|
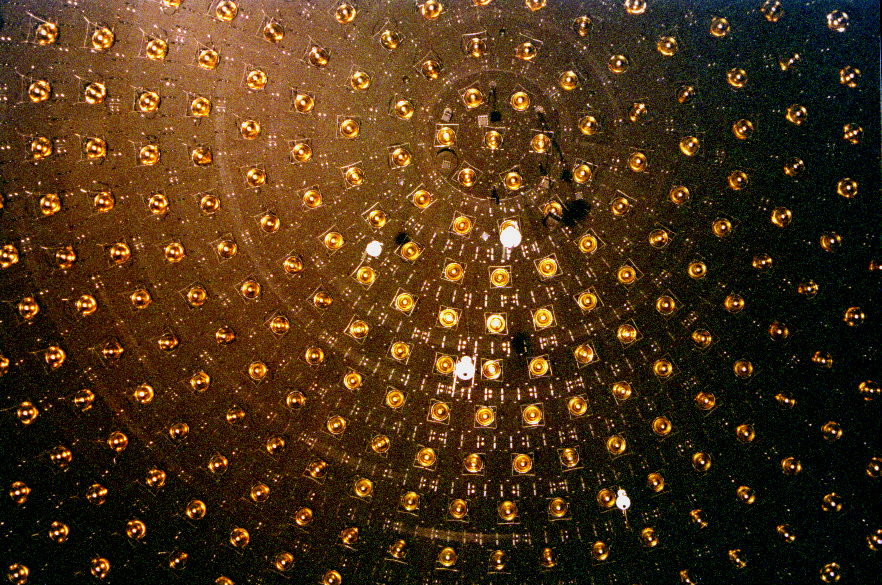
KamLAND
The Kamioka Liquid Scintillator Antineutrino Detector (KamLAND) is an electron antineutrino detector at the Kamioka Observatory, an underground neutrino detection facility in Hida, Gifu, Japan. The device is situated in a drift mine shaft in the old KamiokaNDE cavity in the Japanese Alps. The site is surrounded by 53 Japanese commercial nuclear reactors. Nuclear reactors produce electron antineutrinos (\bar_e) during the decay of radioactive fission products in the nuclear fuel. Like the intensity of light from a light bulb or a distant star, the isotropically-emitted \bar_e flux decreases at 1/R2 per increasing distance R from the reactor. The device is sensitive up to an estimated 25% of antineutrinos from nuclear reactors that exceed the threshold energy of 1.8 megaelectronvolts (MeV) and thus produces a signal in the detector. If neutrinos have mass, they may oscillate into flavors that an experiment may not detect, leading to a further dimming, or "disappearance," of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KamLAND Schematic
The Kamioka Liquid Scintillator Antineutrino Detector (KamLAND) is an electron antineutrino detector at the Kamioka Observatory, an underground neutrino detection facility in Hida, Gifu, Japan. The device is situated in a drift mine shaft in the old KamiokaNDE cavity in the Japanese Alps. The site is surrounded by 53 Japanese commercial nuclear reactors. Nuclear reactors produce electron antineutrinos (\bar_e) during the decay of radioactive fission products in the nuclear fuel. Like the intensity of light from a light bulb or a distant star, the isotropically-emitted \bar_e flux decreases at 1/R2 per increasing distance R from the reactor. The device is sensitive up to an estimated 25% of antineutrinos from nuclear reactors that exceed the threshold energy of 1.8 megaelectronvolts (MeV) and thus produces a signal in the detector. If neutrinos have mass, they may oscillate into flavors that an experiment may not detect, leading to a further dimming, or "disappearance," of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamioka Observatory
The is a neutrino and gravitational waves laboratory located underground in the Mozumi mine of the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. A set of groundbreaking neutrino experiments have taken place at the observatory over the past two decades. All of the experiments have been very large and have contributed substantially to the advancement of particle physics, in particular to the study of neutrino astronomy and neutrino oscillation. The mine The Mozumi mine is one of two adjacent mines owned by the Kamioka Mining and Smelting Co. (a subsidiary of the Mitsui Mining and Smelting Co. Mitsui Kinzoku'). The mine is famous as the site of one of the greatest mass-poisonings in Japanese history. From 1910 to 1945, the mine operators released cadmium from the processing plant into the local water. This cadmium caused what the locals called itai-itai disease. The disease caused weakening of the bones and extreme pain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Detector
A neutrino detector is a physics apparatus which is designed to study neutrinos. Because neutrinos only Weak interaction, weakly interact with other particles of matter, neutrino detectors must be very large to detect a significant number of neutrinos. Neutrino detectors are often built underground, to isolate the detector from cosmic rays and other background radiation. The field of neutrino astronomy is still very much in its infancy – the only confirmed extraterrestrial sources are the Sun and the SN 1987A, supernova 1987A in the nearby Large Magellanic Cloud. Another likely source (three standard deviations) is the blazar TXS 0506+056 about 3.7 billion light years away. Neutrino observatories will "give astronomers fresh eyes with which to study the universe". Various detection methods have been used. Super Kamiokande is a large volume of water surrounded by phototubes that watch for the Cherenkov radiation emitted when an incoming neutrino creates an electron or muon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of , but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles; that is, it is a fundamental particle. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the non-elementary neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherenkov Detector
A Cherenkov detector (pronunciation: /tʃɛrɛnˈkɔv/; Russian: Черенко́в) is a particle detector using the speed threshold for light production, the speed-dependent light output or the speed-dependent light direction of Cherenkov radiation. Fundamental A particle passing through a material at a velocity greater than that at which light can travel through the material emits light. This is similar to the production of a sonic boom when an airplane is traveling through the air faster than sound waves can move through the air. The direction this light is emitted is on a cone with angle θc about the direction in which the particle is moving, with cos(θc) = (c = the vacuum speed of light, n = the refractive index of the medium, and v is the speed of the particle). The angle of the cone θc thus is a direct measure of the particle's speed. The Frank–Tamm formula = sin2θc gives the number of photons produced. Aspects Most Cherenkov detectors aim a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
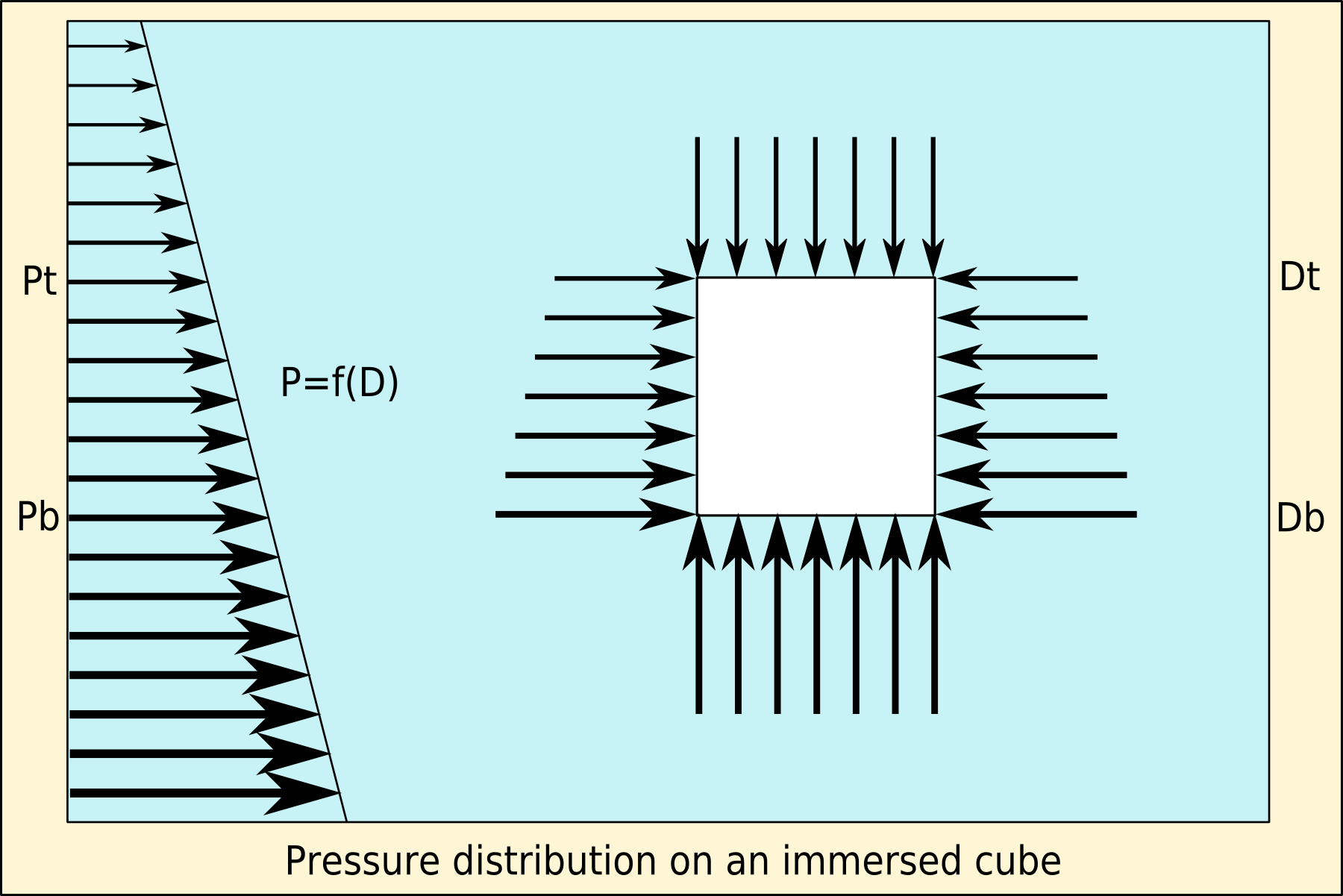
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corrosion resistance, resistance to corrosion results from the chromium, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that can protect the material and self-healing material, self-heal in the presence of oxygen. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for chemicals and food products. The biological cleanability of stainless steel is superior to both alumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major industrial chemical, it finds limited use in consumer items because of its toxicity. History Discovery The word "''benzene''" derives from "''gum benzoin''" (benzoin res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Oil
Mineral oil is any of various colorless, odorless, light mixtures of higher alkanes from a mineral source, particularly a distillate of petroleum, as distinct from usually edible vegetable oils. The name 'mineral oil' by itself is imprecise, having been used for many specific oils over the past few centuries. Other names, similarly imprecise, include 'white oil', 'paraffin oil', ' liquid paraffin' (a highly refined medical grade), (Latin), and 'liquid petroleum'. Most often, mineral oil is a liquid by-product of refining crude oil to make gasoline and other petroleum products. This type of mineral oil is a transparent, colorless oil, composed mainly of alkanes and cycloalkanes, related to petroleum jelly. It has a density of around . Nomenclature Some of the imprecision in the definition of the names used for mineral oil (such as 'white oil') reflects usage by consumers and merchants who did not know, and usually had no need of knowing, the oil's precise chemical makeup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




2.png)
