|
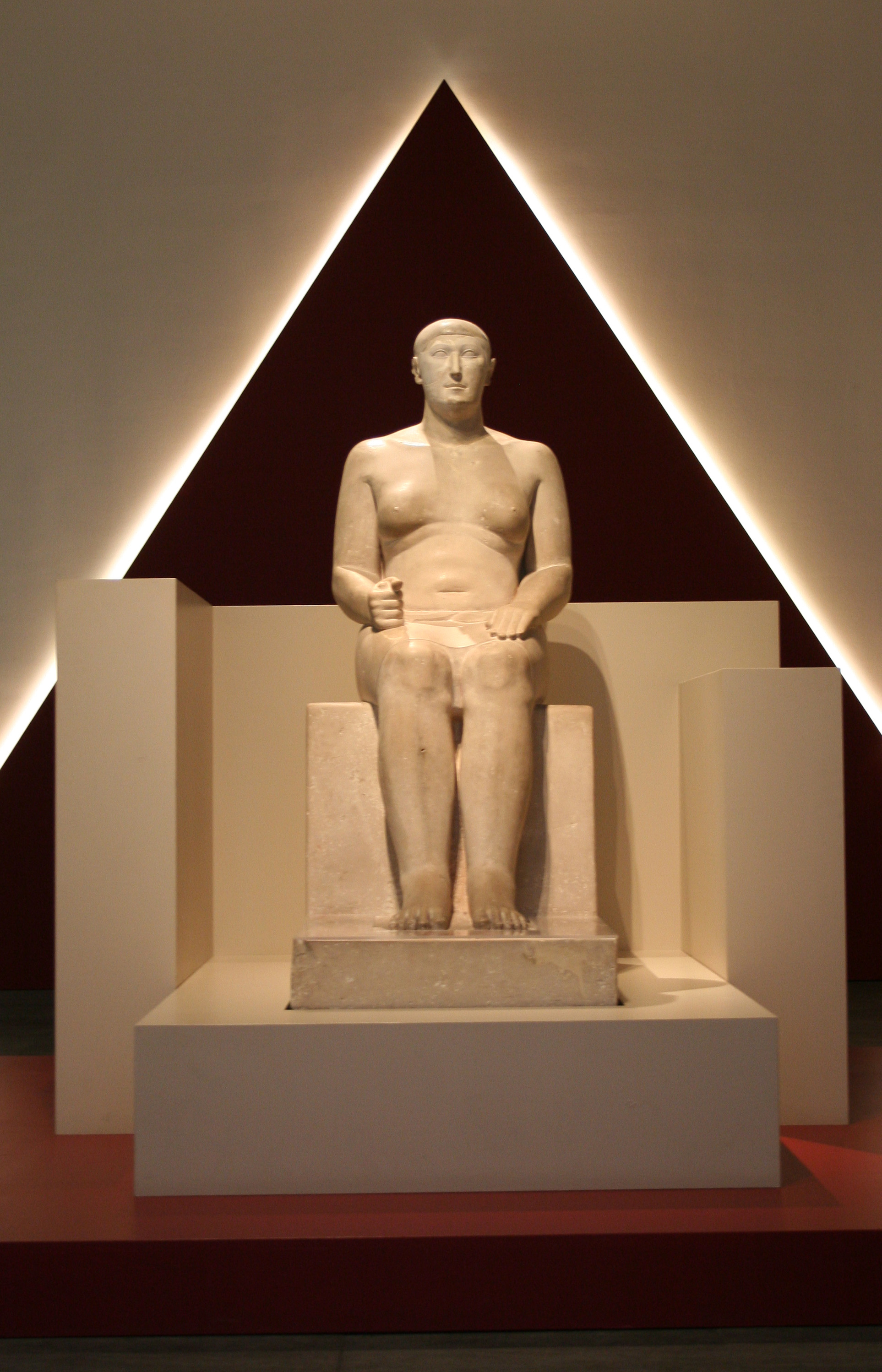
Kagemni I
Kagemni I was an ancient Egyptian who lived from the end of the 3rd Dynasty to the beginning of the 4th Dynasty. He was a vizier to both Pharaoh Huni and Pharaoh Sneferu. History Kagemni may have written a set of instructions, known as the ''Instructions of Kagemni'', for his sons. The instructions are part of the Prisse Papyrus, which also contains the teachings of Ptahhotep. At the end of the text regarding Kagemni, it is mentioned that after he learnt all he could about the nature of men, he wrote down what he had learnt so as to pass it onto his children. The text then proceeds to mention that the King of Upper and Lower Egypt Huni had died and was succeeded by Sneferu. Kagemni was appointed as overseer of the pyramid town and Vizier by Sneferu.Alan H. Gardiner, ''The Instruction Addressed to Kagemni and His Brethren'', ''The Journal of Egyptian Archaeology'', Vol. 32 (Dec., 1946), pp. 71-74 Kagemni should not be confused with vizier Kagemni from the time of Pharaoh Teti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is documented. The Fourth Dynasty heralded the height of the pyramid-building age. The relative peace of the Third Dynasty allowed the Dynasty IV rulers the leisure to explore more artistic and cultural pursuits. King Sneferu's building experiments led to the evolution from the mastaba-styled step pyramids to the smooth sided “true” pyramids, such as those on the Giza Plateau. No other period in Egypt's history equaled Dynasty IV's architectural accomplishments.Egypt: Land and Lives of the Pharaohs Revealed, (2005), pp. 80–90, Global Book Publishing: Australia Each of the rulers of this dynasty (except for Shepseskaf, the last) commissioned at least one pyramid to serve as a tomb or cenotaph. The Fourth Dynasty was the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huni
Huni (original reading unknown) was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC. Huni's chronological position as the last king of the third dynasty is seen as fairly certain, but there is still some uncertainty on the succession order of rulers at the end of the 3rd dynasty. It is also unclear under which Hellenized name the ancient historian Manetho could have listed him in his historical writing ''Aegyptiacae''. Most possibly he is to be identified with the Hellenized name Aches, as Winfried Barta proposes. Many Egyptologists believe that Huni was the father and direct predecessor of king Sneferu, but this is questioned by other scholars. Huni is seen by scholars as a confusing figure in Egyptian history, because he was long remembered in Egyptian traditions, but very few documents, objects or monuments f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
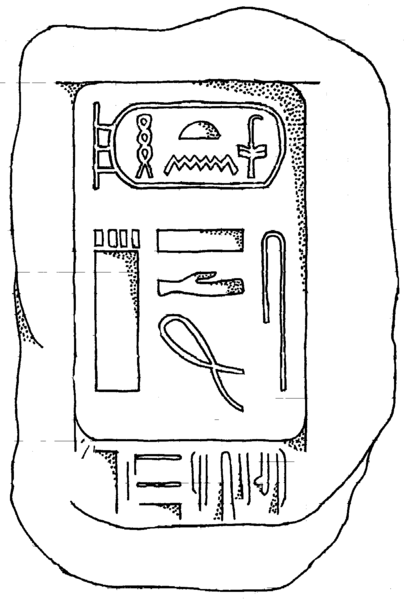
Sneferu
Sneferu ( snfr-wj "He has perfected me", from ''Ḥr-nb-mꜣꜥt-snfr-wj'' "Horus, Lord of Maat, has perfected me", also read Snefru or Snofru), well known under his Hellenized name Soris ( grc-koi, Σῶρις by Manetho), was the founding pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Estimates of his reign vary, with for instance ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'' suggesting a reign from around 2613 to 2589 BC, a reign of 24 years, while Rolf Krauss suggests a 30-year reign, and Rainer Stadelmann a 48-year reign. He built at least three pyramids that survive to this day and introduced major innovations in the design and construction of pyramids. Reign length The 24-year Turin Canon figure for Sneferu's reign is considered today to be an underestimate since this king's highest-known date is an inscription discovered at the Red Pyramid of Dahshur and mentioning Sneferu's 24th cattle count, corresponding to at least 24 full years. Sneferu, however, was kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Dynasty
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth, Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth and Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis, Egypt, Memphis. Overview After the turbulent last years of the Second dynasty of Egypt, Second Dynasty, which might have included civil war, Egypt came under the rule of Djoser, marking the beginning of the Third Dynasty.Dodson, Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 Both the Turin King List and the Abydos King List record five kings,Toby A.H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge, 2001 while the Saqqara Tablet only records four, and Manetho records nine,Aidan Dodson: ''The Layer Pyramid of Zawiyet el-Aryan: Its Layout and Context.'' In: ''Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt (JARCE)'', No. 37 (2000). American Researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Dynasty
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is documented. The Fourth Dynasty heralded the height of the pyramid-building age. The relative peace of the Third Dynasty allowed the Dynasty IV rulers the leisure to explore more artistic and cultural pursuits. King Sneferu's building experiments led to the evolution from the mastaba-styled step pyramids to the smooth sided “true” pyramids, such as those on the Giza Plateau. No other period in Egypt's history equaled Dynasty IV's architectural accomplishments.Egypt: Land and Lives of the Pharaohs Revealed, (2005), pp. 80–90, Global Book Publishing: Australia Each of the rulers of this dynasty (except for Shepseskaf, the last) commissioned at least one pyramid to serve as a tomb or cenotaph. The Fourth Dynasty was the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier (Ancient Egypt)
The vizier () was the highest official in ancient Egypt to serve the pharaoh (king) during the Old, Middle, and New Kingdoms. Vizier is the generally accepted rendering of ancient Egyptian , etc., among Egyptologists. The ''Instruction of Rekhmire'' (''Installation of the Vizier''), a New Kingdom text, defines many of the duties of the , and lays down codes of behavior. The viziers were often appointed by the pharaoh. During the 4th Dynasty and early 5th Dynasty, viziers were exclusively drawn from the royal family; from the period around the reign of Neferirkare Kakai onwards, they were chosen according to loyalty and talent or inherited the position from their fathers. Responsibilities The viziers were appointed by the pharaohs and often belonged to a pharaoh's family. The vizier's paramount duty was to supervise the running of the country, much like a prime minister. At times this included small details such as sampling the city's water supply. All other lesser supervis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instructions Of Kagemni
The ''Instructions of Kagemni'' is an ancient Egyptian instructional text of wisdom literature which belongs to the ''sebayt'' ('teaching') genre. Although the earliest evidence of its compilation dates to the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, its authorship has traditionally yet dubiously been attributed to Kagemni,Lichtheim (1996), p. 244. a vizier who served during the reign of the Pharaoh Sneferu (r. 2613–2589 BC), founder of the Fourth Dynasty (belonging to the Old Kingdom). Dating The earliest known source for the ''Instructions of Kagemni'' is the Prisse Papyrus. This text dates to the much later twelfth dynasty of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt (perhaps by the reign of Amenemhat II from 1929 BC to 1895 BC, or a bit later in the twelfth dynasty). It is written in the Middle Egyptian language and in an archaic style of cursive hieratic.Parkinson (2002), pp. 46, 50, 313. Content Only the end of this teaching text has survived; on the Prisse Papyrus, it is followed by the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisse Papyrus
The Prisse Papyrus is an ancient Egyptian papyrus datable to the Middle Kingdom and is now in the Bibliothèque nationale de France in Paris. Inhabitants of Kurna originally found the papyrus inside the rishi coffin of pharaoh Sekhemre-Wepmaat Intef of the 17th Dynasty, whose tomb was probably located in Dra' Abu el-Naga' near Thebes. The papyrus document contains the last two pages of the ''Instructions of Kagemni'', who purportedly served under pharaoh Sneferu of the 4th Dynasty, and is a compilation of moral maxims and admonitions on the practice of virtue (''sebayt''). The conclusion of the ''Instructions of Kagemni'' is followed by the only complete surviving copy of the '' Instruction of Ptahhotep''. Battiscombe Gunn, "THE WISDOM OF THE EAST, THE INSTRUCTION OF PTAH-HOTEP AND THE INSTRUCTION OF KE'GEMNI: THE OLDEST BOOKS IN THE WORLD", LONDON, JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET, 1906, https://www.gutenberg.org/files/30508/30508-h/30508-h.htm See also *List of ancient Egyptia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagemni
Kagemni was a vizier from the early part of the reign of King Teti of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt. Kagemni's wife Nebtynubkhet Sesheshet was a King's Daughter and likely the daughter of Teti.Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. 2004. Biography Kagemni held a great number of titles. He was an overseer of the two houses of gold and an overseer of the two treasuries. He also held several religious positions, including that of High Priest of Re and Stolist of Min. Other duties were related to the royal palace: overseer of the two chambers of the king's adornment, director of the Mansions of the White and Red Crowns and keeper of the head ornaments. As vizier, Kagemni also held the positions of overseer of the scribes of the king's documents, overseer of all the works of the king, and overseer of the six great courts.Naguib Kanawati, Conspiracies in the Egyptian Palace: Unis to Pepy I, (Routledge, 2002). . Tomb Kagemni was bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



