|
Karl Bormann
Karl Bormann (November 23, 1928 in Monheim am Rhein, Monheim, – August 17, 2015 in Langenfeld, Rhineland, Langenfeld) was a German historian of philosophy. His area of research was ancient and medieval philosophy, in particular the work of the catholic Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal Nicholas of Cusa. Biography Bormann spent his entire scientific career at the University of Cologne. After graduating from the state humanistic high school in Cologne-Mülheim in 1949, he studied classical philology and philosophy with the professors Josef Koch, Günther Jachmann and Josef Kroll and received his doctorate in 1955 with a dissertation on Philon's theory of ideas and logos, in which Bormann explained Philon's concept of the logos in critical examination of Harry Austryn Wolfson's interpretation. From 1954 to 1959, Bormann was a research associate for Josef Koch at the Thomas-Institut of the University of Cologne, then until 1965 an assistant at Paul Wilpert's Philosophical Sem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Philosophy
Western philosophy encompasses the philosophical thought and work of the Western world. Historically, the term refers to the philosophical thinking of Western culture, beginning with the ancient Greek philosophy of the pre-Socratics. The word ''philosophy'' itself originated from the Ancient Greek (φιλοσοφία), literally, "the love of wisdom" grc, φιλεῖν , "to love" and σοφία '' sophía'', "wisdom"). History Ancient The scope of ancient Western philosophy included the problems of philosophy as they are understood today; but it also included many other disciplines, such as pure mathematics and natural sciences such as physics, astronomy, and biology (Aristotle, for example, wrote on all of these topics). Pre-Socratics The pre-Socratic philosophers were interested in cosmology; the nature and origin of the universe, while rejecting mythical answers to such questions. They were specifically interested in the (the cause or first principle) of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
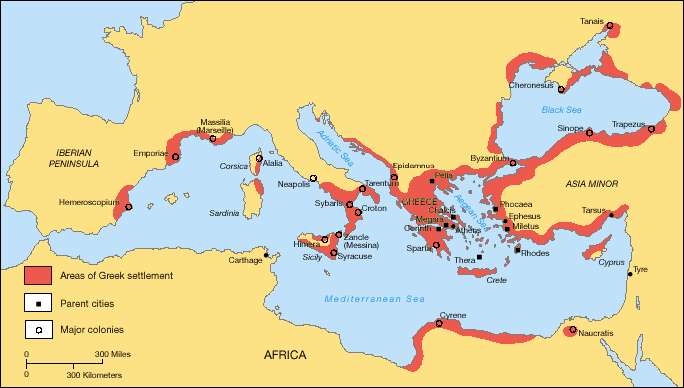
Pre-Socratic Philosophy
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of these early philosophers spanned the workings of the natural world as well as human society, ethics, and religion. They sought explanations based on natural law rather than the Divinity, actions of gods. Their work and writing has been almost entirely lost. Knowledge of their views comes from ''testimonia'', i.e. later authors' discussions of the work of pre-Socratics. Philosophy found fertile ground in the ancient Greek world because of the close ties with neighboring civilizations and the rise of autonomous civil entities, ''polis, poleis''. Pre-Socratic philosophy began in the 6th century BCE with the three Milesian school, Milesians: Thales, Anaximander, and Anaximenes of Miletus, Anaximenes. They all attributed the ''arche'' (a word that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato Pio-Clemetino Inv305
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar Server
An altar server is a lay assistant to a member of the clergy during a Christian liturgy. An altar server attends to supporting tasks at the altar such as fetching and carrying, ringing the altar bell, helps bring up the gifts, brings up the book, among other things. If young, the server is commonly called an altar boy or altar girl. In some Christian denominations, altar servers are known as acolytes. Latin Church While the function of altar server is commonly associated with children, it can be and is carried out by people of any age or dignity. A according to the ''General Instruction of the Roman Missal'', "Mass should not be celebrated without a minister, or at least one of the faithful, except for a just and reasonable cause." The term "acolyte" As in other churches, altar servers are sometimes called acolytes in the Latin Church. Pope Benedict XVI spoke of Saint Tarcisius as "presumably an acolyte, that is, an altar server". However, within the Latin Church, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dachau Concentration Camp
, , commandant = List of commandants , known for = , location = Upper Bavaria, Southern Germany , built by = Germany , operated by = ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) , original use = Political prison , construction = , in operation = March 1933 – April 1945 , gas chambers = , prisoner type = Political prisoners, Poles, Romani, Jews, homosexuals, Jehovah's Witnesses, Catholic priests, Communists , inmates = Over 188,000 (estimated) , killed = 41,500 (per Dachau website) , liberated by = U.S. Army , notable inmates = , notable books = , website = Dachau () was the first concentration camp built by Nazi Germany, opening on 22 March 1933. The camp was initially intended to intern Hitler's political opponents which consisted of: communists, social democrats, and other dissidents. It is located on the grounds of an abandoned munitions factory northeast of the medieval town of Dachau, about northwest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Boehm (resistance Fighter)
Franz Boehm (October 3, 1880 in Boleszyn – February 13, 1945 in Dachau concentration camp) was a Roman Catholic priest of the Archdiocese of Cologne, resistance fighter and martyr. Life Franz Boehm came from a German-Polish family of teachers. He spent his primary school years in the Rhineland. He was graduated from a secondary school in Mönchengladbach. After his philosophical and theological studies in Bonn, he was ordained a priest for the Archdiocese of Cologne in 1906. At his three chaplain positions in the Ruhr area, he was also active in the Polish pastoral care, as he speaks the Polish language. He also baptized in his mother tongue and not in Latin, as originally intended. He took up his first pastor's post in 1917 in St. Katharina in Düsseldorf. In 1923 he became a pastor in Sieglar. Resistance to National Socialism Supported by the mayor of Sieglar, the Gestapo repeatedly investigated Boehm and imposed numerous sanctions. In 1934 there were criminal proceedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heidelberg Academy Of Sciences And Humanities
The Heidelberg Academy of Sciences and Humanities (German: ''Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften''), established in 1909 in Heidelberg, Germany, is an assembly of scholars and scientists in the German state of Baden-Wuerttemberg. The Academy is a member of the Union of German Academies of Sciences and Humanities The Union of German Academies of Sciences and Humanities (German: Union der deutschen Akademien der Wissenschaften) is an umbrella organisation for eight German academies of sciences and humanities. The member academies are: *Berlin-Brandenburg Ac .... References External linksHeidelberg Academy of Sciences and Humanities website 1909 establishments in Germany Scientific organizations established in 1909 Union of German Academies of Sciences and Humanities Education in Heidelberg {{Germany-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry Austryn Wolfson
Harry Austryn Wolfson (November 2, 1887 – September 19, 1974) was an American scholar, philosopher, and historian at Harvard University, and the first chairman of a Judaic Studies Center in the United States. He is known for his seminal work on the Jewish philosopher Philo, but he also authored an astonishing variety of other works on Crescas, Maimonides, Averroes, Spinoza, the Kalam, the Church Fathers, and the foundations of Western religion. He collapsed the artificial barriers that isolated the study of Christian philosophy from Islamic philosophy and from Jewish philosophy . Being the first Judaica scholar to progress through an entire career at a top-tier university , in Wolfson is also represented the fulfillment of the goals of the 19th-century ''Wissenschaft des Judentums'' movement. Biography Wolfson was born to Sarah Savitsky and Max Mendel Wolfson in Astryna (Yiddish: Ostrin), Vilna Governorate (in present-day Shchuchyn district, Grodno Region, Belarus), and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal (Catholic Church)
A cardinal ( la, Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae cardinalis, literally 'cardinal of the Holy Roman Church') is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church. Cardinals are created by the ruling pope and typically hold the title for life. Collectively, they constitute the College of Cardinals. Their most solemn responsibility is to elect a new pope in a conclave, almost always from among themselves (with a few historical exceptions), when the Holy See is vacant. During the period between a pope's death or resignation and the election of his successor, the day-to-day governance of the Holy See is in the hands of the College of Cardinals. The right to participate in a conclave is limited to cardinals who have not reached the age of 80 years by the day the vacancy occurs. In addition, cardinals collectively participate in papal consistories (which generally take place annually), in which matters of importance to the Church are considered and new cardinals may be created. Cardina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas, OP (; it, Tommaso d'Aquino, lit=Thomas of Aquino; 1225 – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican friar and priest who was an influential philosopher, theologian and jurist in the tradition of scholasticism; he is known within the tradition as the , the , and the . The name ''Aquinas'' identifies his ancestral origins in the county of Aquino in present-day Lazio, Italy. Among other things, he was a prominent proponent of natural theology and the father of a school of thought (encompassing both theology and philosophy) known as Thomism. He argued that God is the source of both the light of natural reason and the light of faith. He has been described as "the most influential thinker of the medieval period" and "the greatest of the medieval philosopher-theologians". His influence on Western thought is considerable, and much of modern philosophy is derived from his ideas, particularly in the areas of ethics, natural law, metaphysics, and political theory. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |