|
Kaunas Prison
Kaunas Prison ( lt, Kauno tardymo izoliatorius) is a prison in the center of Kaunas, second largest city of Lithuania. As of 2007, it houses approximately 300 prisoners and employs around 230 prison guards. Most prisoners are there under temporary arrest awaiting court decisions or transfers to other detention facilities. History The Kaunas Prison was completed in 1864, just after the January Uprising during the times of the Russian Empire. At the time it was a modern prison in the whole region. It had 300 places for prisoners, a chapel, administrative-household premises, and apartments for employees were planned. But later there the number of places for prisoners grew up to 550. Kaunas Prison was seen far in environs of Kaunas center and aroused terror in everybody. Sometimes it was even called “Kaunas Bastille”. During the period of 1905 Revolution, the prison was overcrowded with political prisoners. The branch of Kaunas Prison was established in the Ninth Fort of Kaunas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kauno Kalejimas 2006 07 16
Kaunas (; ; also see #Etymology, other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Trakai Voivodeship, Trakai Palatinate since 1413. In the Russian Empire, it was the capital of the Kovno Governorate, Kaunas Governorate from 1843 to 1915. During the interwar period, it served as the temporary capital of Lithuania, when Vilnius was Polish–Lithuanian War, seized and controlled by Second Polish Republic, Poland between 1920 and 1939. During that period Kaunas was celebrated for its rich cultural and academic life, fashion, construction of countless Art Deco and Lithuanian National Romanticism architectural-style buildings as well as popular furniture, the interior design of the time, and a widespread café culture. The city interwar architecture is regarded as among the fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michał Elwiro Andriolli
Michał Elwiro Andriolli ( lt, Mykolas Elvyras Andriolis, it, Elviro Michele Andriolli; 2 November 1836, in Vilnius 23 August 1893, in Nałęczów) was a Polish illustrator, painter and architect of Italian descent. He is notable for his illustrations to Mickiewicz's '' Pan Tadeusz'', as well as a distinctive style of villas built outside Warsaw. He was probably most well known for his architecture – Świdermajer. This was a regional architectural style common in the Otwock, Poland region. These structures were wooden in construction and were popularized from the turn of the 19th and 20th centuries. Its creator was Michał Elwiro Andriolli. It is characterized by gazebos and decorations above the windows, some of the houses also had turrets. Pine trees were planted together with the buildings as part of the composition. Life Andriolli was born on 2 November 1836 in Wilno (modern Vilnius), then part of the Russian Empire. He was the son of Francesco Andriolli, an Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1864 Establishments In The Russian Empire
Events January–March * January 13 – American songwriter Stephen Foster ("Oh! Susanna", "Old Folks at Home") dies aged 37 in New York City, leaving a scrap of paper reading "Dear friends and gentle hearts". His parlor song " Beautiful Dreamer" is published in March. * January 16 – Denmark rejects an Austrian-Prussian ultimatum to repeal the Danish Constitution, which says that Schleswig-Holstein is part of Denmark. * January 21 – New Zealand Wars: The Tauranga campaign begins. * February – John Wisden publishes '' The Cricketer's Almanack for the year 1864'' in England; it will go on to become the major annual cricket reference publication. * February 1 – Danish-Prussian War (Second Schleswig War): 57,000 Austrian and Prussian troops cross the Eider River into Denmark. * February 15 – Heineken brewery founded in Netherlands. * February 17 – American Civil War: The tiny Confederate hand-propelled submarine ''H. L. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antanas Sniečkus
Antanas Sniečkus ( – 22 January 1974) was a Lithuanian communist politician who served as the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Lithuania from 15 August 1940 to 22 January 1974. Biography Sniečkus was born in 1903, in the village of Būbleliai, near Šakiai. During the First World War, his family fled to Russia where he observed the Russian revolution of 1917. In 1919, his family returned to Lithuania; by 1920 he was already a member of the Bolshevik Party. In the same year, he was arrested for anti-government activities. He was released from prison on bail, but fled to Moscow, and became an agent of the Comintern. In Moscow, he earned the trust of Zigmas Angarietis and Vincas Mickevičius-Kapsukas, and became a member of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Lithuania. In 1926, the Comintern sent Sniečkus to Lithuania to replace the recently executed Karolis Požėla as head of the banned and underground Communist Party of Lithuania. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazys Skučas
Kazys Skučas (3 March 1894 in Mauručiai, Marijampolė district – 30 July 1941 in the Butyrka prison) was a Lithuanian politician and General of the Lithuanian Army. Skučas was the last Minister of the Interior of independent Lithuania. He was a target of anti-Lithuanian Soviet propaganda in the days leading to the 1940 Soviet ultimatum and occupation of Lithuania. Right after the Red Army invaded Lithuania on 15 June 1940, Skučas was directed to leave the country by the then-President Antanas Smetona but was arrested at the border several days later by the then acting Lithuanian President Antanas Merkys and handed over to the Russians, transported to Moscow, and executed in 1941. Early life and career After graduation from the Veiveriai Pedagogical Seminary in 1912, Skučas worked as a teacher for a few years. He then enrolled to the Pedagogical Institute of Petrograd. However, in 1915 he was drafted into the Imperial Russian Army and served in the Romanian front with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Army
The Lithuanian Armed Forces () are the military of Lithuania. The Lithuanian Armed Forces consist of the Lithuanian Land Forces, the Lithuanian Naval Force and the Lithuanian Air Force. In wartime, the Lithuanian State Border Guard Service (which is under the supervision of the Ministry of the Interior in peacetime) becomes part of the Lithuanian Armed Forces. A special security department handles VIP protection and communications security. The purpose of the Lithuanian Armed Forces are to be the principal deterrent against any security threat to the nation. Lithuania's defence system is based on the concept of "total and unconditional defence" mandated by Lithuania's ''National Security Strategy''. The goal of Lithuania's defence policy is to prepare their society for general defence and to integrate Lithuania into Western security and defence structures. The Ministry of National Defence is responsible for combat forces, search and rescue, and intelligence operations. Male ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustinas Povilaitis
Augustinas Povilaitis (24 February 1900 in Pašventys, Jurbarkas district – 12 July 1941 in Moscow) was a captain of the Lithuanian Army and Director of the State Security Department of Lithuania. Together with Minister of the Interior Kazys Skučas, Povilaitis was a target of anti-Lithuanian Soviet propaganda in the days leading to the 1940 Soviet ultimatum to Lithuania, 1940 Soviet ultimatum and occupation of Lithuania. Directly after the Red Army invaded Lithuania on 15 June 1940, Povilaitis was arrested and transported to Moscow; he was executed in 1941. In 2006 he was awarded the Order of the Cross of Vytis. Early life and career In 1919, Povilaitis volunteered for the Lithuanian Army and participated in the Lithuanian Wars of Independence with the Bermontians. In the army he rose to the rank of a captain. From 1920 to 1931 he worked as on officer in the security and criminal police. As a volunteer in the army, Povilaitis received of land in Giedriai village and established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vytautas Petrulis
Vytautas Petrulis (born February 3, 1890 in Katelišės, near Vabalninkas; executed in 1942, near Uchta, RSFSR) was a Lithuanian politician, one of the main figures in the Lithuanian Christian Democratic Party, and an accountant. He is often nicknamed "the father of the Litas" as it was during his term as Minister of Finance that the Lithuanian litas was introduced. In summer 1918, Petrulis became a member of the Council of Lithuania. Later he was acting Minister of Finance in the 3rd Cabinet of Lithuania. He was Minister of Finance, Trade and Industry in the 7th, 8th, and 9th cabinets. In the 10th cabinet he was appointed as Minister of Finance. He was Prime Minister of Lithuania in the 11th Cabinet, also acting as Minister of Finance. He was the speaker of Seimas from 1925 to 1926. On July 11, 1940 he was arrested by the Soviets and sent to the Kaunas Prison. In 1942, he was executed by firing squad Execution by firing squad, in the past sometimes called fusillading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priesthood (Catholic Church)
The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned ("ordained") with the Holy orders of the Catholic Church. Technically, bishops are a priestly order as well; however, in layman's terms ''priest'' refers only to presbyters and pastors (parish priests). The church's doctrine also sometimes refers to all baptised (lay) members as the "common priesthood", which can be confused with the ministerial priesthood of the consecrated clergy. The church has different rules for priests in the Latin Church–the largest Catholic particular church–and in the 23 Eastern Catholic Churches. Notably, priests in the Latin Church must take a vow of celibacy, whereas most Eastern Catholic Churches permit married men to be ordained. Deacons are male and usually belong to the diocesan clergy, but, unlike almost all Latin Church (Western Catholic) priests and all bishops from Eastern or Western Catholicism, they may marry as laymen before their ordination as cler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antanas Mackevičius
Antanas Mackevičius ( pl, Antoni Mackiewicz; 26 June 1828 – 28 December 1863) was a Lithuanian Roman Catholic priest The priesthood is the office of the ministers of religion, who have been commissioned ("ordained") with the Holy orders of the Catholic Church. Technically, bishops are a priestly order as well; however, in layman's terms ''priest'' refers only ... who was one of the leaders and initiators of the Uprising of 1863 in Lithuania. Mackevičius was born to a family of Petty nobility, petty nobles. He studied in Kyiv and Varniai. He became involved in the uprising conspiracy. After the outbreak of the January Uprising in Warsaw on January 22, he announced the manifesto of the Polish National Government (January Uprising), National Government on March 8 and formed a unit in Paberžė, Kėdainiai, Paberžė, which consisted mainly of the local Lithuanian peasants that enthusiastically joined his units. Mackevičius, dressed in the priest's Cassock coat himself, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated as VChK ( rus, ВЧК, p=vɛ tɕe ˈka), and commonly known as Cheka ( rus, Чека, p=tɕɪˈka; from the initialism russian: ЧК, ChK, label=none), was the first of a succession of Soviet secret-police organizations. Established on December 5 (Old Style) 1917 by the Sovnarkom, it came under the leadership of Felix Dzerzhinsky, a Polish aristocrat-turned-Bolshevik. By late 1918, hundreds of Cheka committees had sprung up in the RSFSR at the oblast, guberniya, raion, uyezd, and volost levels. Ostensibly set up to protect the revolution from reactionary forces, i.e., "class enemies" such as the bourgeoisie and members of the clergy, it soon became the repression tool against all political opponents of the communist regime. At the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Dzerzhinsky
Felix Edmundovich Dzerzhinsky ( pl, Feliks Dzierżyński ; russian: Фе́ликс Эдму́ндович Дзержи́нский; – 20 July 1926), nicknamed "Iron Felix", was a Bolshevik revolutionary and official, born into Poland, Polish nobility. From 1917 until his death in 1926, Dzerzhinsky led the first two Soviet National Security, state-security organizations, the Cheka and the OGPU, establishing a Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, secret police for the Russian Revolution, post-revolutionary Sovnarkom, Soviet regime. He was one of the architects of the Red Terror and decossackization. Early life Felix Dzerzhinsky was born on 11 September 1877 to ethnically Poles, Polish parents of noble descent, at the Dzerzhinovo family estate, about from the small town of Ivyanets in the Minsk Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Belarus). In the Russian Empire, his family was of a type known as "Uradel, column-listed nobility" (russian: столбовое двор ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
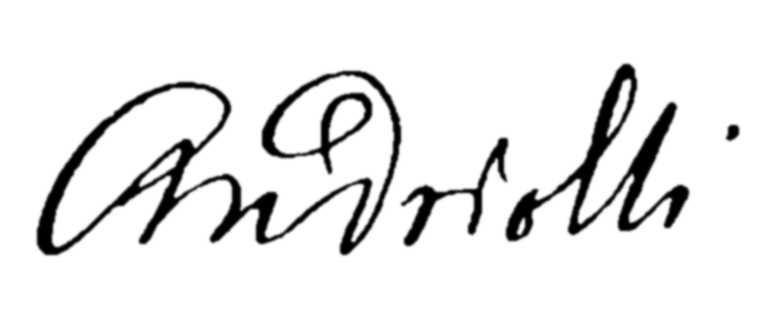


.jpg)



