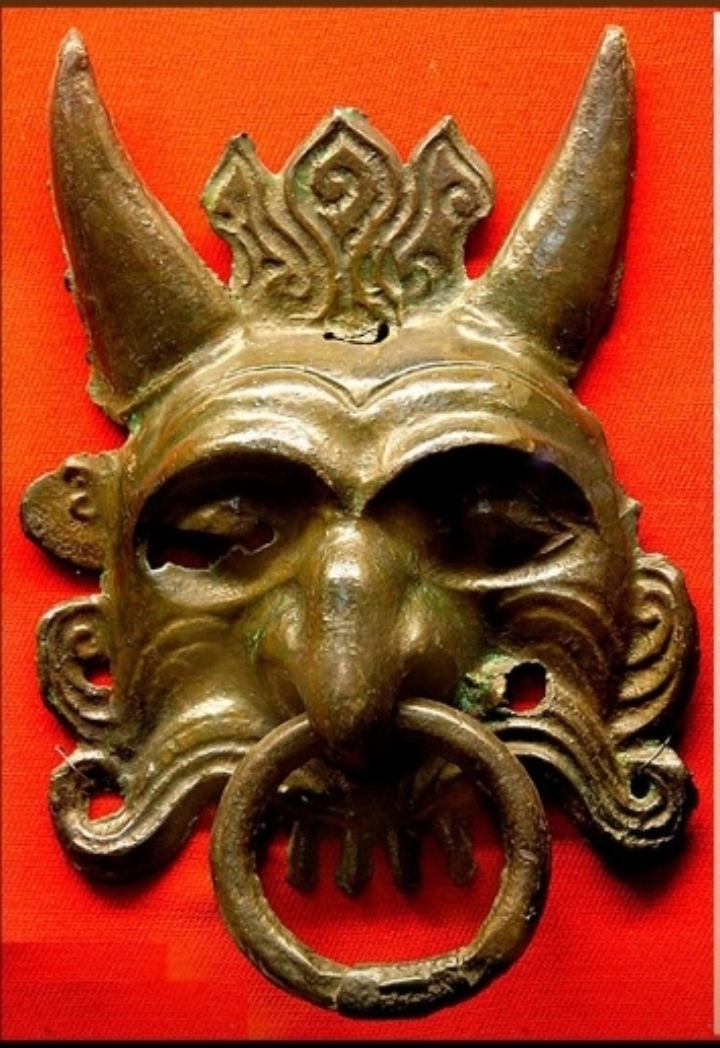 |
Erlik
Erlik, Erlig, Erlik Khan, Erleg or Yerleg (Hungarian mythology equivalent to ''Ördög'') is the god of death and the underworld, sometimes referred to as ''Tamag'' (hell) in Turkic mythology. ''Er'' (or ''yer'') means ''Earth'', in the depths of which Erlik lives in. From the underworld, Erlik brings forth death, plague and evil spirits to torment humans and take their souls into his realm. Since Tengrism is not based on a written corpus but encompasses the experienced spiritual life of Turkic people, there are no unanimous beliefs among all Turkic people. Legends In the Turkic mythology, Erlik was involved in the creation of humanity.Çoban, Ramazan Volkan. Türk Mitolojisinde Kötülük Tanrısı Erlik'in İnanıştaki Yeri, Tasviri ve Kökeni (Turkish)' He slew the messenger-god, Maidere/Maydere, and is a teacher of sin. He is sometimes represented by a totemic bear. In Turkic mythology, Erlik was the deity of evil, darkness, lord of the lower world and judge of the dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ak Ana
Ak Ana (Ağ Ana or Ak Ene), the "Holy Mother", is the primordial creator-goddess of Turkic people and the Khanty and Mansi peoples of Siberia. She is also known as the goddess of the water. She was the consort and daughter of Kayra Han. Water had been created earlier than Earth. Therefore, she was believed to be the elder sister of Earth. The beginning of the Earth emanated from Water. In ancient Turkic beliefs, Tengri Tengri ( zh, 騰格里; otk, 𐰚𐰇𐰚:𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, Kök Teŋri/Teŋiri, lit=Blue Heaven; Old Uyghur: ''tängri''; Middle Turkic: تآنغرِ; ky, теңир; tr, Tanrı; az, Tanrı; bg, Тангра; Proto-Turkic *''teŋri / * ... (God) Kaira Khan is a pure, white goose that flies constantly over an endless expanse of water (time). But before Ak-Ana appears to urge Kaira Khan to create, he experiences a disturbance of his calm. From the bottom of the Water a "sacred duck" Lura lifted the sand, clay and silt, from which the Earth was created. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Koyash
Koyash (Orkhon: 𐰸𐰆𐰖𐰽𐰴) is the god of sun in Turkic mythology. Kök Tengri created the earth with rays of sun light, thus, Koyash took part in the creation of Earth. Solar rays are also considered to be "strings" between the Sun and the spirits of plants, animals and humans. Turks who worship Koyash turn towards the sunrise when praying. Koyash is the son of Kayra and the Earth Goddess. The power and vital force of the Sun God, making it a priority to bow to him each morning as he rises. Solar rays are strings that link the spirits of plants to heaven, and considered a medium for transmitting Tengri into infants. Koyash is often depicted as a fiery bird or a winged horse. These images are often used to adorn things such as ceramic pots and earrings in ancient times. The sun god Koyash can make "solar strands" from his hands capable of ensnaring and burning his victims. To the Altai people, the Sun represented light, warmth, and growth. This made the sun deity very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ülgen
Bai-Ülgen or Ülgen (Old Turkic: Bey Ülgen; also spelled Bai-Ulgen, Bai-Ülgen, Bay-Ulgan, Bay-Ulgen, or Bay-Ülgen; Khakas, Shor and alt, Ӱлген; mn, Үлгэн; russian: Ульге́нь) is a Turkic and Mongolian creator-deity, usually distinct from Tengri but sometimes identified with him in the same manner as Helios and Apollo. His name is from Old Turkic ''bay'', "rich", and ''ülgen'', "magnificent". Ülgen is believed to be without either beginning or end. Features In Turkic and Mongolian mythology, the birch tree, regarded as a cosmic axis between earth and sky, was regarded as sacred to him, as was the horse (horse-sacrifice was a part of his worship). Ülgen symbolizes goodness, welfare, abundance, plentiness of food, water, etc. Furthermore, he created earth, heaven and all living beings. In addition, he controls the atmospheric events and movements of stars. He creates land for people to live on, the heads of both humans and animals and the rainbow. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Ay Dede
Ay Ata ( Old Turkic: 𐰖:𐱃𐰀) is one of the mythological entities in Turkic mythology and Tengrism. In English, the meanings are: Ay Ata: ''Father Moon'', Ay Dede: ''Grandfather Moon'' and Ay Tanrı: ''The Moon God''. In Turkic languages * Tuvan: ''Ай Ата'' * Uzbek: ''Oy Ota'' * Tatar: ''Ай Әти / Ата'' or ''Ay Ata'' *Kazakh: ''Ай Ата'' * Chuvash: ''Уйăх Атте'' or ''Уйӑх Ашшӗ'' * Bashkort: ''Ай Атай'' * Sakha: ''Ый Аҕа'' *Turkmen: ''Aý Ata'' * Uyghur: ''ئاي ئاتا'' *Turkish: ''Ay Ata'' or ''Ay Tanrı'' or ''Ay Dede'' *Kyrgyz: ''Ай Ата'' *Altai: ''Ай Ада'' * Khakas: ''Ай Аба'' or ''Ай Ада'' *Balkar: ''Ай Ата'' Description According to the mythology, he is a moon god, and he has been living in sixth floor of the sky with Gun Ana ( tr, Gün Ana), the sun goddess, who he is coupled with. While Gün Ana is symbol of warmness and hotness, Ay Dede is the symbol of cold. In Turkey, he is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.jpg) |
Tengri
Tengri ( zh, 騰格里; otk, 𐰚𐰇𐰚:𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, Kök Teŋri/Teŋiri, lit=Blue Heaven; Old Uyghur: ''tängri''; Middle Turkic: تآنغرِ; ky, теңир; tr, Tanrı; az, Tanrı; bg, Тангра; Proto-Turkic *''teŋri / *taŋrɨ''; Mongolian script: , ''T'ngri''; Modern Mongolian: Тэнгэр, ''Tenger''; Uyghur: تەڭرى ''tengri'' ) is the All-Encompassing God of Heaven in the traditional Turko-Mongolian religious beliefs. It is also one of the names for the primary chief deity of the early Turkic and Mongolic peoples. Worship of Tengri is Tengrism. The core beings in Tengrism are the Heavenly-Father (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) and the Earth Mother ( Eje/Gazar Eej). It involves shamanism, animism, totemism and ancestor worship. Name The oldest form of the name is recorded in Chinese annals from the 4th century BC, describing the beliefs of the Xiongnu. It takes the form 撑犁/''Cheng-li'', which is hypothesized to be a Chinese transcription of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
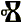 |
Yer Tanrı
A yer is either of two letters in Cyrillic alphabets, ъ (ѥръ, ''jerŭ'') and ь (ѥрь, ''jerĭ''). The Glagolitic alphabet used, as respective counterparts, the letters (Ⱏ) and (Ⱐ). They originally represented phonemically the "ultra-short" vowels in Slavic languages, including Old Church Slavonic, and are collectively known as the yers. In all modern Slavic languages, they either evolved into various "full" vowels or disappeared, in some cases causing the palatalization of adjacent consonants. The only Slavic language that still uses "ъ" as a vowel sign (pronounced /ɤ/) is Bulgarian, but in many cases, it corresponds to an earlier ѫ (big yus), originally pronounced /õ/, used in pre 1945 Bulgarian orthography. Many languages that use the Cyrillic alphabet have kept one or more of the yers to serve specific orthographic functions. The back yer (Ъ, ъ, italics ) of the Cyrillic script, also spelled ''jer'' or ''er'', is known as the ''hard sign'' in the mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Umay
Umay (also known as Umai; otk, 𐰆𐰢𐰖; kk, Ұмай ана, ''Umay ana''; ky, Умай эне, ''Umay ene''; russian: Ума́й / Ымай, ''Umáj / Ymaj'', tr, Umay (Ana)) is the goddess of fertility in Turkic mythology and Tengriism and as such related to women, mothers and children. Umay resembles earth-mother goddesses found in various other world religions. Etymology In Turkic mythology, earth was considered a "mother" symbolically. The Turkic root ''umāy'' originally meant 'placenta, afterbirth', and this word was used as the name for the goddess whose function was to look after women and children, possibly because the placenta was thought to have magic qualities. In Mongolian, ''Umai'' means 'womb' or 'uterus'. In Old Turkic and modern-day Turkmen, the word “eje” means 'mother', in Mongolian, "eje" or "eej" literally means "mother" as well. Goddess of Children The name appeared in the 8th-century inscription of Kul Tigin in the phrase ''Umay teg ö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Old Turkic
Old Turkic (also East Old Turkic, Orkhon Turkic language, Old Uyghur) is the earliest attested form of the Turkic languages, found in Göktürk and Uyghur Khaganate inscriptions dating from about the eighth to the 13th century. It is the oldest attested member of the Siberian Turkic branch of Turkic, which is extant in the modern Western Yugur language. It is not the ancestor of the Uyghur language; the contemporaneous ancestor of Uyghur is called Middle Turkic, later Chagatai or Turki. Old Turkic is attested in a number of scripts, including the Old Turkic script, the Old Uyghur alphabet (a form of the Sogdian alphabet), the Brahmi script, and the Manichaean script. Old Turkic often refers not to a single language, but collectively to the closely related and mutually intelligible stages of various Common Turkic languages spoken during the late first millennium. Sources The sources of Old Turkic are divided into two corpora: *the 8th to 10th century Orkhon inscri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |