|
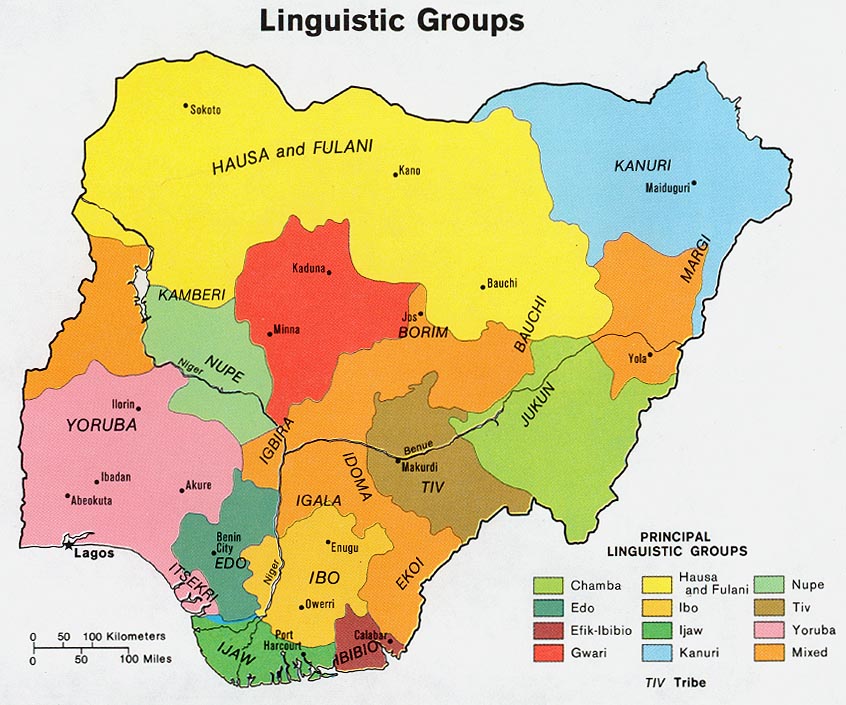
Kanuri Language
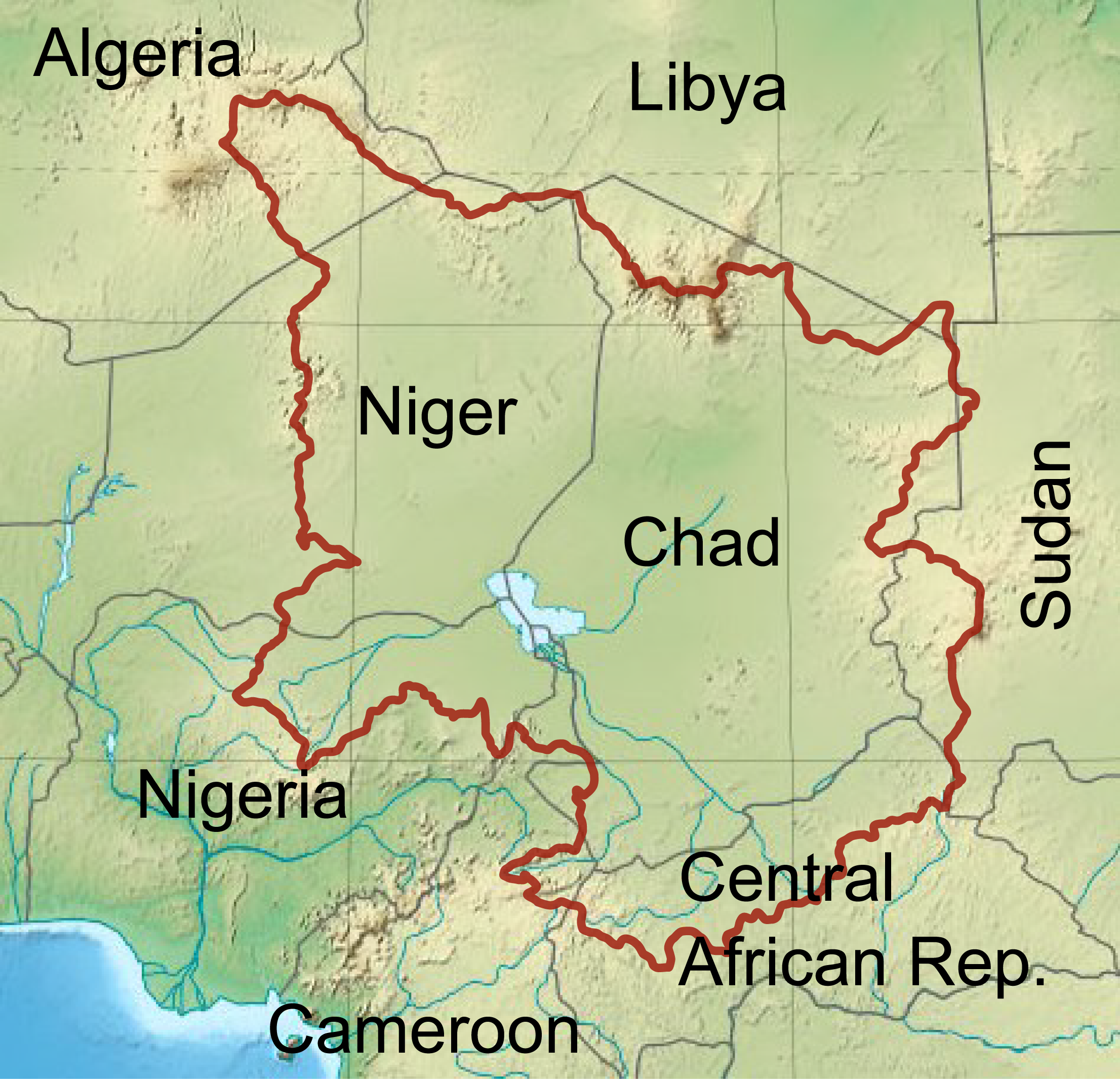
Kanuri () is a dialect continuum spoken in Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon, as well as in small minorities in southern Libya and by a diaspora in Sudan. Background At the turn of the 21st century, its two main dialects, Manga Kanuri and Yerwa Kanuri (also called Beriberi, which its speakers consider to be pejorative), were spoken by 9,700,000 people in Central Africa. It belongs to the Western Saharan subphylum of Nilo-Saharan. Kanuri is the language associated with the Kanem and Bornu empires that dominated the Lake Chad region for a thousand years. The basic word order of Kanuri sentences is subject–object–verb. It is typologically unusual in simultaneously having postpositions and post-nominal modifiers – for example, "Bintu's pot" would be expressed as ''nje Bintu-be'', "pot Bintu-of". Kanuri has three tones: high, low, and falling. It has an extensive system of consonantal lenition; for example, "they" + "have eaten" → "they have eaten". Traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. It covers an area of , and with a population of over 225 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising of States of Nigeria, 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where the capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Africa
Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Rwanda, and São Tomé and Príncipe are members of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS). Six of those states (the Central African Republic, Chad, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon) are also members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) and share a common currency, the Central African CFA franc. The African Development Bank defines Central Africa as the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon. Middle Africa is an analogous term used by the United Nations in its geoscheme for Africa. It includes the same countries as the African Development Bank's definiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumari Kanuri
Kanuri () is a dialect continuum spoken in Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon, as well as in small minorities in southern Libya and by a diaspora in Sudan. Background At the turn of the 21st century, its two main dialects, Manga Kanuri and Yerwa Kanuri (also called Beriberi, which its speakers consider to be pejorative), were spoken by 9,700,000 people in Central Africa. It belongs to the Western Saharan subphylum of Nilo-Saharan. Kanuri is the language associated with the Kanem and Bornu empires that dominated the Lake Chad region for a thousand years. The basic word order of Kanuri sentences is subject–object–verb. It is typologically unusual in simultaneously having postpositions and post-nominal modifiers – for example, "Bintu's pot" would be expressed as ''nje Bintu-be'', "pot Bintu-of". Kanuri has three tones: high, low, and falling. It has an extensive system of consonantal lenition; for example, "they" + "have eaten" → "they have eaten". Traditionally a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' isn't ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and autonyms, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chad Basin
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is roughly coterminous with the sedimentary basin of the same name, but extends further to the northeast and east. The basin spans eight countries, including most of Chad and a large part of Niger. The region has an ethnically diverse population of about 30 million people as of 2011, growing rapidly. A combination of dams, increased irrigation, climate change, and reduced rainfall are causing water shortages, contributing to terrorism and the rise of Boko Haram in the region. Lake Chad continues to shrink. Geology The geological basin, which is smaller than the drainage basin, is a Phanerozoic sedimentary basin formed during the plate divergence that opened the South Atlantic Ocean. The basin lies between the West African Craton and Congo Craton, and formed around the same time as the Benue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Language
Hausa (; /; Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologue estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa-speaking film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic language family. Geographic distribution Native speakers of Hausa, the Hausa people, are mostly found in southern Niger and northern Nigeria. The language is used as a lingua franca by n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Lingua francas have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th centuries. A world language – a language spoken internationally an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them more sonorous. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language at a particular point in time) and diachronically (as a language changes over time). Lenition can involve such changes as voicing a voiceless consonant, causing a consonant to relax occlusion, to lose its place of articulation (a phenomenon called ''debuccalization'', which turns a consonant into a glottal consonant like or ), or even causing a consonant to disappear entirely. An example of synchronic lenition is found in most varieties of American English, in the form of flapping: the of a word like ''wait'' is pronounced as the more sonorous in the related form ''waiting'' . Some varieties of Spanish show debuccalization of to at the end of a syllable, so that a word like "we are" is pronounced . An example of diachronic leniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postposition
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions (or broadly, in traditional grammar, simply prepositions), are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in'', ''under'', ''towards'', ''before'') or mark various semantic roles (''of'', ''for''). A preposition or postposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. A preposition comes before its complement; a postposition comes after its complement. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in'', ''under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as ''in England'', ''under the table'', ''of Jane'' – although there are a few exceptions including "ago" and "notwithstanding", as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead, or have both types. The phrase formed by a preposition or postposition together with its com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |