|
Kaby Lake (microarchitecture)
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's previous " tick–tock" manufacturing and design model, Kaby Lake represents the optimized step of the newer process–architecture–optimization model. Kaby Lake began shipping to manufacturers and OEMs in the second quarter of 2016, and mobile chips have started shipping while Kaby Lake (desktop) chips were officially launched in January 2017. In August 2017, Intel announced Kaby Lake Refresh (Kaby Lake R) marketed as the 8th generation mobile CPUs, breaking the long cycle where architectures matched the corresponding generations of CPUs. Skylake was anticipated to be succeeded by the 10 nanometer Cannon Lake, but it was announced in July 2015 that Cannon Lake had been delayed until the second half of 2017. In the meantime, Intel rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14 Nanometer
The 14 nm process refers to the MOSFET technology node that is the successor to the 22nm (or 20nm) node. The 14nm was so named by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Until about 2011, the node following 22nm was expected to be 16nm. All 14nm nodes use FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, a type of multi-gate MOSFET technology that is a non-planar evolution of planar silicon CMOS technology. Samsung Electronics taped out a 14 nm chip in 2014, before manufacturing 10 nm class NAND flash chips in 2013. The same year, SK Hynix began mass-production of 16nm NAND flash, and TSMC began 16nm FinFET production. The following year, Intel began shipping 14nm scale devices to consumers. History Background The basis for sub-20nm fabrication is the FinFET (Fin field-effect transistor), an evolution of the MOSFET transistor. FinFET technology was pioneered by Digh Hisamoto and his team of researchers at Hitachi Central Research Laborato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trusted Execution Technology
Intel Trusted Execution Technology (Intel TXT, formerly known as LaGrande Technology) is a computer hardware technology whose primary goals are: * Attestation of the authenticity of a platform and its operating system. * Assuring that an authentic operating system starts in a trusted environment, which can then be considered trusted. * Provision of a trusted operating system with additional security capabilities not available to an unproven one. Intel TXT uses a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and cryptographic techniques to provide measurements of software and platform components so that system software as well as local and remote management applications may use those measurements to make trust decisions. It complements Intel Management Engine. This technology is based on an industry initiative by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) to promote safer computing. It defends against software-based attacks aimed at stealing sensitive information by corrupting system or BIOS code, or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Codenames
Intel has historically named integrated circuit (IC) development projects after geographical names of towns, rivers or mountains near the location of the Intel facility responsible for the IC. Many of these are in the American West, particularly in Oregon (where most of Intel's CPU projects are designed; see famous codenames). As Intel's development activities have expanded, this nomenclature has expanded to Israel and India, and some older codenames refer to celestial bodies. The following table lists known Intel codenames along with a brief explanation of their meaning and their likely namesake, and the year of their earliest known public appearance. Most processors after a certain date were named after cities that could be found on a map of the United States. This was done for trademark considerations. Banias was the last of the non-US city names. Gesher was renamed to Sandy Bridge to comply with the new rule. Dothan is a city both in Israel and in Alabama. See also * Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series of instruction sets, the instruction sets found in most personal computers (PCs). Delaware General Corporation Law, Incorporated in Delaware, Intel ranked No. 45 in the 2020 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 fiscal years. Intel supplies microprocessors for List of computer system manufacturers, computer system manufacturers such as Acer Inc., Acer, Lenovo, HP Inc., HP, and Dell Technologies, Dell. Intel also manufactures motherboard chipsets, network interface controllers and integrated circuits, flash memory, Graphics processing unit, graphics chips, Embedded system, embedded processors and other devices related to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. ''Ars Technica'' was privately owned until May 2008, when it was sold to Condé Nast Digital, the online division of Condé Nast Publications. Condé Nast purchased the site, along with two others, for $25 million and added it to the company's ''Wired'' Digital group, which also includes '' Wired'' and, formerly, Reddit. The staff mostly works from home and has offices in Boston, Chicago, London, New York City, and San Francisco. The operations of ''Ars Technica'' are funded primarily by advertising, and it has offered a paid subscription service since 2001. History Ken Fisher, who serves as the website's current editor-in-chief, and Jon Stokes created ''Ars Technica'' in 1998. Its purpose w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AnandTech
''AnandTech'' is an online computer hardware magazine owned by Future plc. It was founded in 1997 by then-14-year-old Anand Lal Shimpi, who served as CEO and editor-in-chief until August 30, 2014, with Ryan Smith replacing him as editor-in-chief. The web site is a source of hardware reviews for off-the-shelf components and exhaustive benchmarking, targeted towards computer building enthusiasts, but later expanded to cover mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.For instance by: * * * * * Its investigative articles have been cited by other technology news sites like PC Magazine and The Inquirer. Some of their articles on mass-market products such as mobile phones are syndicated by CNNMoney. The large accompanying forum is recommended by some books for bargain hunting in the technology field. AnandTech was acquired by Purch on 17 December 2014. Purch was acquired by Future in 2018. History In its early stages, Matthew Witheiler served as co-owner and Senior Hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Lake (microarchitecture)
Cascade Lake is an Intel codename for a 14 nm server, workstation and enthusiast processor microarchitecture, launched in April 2019. In Intel's Process-Architecture-Optimization model, Cascade Lake is an optimization of Skylake. Intel states that this will be their first microarchitecture to support 3D XPoint-based memory modules. It also features Deep Learning Boost instructions and mitigations for Meltdown and Spectre Spectre, specter or the spectre may refer to: Religion and spirituality * Vision (spirituality) * Apparitional experience * Ghost Arts and entertainment Film and television * ''Spectre'' (1977 film), a made-for-television film produced and writ .... Intel officially launched new Xeon Scalable SKUs on February 24, 2020. Variants *Server: Cascade Lake-SP, Cascade Lake-AP *Workstation: Cascade Lake-W *Enthusiast: Cascade Lake-X List of Cascade Lake processors Cascade Lake-X (Enthusiast) Cascade Lake-AP (Advanced Performance) Cascade Lake-AP is branded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whiskey Lake (microprocessor)
Whiskey Lake is Intel's codename for a family of third 14 nm generation Skylake low-power mobile processors. Intel announced Whiskey Lake on August 28, 2018. Changes * 14++ nm process, same as Coffee Lake * Increased turbo clocks (300–600 MHz) * 14 nm PCH * Native USB 3.1 gen 2 support (10 Gbit/s) * Integrated Wi-Fi 802.11ac 160 MHz / WiFi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0 * Intel Optane Memory support List of Whiskey Lake CPUs Mobile processors The TDP for these CPUs is 15 W, but is configurable. Core i5-8365U and i7-8665U support Intel vPro Technology Pentium Gold and Celeron CPUs lack AVX2 Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) are extensions to the x86 instruction set architecture for microprocessors from Intel and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). They were proposed by Intel in March 2008 and first supported by Intel with the Sandy Bridg ... support. References {{IntelProcessorRoadmap Intel microarchitectures Intel x86 microprocessors X86 microa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee Lake
Coffee Lake is Intel's codename for its eighth generation Core microprocessor family, announced on September 25, 2017. It is manufactured using Intel's second 14 nm process node refinement. Desktop Coffee Lake processors introduced i5 and i7 CPUs featuring six cores (along with hyper-threading in the case of the latter) and Core i3 CPUs with four cores and no hyperthreading. On October 8, 2018, Intel announced what it branded its ninth generation of Core processors, the Coffee Lake Refresh family. To avoid running into thermal problems at high clock speeds, Intel soldered the integrated heat spreader (IHS) to the CPU die instead of using thermal paste as on the Coffee Lake processors. The generation was defined by another increase of core counts. Coffee Lake is used with the 300-series chipset, and officially does not work with the 100- and 200-series chipset motherboards. Although desktop Coffee Lake processors use the same physical LGA 1151 socket as Skylake and Kaby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGA 2066
LGA 2066, also called ''Socket R4'', is a CPU socket by Intel that debuted with Skylake-X and Kaby Lake-X processors in June 2017. It replaces Intel's LGA 2011-3 (R3) in the performance, high-end desktop and Workstation platforms (based on the X299 "Basin Falls" and C422 chipsets), while LGA 3647 (Socket P) replaces LGA 2011-3 (R3) in the server platforms based on Skylake-SP (Xeon "Purley"). Compatible processors High-End Desktop (HEDT) All of these CPUs require the Intel X299 chipset to work. So, the C422 chipset is strictly limited to work with workstation processors only. Kaby Lake-X Kaby Lake-X processors were discontinued in May 2018. Starting October 2019, BIOS updates for most of the X299-based motherboards removed support for Kaby Lake-X processors. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
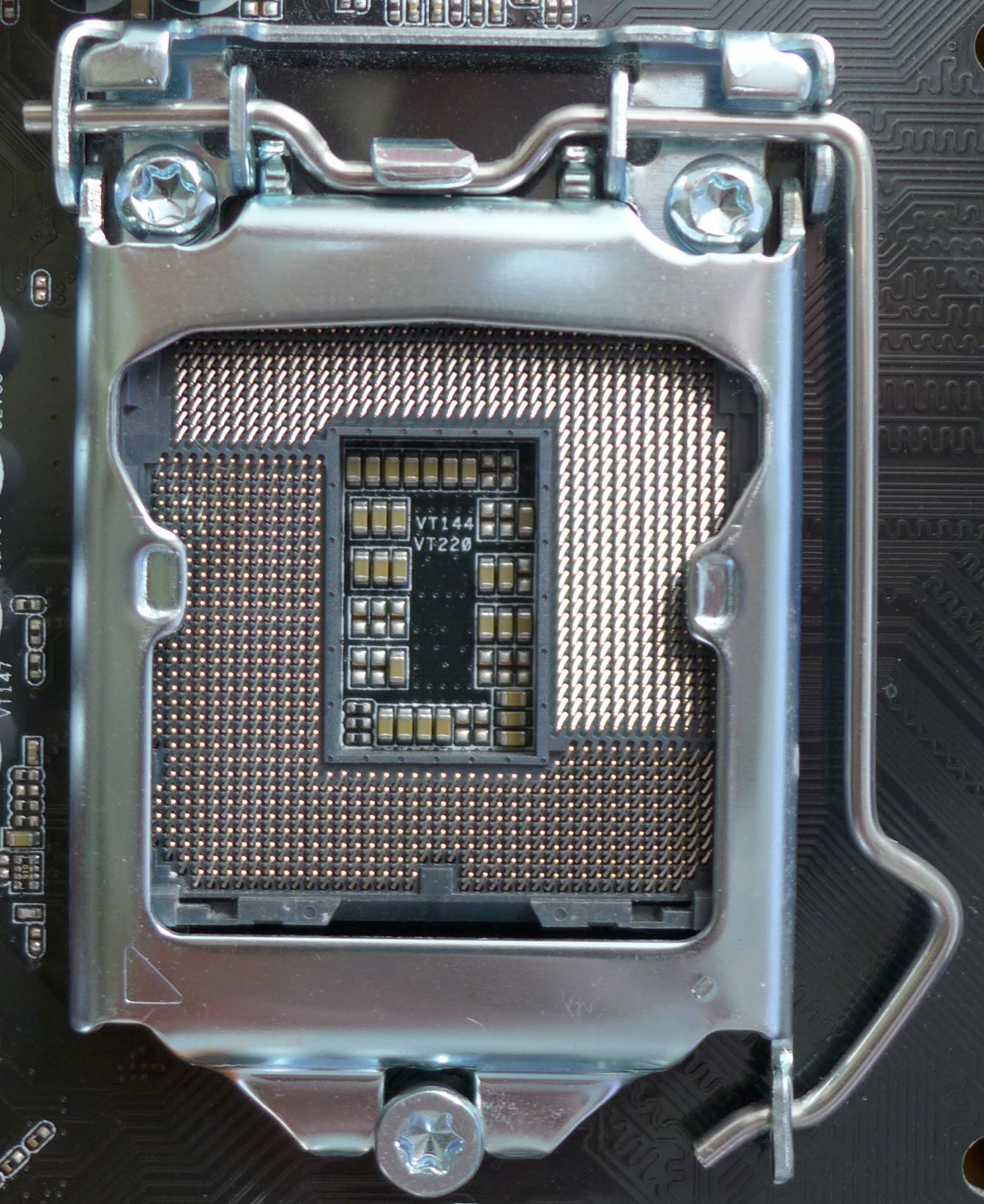
LGA 1151
LGA 1151, also known as Socket H4, zero insertion force flip-chip land grid array (LGA) socket for Intel desktop processors which comes in two distinct versions: the first revision which supports both Intel's Skylake and Kaby Lake CPUs, and the second revision which supports Coffee Lake CPUs exclusively. LGA 1151 is designed as a replacement for the LGA 1150 (known as ''Socket H3''). LGA 1151 has 1151 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor. The Fully Integrated Voltage Regulator, i.e. a voltage regulator which integrated on the CPU's die, introduced with Haswell and Broadwell, has again been moved to the motherboard. Most motherboards for the first revision of the socket support solely DDR4 memory, a lesser number support DDR3(L) memory, and the least number have slots for both DDR4 or DDR3(L) but only one memory type can be installed. Some have UniDIMM support, enabling either type of memory to be placed in the same DIMM, rather than ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel VT-d
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU. In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities while attaining reasonable performance. In 2005 and 2006, both Intel ( VT-x) and AMD (AMD-V) introduced limited hardware virtualization support that allowed simpler virtualization software but offered very few speed benefits. Greater hardware support, which allowed substantial speed improvements, came with later processor models. Software-based virtualization The following discussion focuses only on virtualization of the x86 architecture protected mode. In protected mode the operating system kernel runs at a higher privilege such as ring 0, and applications at a lower privilege such as ring 3. In software-based virtualization, a host OS has direct access to hardware while the guest OSs have limited a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |