|
Kane Quantum Computer
The Kane quantum computer is a proposal for a scalable quantum computer proposed by Bruce Kane in 1998,Kane, B.E. (1998A silicon-based nuclear spin quantum computer , ''Nature'', 393, p133 who was then at the University of New South Wales. Often thought of as a hybrid between quantum dot and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) quantum computers, the Kane computer is based on an array of individual phosphorus donor atoms embedded in a pure silicon lattice. Both the nuclear spins of the donors and the spins of the donor electrons participate in the computation. Unlike many quantum computation schemes, the Kane quantum computer is in principle scalable to an arbitrary number of qubits. This is possible because qubits may be individually addressed by electrical means. Description The original proposal calls for phosphorus donors to be placed in an array with a spacing of 20 nm, approximately 20 nm below the surface. An insulating oxide layer is grown on top of the silicon. Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computer
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Though current quantum computers may be too small to outperform usual (classical) computers for practical applications, larger realizations are believed to be capable of solving certain computational problems, such as integer factorization (which underlies RSA encryption), substantially faster than classical computers. The study of quantum computing is a subfield of quantum information science. There are several models of quantum computation with the most widely used being quantum circuits. Other models include the quantum Turing machine, quantum annealing, and adiabatic quantum computation. Most models are based on the quantum bit, or " qubit", which is somewhat analogous to the bit in classical computation. A qubit can be in a 1 or 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Quantum Computer
Nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computing (NMRQC) is one of the several proposed approaches for constructing a quantum computer, that uses the spin states of nuclei within molecules as qubits. The quantum states are probed through the nuclear magnetic resonances, allowing the system to be implemented as a variation of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR differs from other implementations of quantum computers in that it uses an ensemble of systems, in this case molecules, rather than a single pure state. Initially the approach was to use the spin properties of atoms of particular molecules in a liquid sample as qubits - this is known as liquid state NMR (LSNMR). This approach has since been superseded by solid state NMR (SSNMR) as a means of quantum computation. Liquid state NMR The ideal picture of liquid state NMR (LSNMR) quantum information processing (QIP) is based on a molecule in which some of its atom's nuclei behave as spin-½ systems. Depending on which nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin Qubit Quantum Computer
The spin qubit quantum computer is a quantum computer based on controlling the spin of charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) in semiconductor devices. The first spin qubit quantum computer was first proposed by Daniel Loss and David P. DiVincenzo in 1997, also known as the Loss–DiVicenzo quantum computer. The proposal was to use the intrinsic spin-½ degree of freedom of individual electrons confined in quantum dots as qubits. This should not be confused with other proposals that use the nuclear spin as qubit, like the Kane quantum computer or the nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computer. Spin qubits so far have been implemented by locally depleting two-dimensional electron gases in semiconductors such a gallium arsenide, silicon and germanium. Spin qubits have also been implemented in graphene. Loss–DiVicenzo proposal The Loss–DiVicenzo quantum computer proposal tried to fulfill DiVincenzo's criteria for a scalable quantum computer,D. P. DiVincenzo, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Morello
Andrea Morello (born 26 June 1972, in Pinerolo, Italy) is the Scientia Professor of quantum engineering in the School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications at the University of New South Wales, and a Program Manager at the ARC Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T). Morello is the head of the Fundamental Quantum Technologies Laboratory at UNSW. Education Morello completed his undergraduate degree in electrical engineering at the Politecnico di Torino in Italy in 1998. His research career began at the Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory where he investigated the magnetic phase diagram of high T_c superconductors. He obtained his PhD in experimental physics from the Kamerlingh Onnes Laboratory in Leiden in 2004, during which he explored the quantum dynamics of molecular nanomagnets at low temperatures. Morello spent two years at the University of British Columbia before joining UNSW Sydney in 2006. Research Morello's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. STM senses the surface by using an extremely sharp conducting tip that can distinguish features smaller than 0.1 nm with a 0.01 nm (10 pm) depth resolution. This means that individual atoms can routinely be imaged and manipulated. Most microscopes are built for use in ultra-high vacuum at temperatures approaching zero kelvin, but variants exist for studies in air, water and other environments, and for temperatures over 1000 °C. STM is based on the concept of quantum tunneling. When the tip is brought very near to the surface to be examined, a bias voltage applied between the two allows electrons to tunnel through the vacuum separating them. The resulting ''tunneling current'' is a function of the tip position, app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelle Simmons
Michelle Yvonne Simmons, (born 14 July 1967) is a Scientia Professor of Quantum Physics in the Faculty of Science at the University of New South Wales and has twice been an Australian Research Council Federation Fellow and is an Australian Research Council Laureate Fellow. She is the Director of the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation & Communication Technology and is recognised internationally as the creator of the field of atomic electronics. She was the inaugural editor-in-chief of ''npj Quantum Information'', an academic journal publishing articles in the emerging field of quantum information science. On 25 January 2018, Simmons was named as the 2018 Australian of the Year for her work and dedication to quantum information science. On 10 June 2019, Simmons was appointed an Officer of the Order of Australia (AO) in the 2019 Queen's Birthday Honours in recognition of her "distinguished service to science education as a leader in quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Clark (physicist)
Robert Graham Clark is an Australian physicist. He was appointed Professor and Chair of Energy Strategy and Policy at University of New South Wales (UNSW) in 2012. Prior to this he was Chief Defence Scientist from 2008 to 2011 and Professor of Experimental Physics at University of New South Wales, where he established the National Magnet Laboratory and Semiconductor Nanofabrication Facility. Clark joined the Royal Australian Navy as a Cadet Midshipman in 1969. He graduated from the RAN college with a Bachelor of Science from the University of New South Wales, then served on eight ships before leaving the navy in 1979. He holds an MA from Oxford and a PhD from the University of New South Wales. He took several positions at UNSW, culminating in Director of the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computer Technology, before taking on the role of Chief Defence Scientist. Clark was appointed an Officer of the Order of Australia on Australia Day 2013 "for di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conduction Band
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature, while the conduction band is the lowest range of vacant electronic states. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the Fermi level, while the conduction band is located above it. The distinction between the valence and conduction bands is meaningless in metals, because conduction occurs in one or more partially filled bands that take on the properties of both the valence and conduction bands. Band gap In semiconductors and insulators the two bands are separated by a band gap, while in semimetals the bands overlap. A band gap is an energy range in a solid where no electron states can exist due to the quantizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
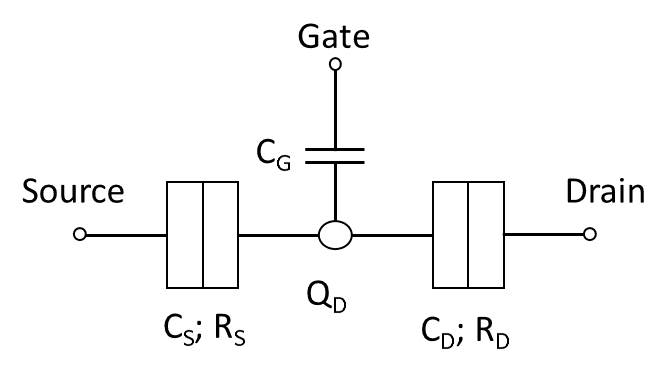
Single-electron Transistor
A single-electron transistor (SET) is a sensitive electronic device based on the Coulomb blockade effect. In this device the electrons flow through a tunnel junction between source/drain to a quantum dot (conductive island). Moreover, the electrical potential of the island can be tuned by a third electrode, known as the gate, which is capacitively coupled to the island. The conductive island is sandwiched between two tunnel junctions modeled by capacitors, C_ and C_, and resistors, R_ and R_, in parallel. History A new subfield of condensed matter physics began in 1977 when David Thouless pointed out that, when made small enough, the size of a conductor affects its electronic properties. This was followed by mesoscopic physics research in the 1980s based on the submicron-size of systems investigated. Thus began research related to the single-electron transistor. The first single-electron transistor based on the phenomenon of Coulomb blockade was reported in 1986 by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Tunneling
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. (Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom.) Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact ( quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing nature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)