|
Kabar (other)
The Kabars ( el, Κάβαροι), also known as Qavars (Qabars) or Khavars were Khazar rebels who joined the Magyar confederation possibly in the 9th century as well as the Rus' Khaganate. Sources The Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII is the principal source of the Kabars' history. He dedicated a whole chapterchapter 39to the Kabars (or ''Kabaroi'') in his '' De Administrando Imperio'', which was completed around 950. The Emperor described the Kabars as "a race of Khazars" who had risen up against the Khagan. The uprising was crushed, and some of them were massacred, but others escaped and joined the Magyars in the Pontic steppes. History The Kabars rebelled against the Khazar Khaganate in the early ninth century; the rebellion was notable enough to be described in Constantine Porphyrogenitus's work '' De Administrando Imperio''. Subsequently the Kabars were expelled from Levedia in the Khazar Khaganate leading the Magyar tribal confederacy called ''Hét-Magyar'' (meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
András Róna-Tas
András Róna-Tas (born 30 December 1931) is a Hungarian historian and linguist. He was born in 1931 in Budapest. Róna-Tas studied under such preeminent professors as Gyula Ortutay and Lajos Ligeti, and received a degree in folklore and eastern linguistics (Tibetan, Mongol, and Turkic.) From 1956, he worked at the Faculty of Humanities of the Eötvös Loránd University. In 1957-58, Róna-Tas conducted anthropological fieldwork in Mongolia, studying the culture, language, and folklore of the nomadic tribes in that country. During the mid-1960s Róna-Tas focused his fieldwork on the Chuvash people of the middle Volga River basin. In 1964, Róna-Tas defended his candidates (CSc) degree, and finally in 1971 he earned a doctorate from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (DSc) with his thesis "The Theory of Linguistic Affinity and the Linguistic Relations between the Chuvash and Mongol Languages", published as ''Linguistic Affinity'' in 1978. From 1968-2002, Róna-Tas was professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Region
The Volga Region (russian: Поволжье, ''Povolzhye'', literally: "along the Volga") is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russia. The Volga Region is culturally separated into three sections: * Upper Volga Region - from the Volga River's source (river), source in Tver Oblast to the Mouth (river), mouth of the Oka River in Nizhny Novgorod * Middle Volga Region - from the mouth of the Oka River to the mouth of the Kama River south of Kazan * Lower Volga Region - from the mouth of the Kama River to the Volga Delta in the Caspian Sea, in Astrakhan Oblast The geographic boundaries of the region are vague, and the term "Volga Region" is used to refer primarily to the Middle and Lower sections, which are included in the Volga Federal District and Volga economic region. Geography The Volga Region is almost entirely within the East European Plain, with a notable disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Alba Iulia and Sighișoara. It is also the home of some of Romania's List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains and the Rosia Montana Mining Cultural Landsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პაჭანიკი, bg, печенеги, pechenegi, bg, печенези, ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, la, Pacinacae, Bisseni were a semi-nomadic Turkic ethnic people from Central Asia who spoke the Pecheneg language which belonged to the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. Ethnonym The Pechenegs were mentioned as ''Bjnak'', ''Bjanak'' or ''Bajanak'' in medieval Arabic and Persian texts, as ''Be-ča-nag'' in Classical Tibetan documents, and as ''Pačanak-i'' in works written in Georgian. Anna Komnene and other Byzantine authors referred to them as ''Patzinakoi'' or ''Patzinakitai''. In medieval Latin texts, the Pechenegs were referred to as ''Pizenaci'', ''Bisseni'' or ''Bessi''. East Slavic peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Árpád
Árpád (; 845 – 907) was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or ''kende'' of the Hungarians, or their military leader or '' gyula'', although most details of his life are debated by historians, because different sources contain contradictory information. Despite this, many Hungarians refer to him as the "founder of our country", and Árpád's preeminent role in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin has been emphasized by some later chronicles. The dynasty descending from Árpád ruled the Kingdom of Hungary until 1301. Biography Early life Árpád was the son of Álmos who is mentioned as the first head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes by all Hungarian chronicles. His mother's name and family are unknown. According to historian Gyula Kristó, Árpád was born around 845. His name derived from the Hungarian word for barley, ''árpa''. The By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bulgarian Monarchs
The monarchs of Bulgaria ruled the country during three periods of Bulgaria's history as an independent country: from the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 to the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria in 1018; from the Uprising of Asen and Peter that established the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185 to the annexation of the rump Bulgarian state into the Ottoman Empire in 1396; and from the re-establishment of an independent Principality of Bulgaria in 1878 to the abolition of monarchy in a referendum held on 15 September 1946. This list does not include the mythical Bulgar rulers and the rulers of Old Great Bulgaria listed in the Nominalia of the Bulgarian rulers, as well as unsuccessful claimants to the throne who are not generally listed among the Bulgarian monarchs, neither rulers of Volga Bulgaria, or other famous Bulgarian rulers as Kuber or Alcek. Early Bulgarian rulers possibly used the title ''Kanasubigi'' (possibly related to Knyaz, Khan) before the 7th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire ( cu, блъгарьско цѣсарьствиѥ, blagarysko tsesarystviye; bg, Първо българско царство) was a medieval Bulgar- Slavic and later Bulgarian state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by defeatingpossibly with the help of local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. It became the foremost cultural and spiritual centre of south Slavic Europe throughout most of the Middle Ages. As the state solidified its position in the Balka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
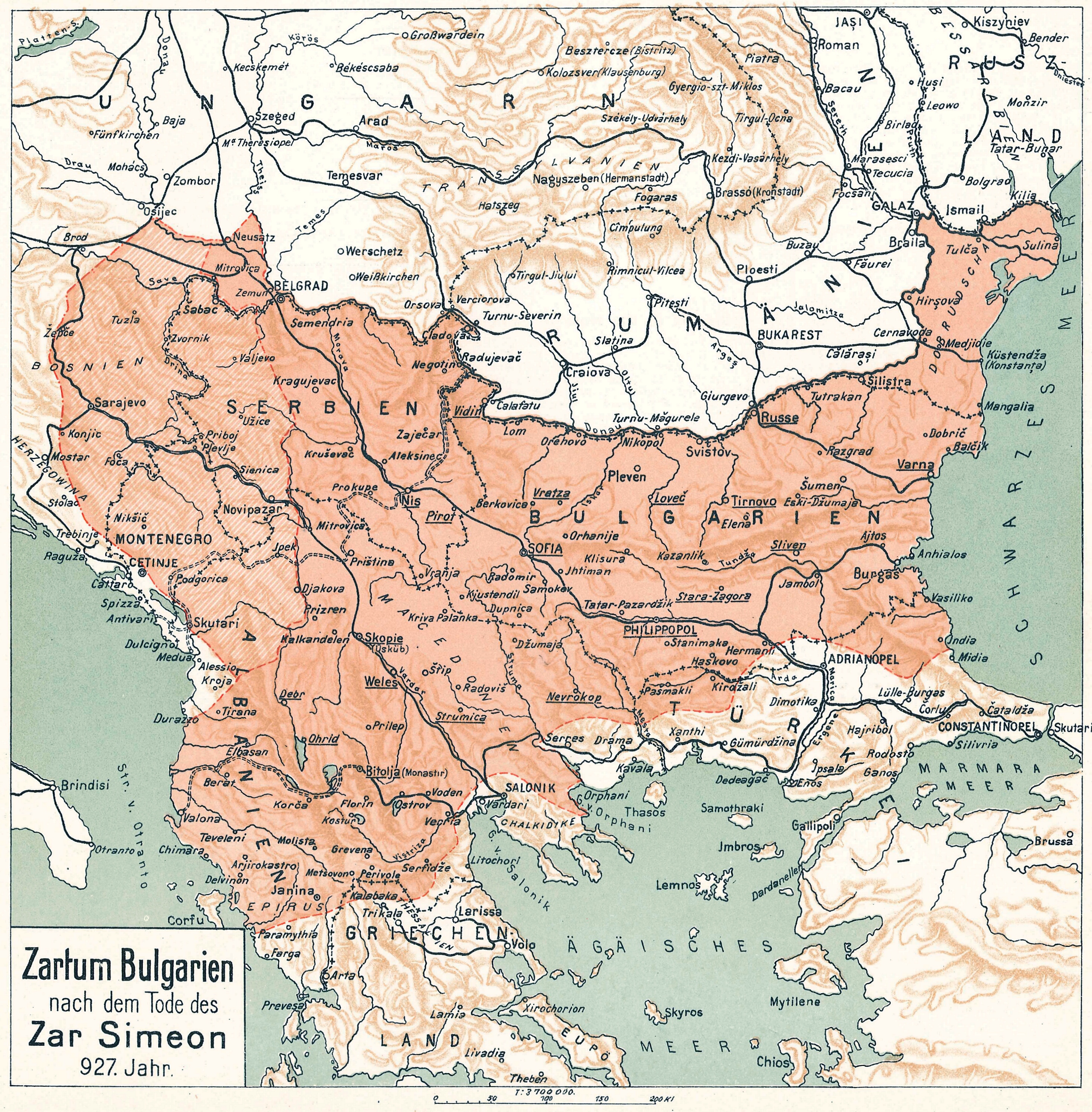
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine–Bulgarian War Of 894–896
The Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896 ( bg, Българо–византийска война от 894–896) was fought between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire as a result of the decision of the Byzantine emperor Leo VI to move the Bulgarian market from Constantinople to Thessalonica which would greatly increase the expenses of the Bulgarian merchants. Following the defeat of the Byzantine army in the initial stages of the war in 894 Leo VI sought aid from the Magyars who at the time inhabited the steppes to the north-east of Bulgaria. Aided by the Byzantine navy, in 895 the Magyars invaded Dobrudzha and defeated the Bulgarian troops. Simeon I called for truce and deliberately protracted the negotiations with the Byzantines until securing the assistance of the Pechenegs. Cornered between the Bulgarians and the Pechanegs, the Magyars suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of the Bulgarian army and had to migrate westwards, settling in Pannonia. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo VI The Wise
Leo VI, called the Wise ( gr, Λέων ὁ Σοφός, Léōn ho Sophós, 19 September 866 – 11 May 912), was Byzantine Emperor from 886 to 912. The second ruler of the Macedonian dynasty (although his parentage is unclear), he was very well read, leading to his epithet. During his reign, the renaissance of letters, begun by his predecessor Basil I, continued; but the Empire also saw several military defeats in the Balkans against Bulgaria and against the Arabs in Sicily and the Aegean. His reign also witnessed the formal discontinuation of several ancient Roman institutions, such as the separate office of Roman consul. Early life Born on 19 September 866 to the empress Eudokia Ingerina, Leo was either the illegitimate son of Emperor Michael III or the second son of Michael's successor, Basil I the Macedonian. Eudokia was both Michael III's mistress and Basil's wife. In 867, Michael was assassinated by Basil, who succeeded him as emperor. As the second-eldest son of the Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabars
The Kabars ( el, Κάβαροι), also known as Qavars (Qabars) or Khavars were Khazar rebels who joined the Magyar confederation possibly in the 9th century as well as the Rus' Khaganate. Sources The Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII is the principal source of the Kabars' history. He dedicated a whole chapterchapter 39to the Kabars (or ''Kabaroi'') in his ''De Administrando Imperio'', which was completed around 950. The Emperor described the Kabars as "a race of Khazars" who had risen up against the Khagan. The uprising was crushed, and some of them were massacred, but others escaped and joined the Magyars in the Pontic steppes. History The Kabars rebelled against the Khazar Khaganate in the early ninth century; the rebellion was notable enough to be described in Constantine Porphyrogenitus's work ''De Administrando Imperio''. Subsequently the Kabars were expelled from Levedia in the Khazar Khaganate leading the Magyar tribal confederacy called ''Hét-Magyar'' (meaning " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |