|
Kanae Yamamoto (artist)
Kanae Yamamoto (, , 24 October 1882 – 8 October 1946) was a Japanese artist, known primarily for his prints and ' Western-style paintings. He is credited with originating the ' ("creative prints") movement, which aimed at self-expressive printmaking, in contrast to the commercial studio systems of ukiyo-e and '. He initiated movements in folk arts and children's art education that continue to be influential in Japan. Kanae trained as a wood engraver in the Western style before studying Western-style painting. While at art school he executed a two-colour print of a fisherman he had sketched on a trip to Chiba. Its publication ignited an interest in the expressive potential of prints that developed into the ' movement. Kanae spent 1912 to 1916 in Europe and brought ideas back to Japan gleaned from exhibitions of peasant crafts and children's art in Russia. In the late 1910s he founded movements that promoted creative peasant crafts and children's art education; the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okazaki, Aichi
is a city located in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 386,999 in 164,087 households, and a population density of 999 persons per km². The total area of the city was . Geography Okazaki is in the coastal plains of southeastern Aichi Prefecture. The ground rises to undulating hills in the former Nukata area to the northeast. About 60 percent of the city area is forested and remains sparsely populated. Okazaki is about from Tokyo, to the southwest. Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa''). The average annual temperature in Okazaki is . The average annual rainfall is with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around , and lowest in January, at around . Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of Okazaki has grown steadily over the past 60 years. This fast population growth reflects the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boshin War
The , sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution or Japanese Civil War, was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a clique seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court. The war stemmed from dissatisfaction among many nobles and young samurai with the shogunate's handling of foreigners following the opening of Japan during the prior decade. Increasing Western influence in the economy led to a decline similar to that of other Asian countries at the time. An alliance of western samurai, particularly the domains of Chōshū, Satsuma, and Tosa, and court officials secured control of the Imperial Court and influenced the young Emperor Meiji. Tokugawa Yoshinobu, the sitting ''shōgun'', realizing the futility of his situation, abdicated and handed over political power to the emperor. Yoshinobu had hoped that by doing this the House of Tokugawa could be preserved and participate in the future gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor of Japan as supreme commander of the army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Later an Inspectorate General of Aviation became the third agency with oversight of the army. During wartime or national emergencies, the nominal command functions of the emperor would be centralized in an Imperial General Headquarters (IGHQ), an ad hoc body consisting of the chief and vice chief of the Army General Staff, the Minister of the Army, the chief and vice chief of the Naval General Staff, the Inspector General of Aviation, and the Inspector General of Military Training. History Origins (1868–1871) In the mid-19th century, Japan had no unified national army and the country was made up of feudal domains (''han'') with the Tokugawa shogunate (''bakufu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harada Naojirō
Harada Naojirō (; 12 October 1863 – 26 December 1899) was a Japanese painter who specialized in the ''yōga'' (Western) style. He was a friend of the novelist Mori Ōgai and served as the model for the protagonist in Ōgai's short story ' (1890). Life and career Early life Harada Naojirō was born in the Koishikawa area of Edo (modern Tokyo) on 12 October 1863. He was the second son of Ai and . Ichidō worked for the military government at the Bansho Shirabesho, where foreign books were studied and translated. He wanted his son to learn French, and to this end had Naojirō enrolled at the Osaka Kaisei School in 1870 and at the in 1873, from where he graduated in 1881. That August he married Ōkubo Sada. From the age of eleven Harada began studying ''yōga'', or Western-style painting under Yamazaki Nariaki, and from 20 under Takahashi Yuichi, who at the time was the most prominent ''yōga'' painter in Japan. Study in Europe Harada moved to Germany in 1884, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaita Murayama
was a Japanese writer and artist. One of his self-portraits appears in the Mie Prefectural Art Museum in Tsu, Mie, Tsu Mie Prefecture, Japan (not pictured here). He trained at the Fine Arts Academy in Tokyo and was influenced by Western art styles. His work is described as being muscular and robust. References 1896 births 1919 deaths Deaths from Spanish flu Japanese writers {{Japan-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San'ya
is an area in the Taitō and Arakawa wards of Tokyo, located south of the Namidabashi intersection, around the Yoshino-dori. A neighborhood named "San'ya" existed until 1966, but the area was renamed and split between several neighborhoods. It is a region with a distinct culture, an area of crowded, cheap rooming houses where day laborers live.Halper 1991, pg. 96 San'ya dates to the Edo period. Lower caste workers, butchers, tanners, leatherworkers, and the like, were forced to live in this undesirable region by the predominantly Buddhist authorities. It has retained its association with both lower class workers and with craftsmen. Within the past few years gentrification has begun to encroach on the area. In recent years, some of the rooming houses have converted to provide cheap accommodation for foreign backpackers. Summary Since the Edo period, Kichinyado (木賃宿, a type of cheap lodging house that does not serve meals) have been located along the sides of the Ōsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
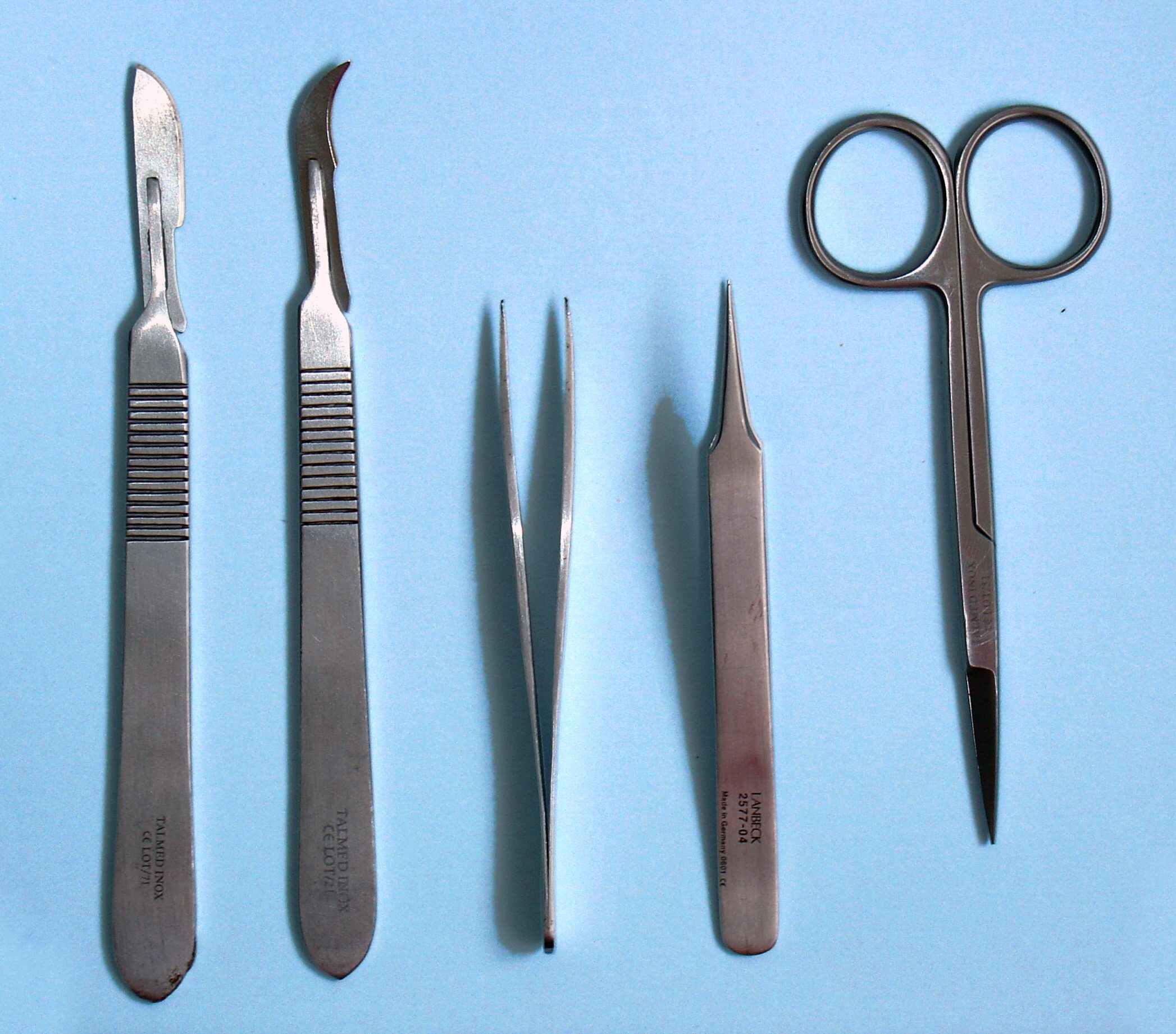
Dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause of death in humans. Less extensive dissection of plants and smaller animals preserved in a formaldehyde solution is typically carried out or demonstrated in biology and natural science classes in middle school and high school, while extensive dissections of cadavers of adults and children, both fresh and preserved are carried out by medical students in medical schools as a part of the teaching in subjects such as anatomy, pathology and forensic medicine. Consequently, dissection is typically conducted in a morgue or in an anatomy lab. Dissection has been used for centuries to explore anatomy. Objections to the use of cadavers have led to the use of alternatives including virtual dissection of computer models. Overview Plant and animal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mori Ōgai
Lieutenant-General , known by his pen name , was a Japanese Army Surgeon general officer, translator, novelist, poet and father of famed author Mari Mori. He obtained his medical license at a very young age and introduced translated German language literary works to the Japanese public. Mori Ōgai also was considered the first to successfully express the art of western poetry in Japanese. He wrote many works and created many writing styles. ''The Wild Geese'' (1911–1913) is considered his major work. After his death, he was considered one of the leading writers who modernized Japanese literature. Biography Early life Mori was born as in Tsuwano, Iwami Province (present-day Shimane Prefecture). His family were hereditary physicians to the ''daimyō'' of the Tsuwano Domain._As_the_eldest_son,_it_was_assumed_that_he_would_carry_on_the_family_tradition;_therefore_he_was_sent_to_attend_classes_in_the_Confucianism.html" "title="DF 23 of 80/nowiki>">DF 23 of 80">"Kamei" at ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Meiji Japan
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan. Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji oligarchy, who overthrew the Tokugawa shogunate. Early developments After the Meiji Restoration, the leaders of the ''samurai'' who overthrew the Tokugawa shogunate had no clear agenda or pre-developed plan on how to run Japan. They did have a number of things in common; according to Andrew Gordon, “It was precisely their intermediate status and their insecure salaried position, coupled with their sense of frustrated ambition and entitlement to rule, that account for the revolutionary energy of the Meiji insurgents and their far-reaching program of reform”. most were in their mid-40s, and most were from the four '' tozama'' domains of western Japan (Chōshū, Satsuma, Tosa and Hizen). Although from lower-ranked ''samurai'' families, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Okazaki In World War II
The was part of the strategic bombing air raids on Japan campaign waged by the United States against military and civilian targets and population centers during the Japan home islands campaign in the closing stages of the Pacific War. Background Although the city of Okazaki was not a major population center and had no major targets of military significance, it was a satellite town supporting the metropolis of Nagoya. The Tōkaidō Main Line railway connecting Tokyo with Osaka also ran through the city, and it became one of the 57 regional population centers added to the list of targets by General Curtis LeMay in June 1945 following the destruction of Japan's main cites. Air raids On July 19, 1945, 126 B-29 Superfortress bombers of the USAAF 20th Air Force, 314th Bombardment Wing departed from Guam in the Mariana Islands. On the same day, air raids were also launched against Fukui, Hitachi, and Chōshi. The B-29s arrived over target at Okazaki after midnight on Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampo
, often known simply as , is the study of traditional Chinese medicine in Japan following its introduction, beginning in the 7th century. It was adapted and modified to suit Japanese culture and traditions. Traditional Japanese medicine uses most of the Chinese methods, including acupuncture, moxibustion, traditional Chinese herbology, and traditional food therapy. History Origins According to Chinese mythology, the origins of traditional Chinese medicine are traced back to the three legendary sovereigns Fuxi, Shennong and Yellow Emperor. Shennong is believed to have tasted hundreds of herbs to ascertain their medicinal value and effects on the human body and help relieve people of their sufferings. The oldest written record focusing solely on the medicinal use of plants was the ''Shennong Ben Cao Jing'' which was compiled around the end of the first century B.C. and is said to have classified 365 species of herbs or medicinal plants. Chinese medical practices were intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_02.jpg)





_derivative.jpg)