|
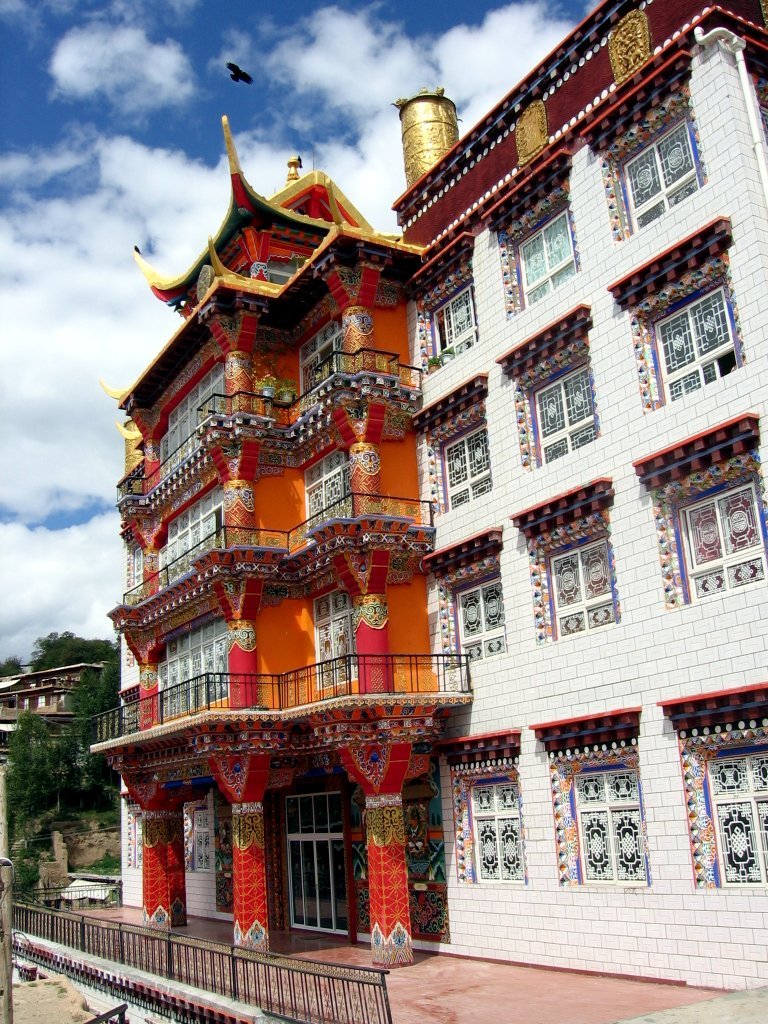
Kandze Monastery
Kandze Monastery (also Ganzi or Garze Monastery or Gompa) is situated 2 km north of Garzê Town on a hilltop overlooking the town, in Tibet. History The monastery was built ''c''. 1642 CE by the Khoshut or Qosot Mongols overlooking their castles known as Mazur and Khangsar. It once housed 1,500 monks making it, with Chamdo, the largest in Kham. The pilgrimage circuit around the monastery was almost eight kilometres long. In the 1909-1918 war the castles were occupied by Chinese troops and are now in ruins. It has been extensively renovated since 1981 and now houses about 700 monks, including three tulkus - one of whom, Lamdark Rinpoche, returned from Switzerland and established a girls' school. Description ;Assembly Hall The main Assembly Hall building has a golden roof and has views of the valley and nearby town. It is approached by a long flight of stairs and the inner sanctum is reached though long passageways formed by red wooden columns. Inside three sets of images are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garzê County
Garzê County or Ganzi County (; ) is one of the 18 subdivisions of the Garzê Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, in northwestern Sichuan province, China. The Yalong River passes just south of the town Garzê, also known as Ganzi, the capital town of the county, which has some 16,920 inhabitants (2010), many of them ethnic Tibetans, and is famous for its Tibetan lamasery. Historically, it is part of the Tibetan cultural region of Kham and now defunct province of Xikang (or Sikang). It lies on the northern section of the Sichuan-Tibet Highway. Geography and climate Due to its elevation, Garzê County has a monsoon-influenced humid continental climate (Köppen ''Dwb'') and subarctic climate, with cold but very dry winters, and warm summers with frequent rain. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from in January to in July, while the annual mean is . Over two-thirds of the annual precipitation of occurs from June thru September. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangka
The tangka (Tibetan: ''Tam'' or = ''silver tangka'') was a currency of Tibet until 1941. It was subdivided into 15 or and, from 1909, it circulated alongside the '' srang'', worth 10 sho. Coins Coins struck to the tangka standard were first minted in 1763/64 and 1785 and in larger numbers from 1791 to 1948. They exhibit a wide array of varieties and yet maintain a consistent fabric and type. Nepali tangkas and mohars for Tibet and the first Tibetan tangkas The first tangkas were struck in Nepal from about 1640. From this period onwards many Nepali tangkas were exported to Tibet. Subsequently silver coins of a reduced weight standard, mohars, were struck by the kings of the three Malla kingdoms which shared the Kathmandu valley. In the 18th century special debased mohars were struck by Nepal for Tibet. In 1763/4 and 1785 the first tangkas were minted in Tibet. These followed the Nepali fabric and type with minor differences to assert their local origins. In 1791, the Tibetan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Monasteries In Sichuan
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in History of India, northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a Bhavana, training of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorten
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spreadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Je Tsongkhapa
Tsongkhapa ('','' meaning: "the man from Tsongkha" or "the Man from Onion Valley", c. 1357–1419) was an influential Tibetan Buddhist monk, philosopher and tantric yogi, whose activities led to the formation of the Gelug school of Tibetan Buddhism.Tsong khapa (2006), pp. ix-x. He is also known by his ordained name Losang Drakpa (, Skt. Sumatikīrti) or simply as "Je Rinpoche" (, "Precious Lord"). He is also known by Chinese as Zongkapa Lobsang Zhaba or just Zōngkàbā (宗喀巴). Tsongkhapa was born in Amdo, the son of a Tibetan Longben Tribal leader who also once served as an official of the Yuan Dynasty. As a monk, he studied under numerous teachers of the various Tibetan Buddhist traditions which flourished in central Tibet, including Sakya, Jonang, Kagyu and Kadam. Tsongkhapa was a prolific author with a broad knowledge of Buddhist philosophy, logic, hermeneutics and practice. He wrote numerous works on madhyamaka philosophy (such as ''Ocean of Reasoning,'' a comment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalokiteśvara
In Buddhism, Avalokiteśvara (Sanskrit: अवलोकितेश्वर, IPA: ) is a bodhisattva who embodies the compassion of all Buddhas. He has 108 avatars, one notable avatar being Padmapāṇi (lotus bearer). He is variably depicted, described, and portrayed in different cultures as either male or female. In East Asian Buddhism, he has evolved into a female form called Guanyin. Etymology The name ''Avalokiteśvara'' combines the verbal prefix ''ava'' "down", ''lokita'', a past participle of the verb ''lok'' "to notice, behold, observe", here used in an active sense; and finally '' īśvara'', "lord", "ruler", "sovereign" or "master". In accordance with sandhi (Sanskrit rules of sound combination), ''a''+''īśvara'' becomes ''eśvara''. Combined, the parts mean "lord who gazes down (at the world)". The word ''loka'' ("world") is absent from the name, but the phrase is implied. It does appear in the Cambodian form of the name, ''Lokesvarak''. The earliest translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangyur
The Tibetan Buddhist canon is a loosely defined collection of sacred texts recognized by various schools of Tibetan Buddhism, comprising the Kangyur or Kanjur ('Translation of the Word') and the Tengyur or Tanjur (Tengyur) ('Translation of Treatises'). Tibetan Buddhist Canon In addition to earlier foundational Buddhist texts from early Buddhist schools, mostly the Sarvastivada and Mahayana texts, the Tibetan canon includes Tantric texts. The last category is not always sharply distinguished from the others: the Tantra division sometimes includes material usually not thought of as Tantric in other traditions, such as the Heart Sutra and even versions of material found in the Pali Canon. The Tibetans did not have a formally arranged Mahayana canon, and so devised their own scheme with two broad categories: the "Words of the Buddha" and later the commentaries; the Kangyur and Tengyur respectively. The Tengyur underwent a final compilation in the 14th century by Bu-ston (1290 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitatapatra
Sitātapatra (Sanskrit: "White Parasol") is a protector against supernatural danger in Buddhism. She is venerated in both the Mahayana and Vajrayana traditions. She is also known as Usnisasitatapatra or ''Uṣṇīṣa Sitātapatra''. It is believed that Sitātapatra is a powerful independent deity emanated by Gautama Buddha from his Uṣṇīṣa. Whoever practices her mantra will be reborn in Amitābha's pure land of Sukhāvatī as well as gaining protection against supernatural danger and witchcraft. Name Her name is composed of ''sita'' ("white") and ''ātapatrā'' ("parasol" or "umbrella"). Forms There are several different forms of Sitatapatra including: with one face and two arms; with three faces and six arms; with three faces and eight arms; with three faces and ten arms; with five faces and ten arms; and, with 1000 faces, 1000 arms and 1000 legs. Mantras ཧཱུཾ་མ་མ་ཧཱུཾ་ནི་སྭཱཧཱ། Hum ma ma hum ni svaha The Śūraṅgama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipamkara
Dipankara (Pali: ''Dīpaṅkara''; Sanskrit: ', "Lamp bearer") or Dipankara Buddha is one of the Buddhas of the past. He is said to have lived on Earth four asankheyyas and one hundred thousand kappas ago. According to some Buddhist or folk traditions, Dipankara was a previous Buddha who attained Enlightenment eons prior to Gautama Buddha, the historical Buddha. Generally, Buddhists believe that there has been a succession of many Buddhas in the distant past and that many more will appear in the future. Dipankara was one of these previous Buddhas, while Gautama Buddha was the current and most recent Enlightened one, and Maitreya will be the next Buddha in the distant future. Chinese Buddhism honors Dipankara as one of many Buddhas of the past. Dipankara, Gautama, and Maitreya are "the Buddhas of Three Times" in Yiguandao. Iconography Dipankara is generally represented as a sitting Buddha, but his depictions as a standing Buddha are common in China, Thailand, and Nepal; with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maitreya
Maitreya (Sanskrit: ) or Metteyya (Pali: ), also Maitreya Buddha or Metteyya Buddha, is regarded as the future Buddha of this world in Buddhist eschatology. As the 5th and final Buddha of the current kalpa, Maitreya's teachings will be aimed at reinstating the dharma, a vital concept in Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. In all branches of Buddhism, he is viewed as the direct successor of Gautama Buddha. In some Buddhist literature, such as the '' Amitabha Sutra'' and the ''Lotus Sutra'', he is referred to as Ajita. Despite many religious figures and spiritual leaders claiming to be Maitreya throughout history, all Buddhists firmly agree that these were false claims, indicating that Maitreya, the Buddha of the Future, is yet to appear. According to Buddhist tradition, Maitreya is a bodhisattva who is prophesied to appear on Earth, achieve complete Enlightenment, and teach the Dharma. According to scriptures, Maitreya's teachings will be similar to those of Gautama Buddha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.jpg)