|
Kanellopoulos Institute Of Chemistry And Agriculture
The Kanellopoulos Institute of Chemistry and Agriculture (, ) is a former research institute in Piraeus, Greece, which operated between 1938 and 1984 in affiliation with the Drapetsona-based (). The Kanellopoulos Institute was a ''sui generis'' institution in Greece. It was the first of its kind to combine high-profile basic research, research with applications in the chemical industry, and dissemination of agrochemical advances to the Greek populace. History The idea for the creation of the Institute belonged to its nameshake, industrialist (1864–1936), one of the founders of AEEChPL. Construction commenced in 1936, as per the request and with the monetary sum Kanellopoulos bequeathed to the future Institute in his will. The institute was inaugurated in 1938, situated at the east side of the AEEChPL industrial complex in Drapetsona. The institute's activities quickly attracted attention within Greece as well as abroad, with distinguished researchers such as Georg-Maria S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piraeus
Piraeus ( ; el, Πειραιάς ; grc, Πειραιεύς ) is a port city within the Athens urban area ("Greater Athens"), in the Attica region of Greece. It is located southwest of Athens' city centre, along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf. The municipality of Piraeus and four other suburban municipalities form the regional unit of Piraeus, sometimes called the Greater Piraeus area, with a total population of 448,997. At the 2011 census, Piraeus had a population of 163,688 people, making it the fifth largest municipality in Greece2011 POPULATION AND HOUSING CENSUS, HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHORITY, http://www.statistics.gr/documents/20181/1215267/A1602_SAM01_DT_DC_00_2011_03_F_EN.pdf/cb10bb9f-6413-4129-b847-f1def334e05e and the second largest (after the municipality of Athens) within the Athens urban area. Piraeus has a long recorded history, dating back to ancient Greece. The city was founded in the early 5th century BC, when plans to make it the new port of Athens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials (oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, and minerals) into more than 70,000 different products. The plastics industry contains some overlap, as some chemical companies produce plastics as well as chemicals. Various professionals are involved in the chemical industry including chemical engineers, chemists and lab technicians. History Although chemicals were made and used throughout history, the birth of the heavy chemical industry (production of chemicals in large quantities for a variety of uses) coincided with the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution. Industrial Revolution One of the first chemicals to be produced in large amounts through industrial processes was sulfuric acid. In 1736 pharmacist Joshua Ward developed a process for its production that involved heating saltpeter, allowing the sulfur to oxidize and combine with water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pest (organism)
A pest is any animal or plant harmful to humans or human concerns. The term is particularly used for creatures that damage crops, livestock, and forestry or cause a nuisance to people, especially in their homes. Humans have modified the environment for their own purposes and are intolerant of other creatures occupying the same space when their activities impact adversely on human objectives. Thus, an elephant is unobjectionable in its natural habitat but a pest when it tramples crops. Some animals are disliked because they bite or sting; snake Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...s, wasps, ants, bed bugs, fleas and ticks belong in this category. Others enter the home; these include houseflies, which land on and contaminate food, beetles, which tunnel into the woodwor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathology
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungus, fungi, oomycetes, bacterium, bacteria, plant virus, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other Plant defense against herbivory, pests that affect plant health by eating Plant tissue, plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
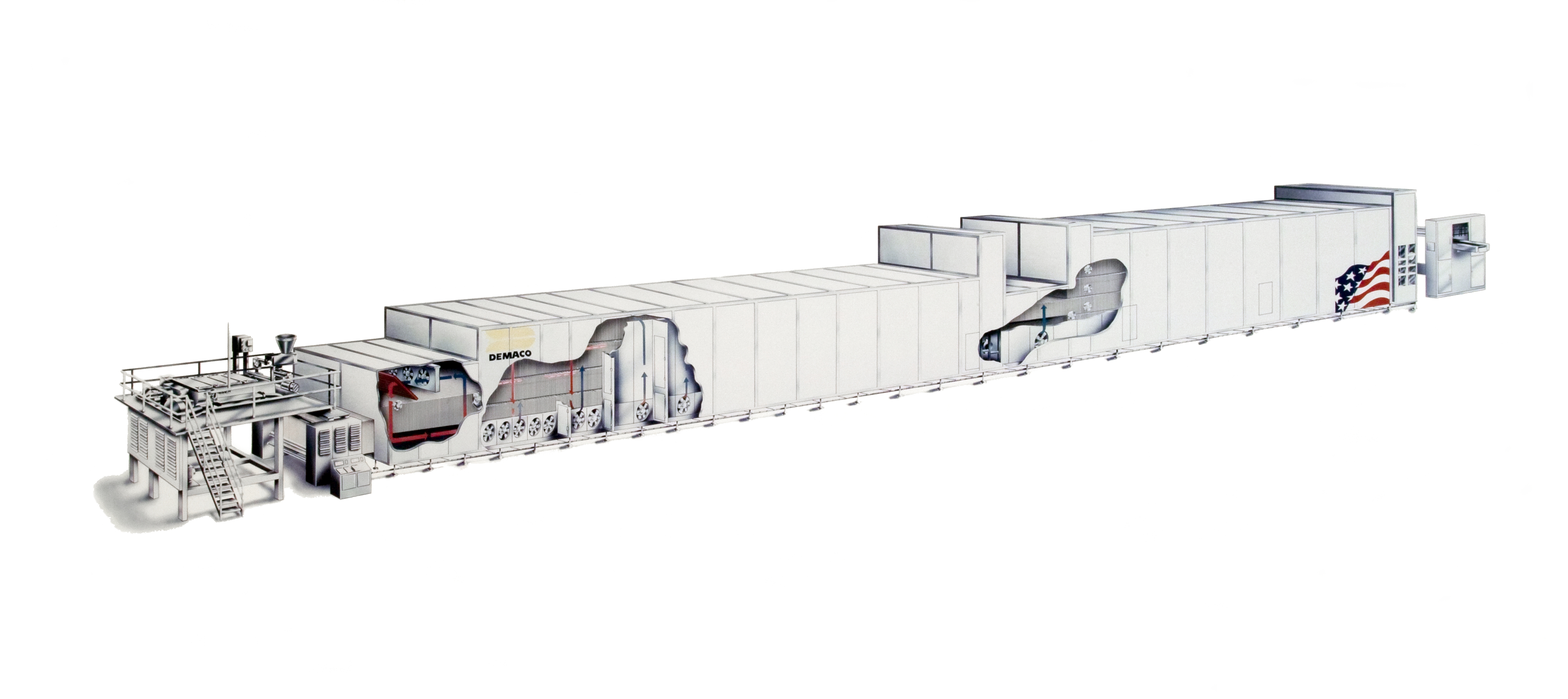
Continuous Production
Continuous production is a flow production method used to manufacture, produce, or process materials without interruption. Continuous production is called a continuous process or a continuous flow process because the materials, either dry bulk or fluids that are being processed are continuously in motion, undergoing chemical reactions or subject to mechanical or heat treatment. Continuous processing is contrasted with batch production. Continuous usually means operating 24 hours per day, seven days per week with infrequent maintenance shutdowns, such as semi-annual or annual. Some chemical plants can operate for more than one to two years without a shutdown. Blast furnaces can run from four to ten years without stopping. Common processes Some common continuous processes are the following: * Oil refining *Chemicals *Synthetic fibers *Fertilizers *Pulp and paper *Blast furnace (iron) *Metal smelting *Power stations *Natural gas processing *Sanitary waste water treatment *Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instrumental Chemistry
Instrumental analysis is a field of analytical chemistry that investigates analytes using scientific instruments. Spectroscopy Spectroscopy measures the interaction of the molecules with electromagnetic radiation. Spectroscopy consists of many different applications such as atomic absorption spectroscopy, atomic emission spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, photoemission spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy, and circular dichroism spectroscopy. Nuclear spectroscopy Methods of nuclear spectroscopy use properties of a nucleus to probe a material's properties, especially the material's local structure. Common methods include nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), Mössbauer spectroscopy (MBS), and perturbed angular correlation (PAC). Mass spectrometry Mass spectrometry measures mass-to-charge ratio of molecules using electric and magnetic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit (e.g. molarity, density, functional activity in enzyme international units, degree of effect in comparison to a standard, etc.). If the assay involves exogenous reactants (the reagents), then their quantities are kept fixed (or in excess) so that the quantity and quality of the target are the only limiting factors. The difference in the assay outcome is used to deduce the unknown quality or quantity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Remediation
Environmental remediation deals with the removal of pollution or contaminants from environmental media such as soil, groundwater, sediment, or surface water. Remedial action is generally subject to an array of regulatory requirements, and may also be based on assessments of human health and ecological risks where no legislative standards exist, or where standards are advisory. Remediation standards In the United States, the most comprehensive set of Preliminary Remediation Goals (PRGs) is from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) ''Regional Screening Levels'' (RSLs). A set of standards used in Europe exists and is often called the Dutch standards. The European Union (EU) is rapidly moving towards Europe-wide standards, although most of the industrialised nations in Europe have their own standards at present. In Canada, most standards for remediation are set by the provinces individually, but the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment provides guidance at a federa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In Greece
Agriculture in Greece is based on small, family-owned dispersed units, while the extent of cooperative organization stays at low comparative levels, against all efforts that have been taken in the last 30 years, mainly under European Union supervision. Greek agriculture employs 528,000 farmers, 12% of the total labor force. It produces more than 14% of the national GDP. Greece produces a wide variety of crops and livestock products. Fisheries are also playing an important role while forestry plays a secondary role. Current production Currently, Greek agriculture is heavily subsidized by the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), with controversial results. Certain deductions of subsidies are planned within the next decade. Greece produced in 2018: * 1.2 million tons of maize; * 1 million tons of olive (5th largest producer in the world, behind Spain, Italy, Morocco and Turkey); * 1 million tons of wheat; * 968 thousand tons of peach (3rd largest producer in the world, behind Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |