|
Katepánō
The ''katepánō'' ( el, κατεπάνω, lit. "[the one] placed at the top", or " the topmost") was a senior Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, military rank and office. The word was Latinized as ''capetanus/catepan'', and its meaning seems to have merged with that of the Italian "capitaneus" (which derives from the Latin word "caput", meaning head). This hybridized term gave rise to the English language term ''wikt:captain, captain'' and its equivalents in other languages (wikt:capitan, Capitan, wikt:kapitan, Kapitan, Kapitän, El Capitán, Il Capitano, Kapudan Pasha etc.) History The ''katepáno'' first appears in the 9th century, when it was used in the generic sense of "the one in charge" by two officials: the head of the ''basilikoi anthrōpoi'' ("imperial men"), a class of low-level court functionaries, and the head of the Mardaites marine detachments of the Byzantine navy, Byzantine naval theme of the Cibyrrhaeots in southern Asia Minor. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Aristocracy And Bureaucracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies and theocratic Christian-Eastern concepts had gained power in the eastern Greek-speaking Mediterranean due to the intervention of Important religious figures there such as Eusebius of Caesarea and Origen of Alexandria who had been key to the constant Christianized world of late antiquity. By the 6th century they had already influenced the definitive power of the monarch as the representative of God on earth and his kingdom as an imitation of God's holy realm. The Byzantine empire was a monarchic theocracy, adopting, following and applying the Hellenistic political systems and philosophies. The monarch was the incarnation of the law '' nomos empsychos'', and his power was immeasurable and divine in origin. He was the ultimate benefactor, carer and saviour of his people, '' Evergétis'', '' Philanthrōpía'' and '' Sōtēr''. They in turn were his '' paroikoi'' (subjects). He was the sole administrator a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire Themes 1025-en
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrian people, Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history, written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
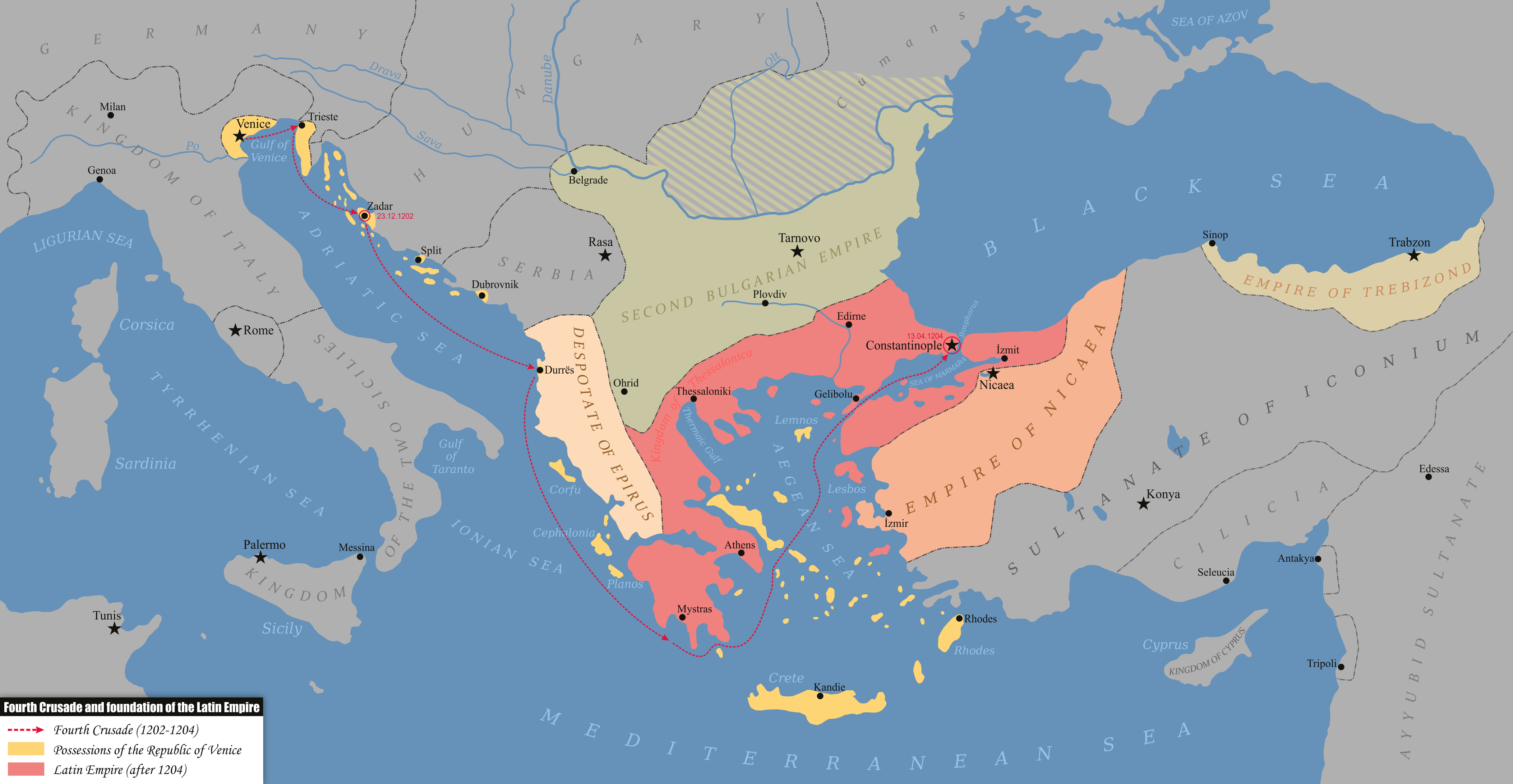
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaiologan Period
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by the Palaiologos dynasty in the period between 1261 and 1453, from the restoration of Byzantine rule to Constantinople by the usurper Michael VIII Palaiologos following its recapture from the Latin Empire, founded after the Fourth Crusade (1204), up to the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire. Together with the preceding Nicaean Empire and the contemporary '' Frankokratia'', this period is known as the late Byzantine Empire. From the start, the regime faced numerous problems.Mango, p. 255 The Turks of Asia Minor had begun conducting raids and expanding into Byzantine territory in Asia Minor by 1263, just two years after the enthronment of the first Palaiologos emperor Michael VIII. Anatolia, which had formed the very heart of the shrinking empire, was systematically lost to numerous Turkic '' ghazis'', whose raids evolved into conquering expeditions inspired by Islamic zeal, the prospect of economic gain, and the desire to seek refuge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komnenian Period
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by emperors of the Komnenos dynasty for a period of 104 years, from 1081 to about 1185. The ''Komnenian'' (also spelled ''Comnenian'') period comprises the reigns of five emperors, Alexios I, John II, Manuel I, Alexios II and Andronikos I. It was a period of sustained, though ultimately incomplete, restoration of the military, territorial, economic and political position of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantium under the Komnenoi played a key role in the history of the Crusades in the Holy Land, while also exerting enormous cultural and political influence in Europe, the Near East, and the lands around the Mediterranean Sea. The Komnenian emperors, particularly John and Manuel, exerted great influence over the Crusader states of Outremer, whilst Alexios I played a key role in the course of the First Crusade, which he helped bring about. Moreover, it was during the Komnenian period that contact between Byzantium and the 'Latin' Christian West, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
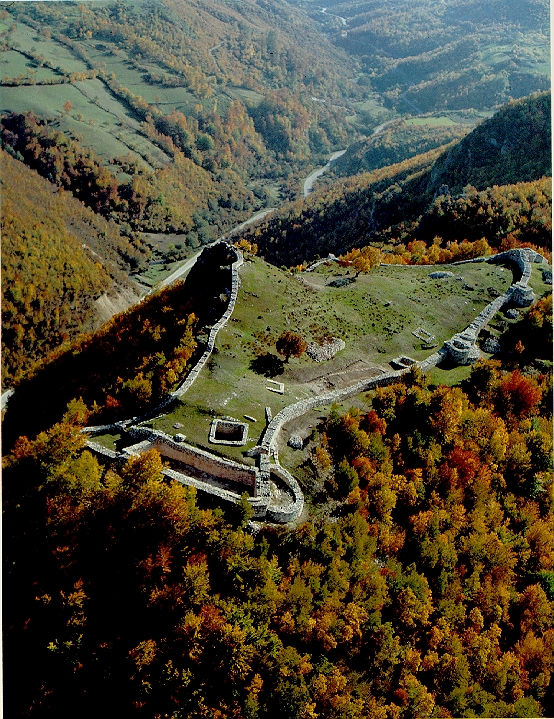
Catepanate Of Ras
The Catepanate of Ras (Byzantine Greek: ) was a province (catepanate) of the Byzantine Empire, established around 971 in central regions of early medieval Serbia, during the rule of Byzantine Emperor John Tzimiskes (969–976). The catepanate was named after the fortified town of Ras, eponymous for the historical region of Raška ( la, Rascia). The province was short-lived, and collapsed soon after 976, following the Byzantine retreat from the region after the restoration of the Bulgarian Empire. History In the middle of the 6th century, during the reign of Byzantine emperor Justinian I (d. 565), a fortress of ''Arsa'' ( gr, Ἄρσα) in the province of Dardania was refortified, as attested by historian Procopius. At the beginning of the 7th century, Byzantine rule collapsed, and the region was settled by Serbs. Up to the middle of the 10th century, the fortress of Ras was a stronghold of the early medieval Principality of Serbia, as attested by the Byzantine emperor and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catepanate Of Serbia
The Catepanate of Ras (Byzantine Greek: ) was a province (catepanate) of the Byzantine Empire, established around 971 in central regions of early medieval Serbia, during the rule of Byzantine Emperor John Tzimiskes (969–976). The catepanate was named after the fortified town of Ras, eponymous for the historical region of Raška ( la, Rascia). The province was short-lived, and collapsed soon after 976, following the Byzantine retreat from the region after the restoration of the Bulgarian Empire. History In the middle of the 6th century, during the reign of Byzantine emperor Justinian I (d. 565), a fortress of ''Arsa'' ( gr, Ἄρσα) in the province of Dardania was refortified, as attested by historian Procopius. At the beginning of the 7th century, Byzantine rule collapsed, and the region was settled by Serbs. Up to the middle of the 10th century, the fortress of Ras was a stronghold of the early medieval Principality of Serbia, as attested by the Byzantine emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars
The Byzantine–Bulgarian wars were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Empire to the southwest after 680 AD. The Byzantines and Bulgarians continued to clash over the next century with variable success, until the Bulgarians, led by Krum of Bulgaria, Krum, inflicted a series of crushing defeats on the Byzantines. After Krum died in 814, his son Omurtag negotiated a thirty-year peace treaty. Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I had multiple successful campaigns against the Byzantines during his rule from 893 to 927. His son Peter I of Bulgaria, Peter I negotiated another long-lasting peace treaty. His rule was followed by a period of decline of the Bulgarian state. In 971 John I Tzimiskes, the Byzantine emperor, subjugated much of the weakening Bulgarian Empire by defeating Boris II of Bulgaria, Boris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escorial Taktikon
The ''Escorial Taktikon'' (other spellings: ''Escurial Taktikon'', ''Escorial Tacticon'', ''Escurial Tacticon''), also known as the ''Taktikon Oikonomides'' after Nicolas Oikonomides who first edited it, is a list of Byzantine offices, dignities, and titles composed in Constantinople during the 970s (971–975 or 975–979). The list contains, among many entries, the commanders (''strategoi'') of the Byzantine Empire's eastern frontier during the Byzantine-Arab Wars, as well as a series of judicial offices.: "It is also worth noting that the Escorial Taktikon of 975 lists a number of judicial offices––''thesmophylax'', ''kensor'', ''mystographos'', ''exaktor'', ''hypatos''––which must have been created in or soon after the reign of Romanos." References Sources * * * * 970s in the Byzantine Empire 10th-century books Byzantine literature Handbooks and manuals 10th century in the Byzantine Empire {{Byzantine-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catepanate Of Italy
The Catepanate (or Catapanate) of Italy ( el, ''Katepaníkion Italías'') was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 965 until 1071. At its greatest extent, it comprised mainland Italy south of a line drawn from Monte Gargano to the Gulf of Salerno. North of that line, Amalfi and Naples also maintained allegiance to Constantinople through the catepan. The Italian region of '' Capitanata'' derives its name from '' katepanikion''. History Following the fall of the Exarchate of Ravenna in 751, Byzantium had been absent from the affairs of southern Italy for almost a century, but the accession of Basil I (reigned 867–886) to the throne of Constantinople changed this: from 868 on, the imperial fleet and Byzantine diplomats were employed in an effort to secure the Adriatic Sea from Saracen raids, re-establish Byzantine dominance over Dalmatia, and extend Byzantine control once more over parts of Italy. As a result of these efforts, Otranto was taken from the Saracens in 873, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)