|
Kabakçı Mustafa
Kabakçı Mustafa ( – 14 July 1808) was a rebel leader who caused the delay of Ottoman reformation in the early 19th century. Yamaks and Kabakçı Yamaks were a special class of soldiers who were responsible in defending Bosphorous against Cossack pirates from Ukraine. Unlike janissaries they were from Black Sea Region of Turkey and not devshirme. But they liked to share the prestige of janissaries and considered themselves as a part of janissary. Kabakçı Mustafa was a sergeant of these yamaks in the castle of Rumelifeneri, on the European side of Bosphorous. He was from Rize, and probably about 35 years of age in 1807. According to legend, prior to being a yamak, he had fought against Russians in Crimean port of Anapa. The epithet Kabakçı which meant leader probably refers to his former battles. But except that almost nothing is known about his origin. He always appeared with two of his younger relatives both using the same name; Mustafa of Of and Mustafa of Pazar. Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selim III
Selim III (; ; was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1789 to 1807. Regarded as an enlightened ruler, he was eventually deposed and imprisoned by the Janissaries, who placed his cousin Mustafa on the throne as Mustafa IV (). A group of assassins subsequently killed Selim. Early life Selim III was the son of Sultan Mustafa III and his wife Mihrişah Sultan. His mother, Mihrişah Sultan was an ethnic Georgian. After she became the Valide sultan, she participated in reforming the government schools and establishing political corporations. His father, Ottoman Sultan Mustafa III, was very well educated and believed in the necessity of reforms. Mustafa III attempted to create a powerful army with professional, well-educated soldiers during peacetime. This was primarily motivated by his fear of a Russian invasion. During the Russo-Turkish War, he fell ill and died of a heart attack in 1774. Sultan Mustafa was aware of the fact that a military reform was necessary. He decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
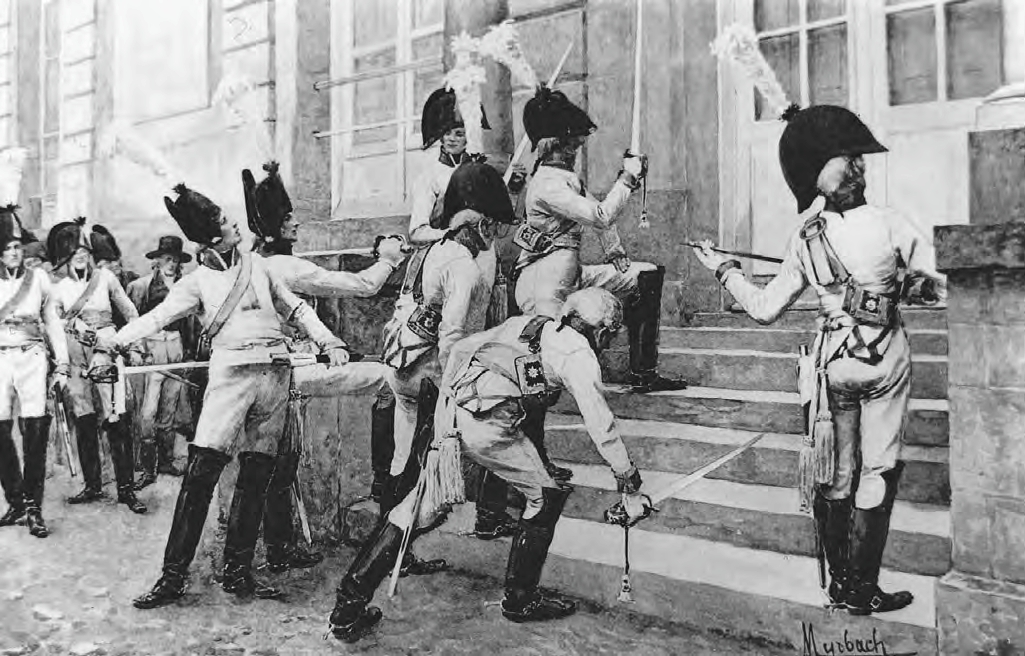
Alemdar Mustafa
Alemdar Mustafa Pasha (also called Bayraktar Mustafa Pasha; 1755 – 15 November 1808) was an Ottoman military commander and grand vizier. He was born into the family of a janissary, possibly in Rusçuk (modern-day Ruse, Bulgaria), although varying information exists about his birthplace. He received the epithet ''bayraktar'' or ''alemdar'', both meaning 'flag-bearer' and probably referring to his military rank in the janissary corps, during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774. After the war, he left the corps and eventually became a powerful notable and military commander in Rumelia. He became a strong supporter of Selim III's reforms and became a rallying point for opponents of the new regime after Selim's deposition in 1807. In July 1808, he took power in a military coup, replacing Sultan Mustafa IV with Mahmud II and becoming grand vizier. He attempted to revive Selim's reform program, but he himself was killed only months later in a rebellion by the janissaries. Alem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', and the act of issuing fatwas is called ''ifta. Fatwas have played an important role throughout Islamic history, taking on new forms in the modern era. Resembling ''jus respondendi'' in Roman law and rabbinic ''responsa'', privately issued fatwas historically served to inform Muslim populations about Islam, advise courts on difficult points of Islamic law, and elaborate substantive law. In later times, public and political fatwas were issued to take a stand on doctrinal controversies, legitimize government policies or articulate grievances of the population. During the era of mass European/Christian invasions, fatwas played a part in mobilizing resistance against foreign aggressors. Muftis acted as independent scholars in the classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahmud II
Mahmud II (, ; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839. Often described as the "Peter the Great of Turkey", Mahmud instituted extensive administrative, military, and fiscal reforms. His disbandment of the conservative Janissary, Janissary Corps removed a major obstacle to his and his successors' reforms in the Empire, creating the foundations of the subsequent Tanzimat era. Mahmud's reign was also marked by further Ottoman military defeats and loss of territory as a result of nationalist uprisings and European intervention. Mahmud ascended the throne following an Ottoman coups of 1807–1808, 1808 coup that deposed his half-brother Mustafa IV. Early in his reign, the Ottoman Empire ceded Bessarabia to Russia at the end of the Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812), 1806–1812 Russo-Turkish War. Greece waged a Greek War of Independence, successful war of independence that started in 1821 with British, French and Russian su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustafa IV
Mustafa IV (; ; 8 September 1779 – 16 November 1808) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1807 to 1808. Early life Mustafa IV was born on 8 September 1779 in Constantinople. He was the son of Sultan Abdul Hamid I (1774–1789) and Sineperver Sultan.Yavuz Bahadıroğlu, Resimli Osmanlı Tarihi, Nesil Yayınları ''(Ottoman History with Illustrations, Nesil Publications)'', 15th Ed., 2009, page 395, Both he and his half-brother, Mahmud II, were the last remaining male members of the House of Osman after their cousin, the reformist Sultan Selim III (1789–1807). They alone were therefore eligible to inherit the throne from Selim, by whom they were treated favorably. Since Mustafa was the elder, he took precedence over his brother to the throne.. During his short reign, Mustafa would save his cousin's life and order him murdered. Mustafa was Sultan Selim III's favourite crown prince, but he deceived his cousin and cooperated with the rebels to take his throne. Reign M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Ul-Islam
Sheikh ( , , , , ''shuyūkh'' ) is an honorific title in the Arabic language, literally meaning " elder". It commonly designates a tribal chief or a Muslim scholar. Though this title generally refers to men, there are also a small number of female sheikhs in history. The title ''Syeikha'' or ''Sheikha'' generally refers to women. In some countries, it is given as a surname to those of great knowledge in religious affairs, by a prestigious religious leader from a chain of Sufi scholars. The word is mentioned in the Qur'an in three places: verse 72 of Hud, 78 of Yusuf, and 23 of al-Qasas. A royal family member of the United Arab Emirates and some other Arab countries, also has this title, since the ruler of each emirate is also the sheikh of their tribe. Etymology and meaning The word in Arabic stems from a triliteral root connected with aging: , ''shīn-yā'-khā. The title carries the meaning leader, elder, or noble, especially in the Arabian Peninsula within the Tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Turkish War (1806–12)
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of these wars ended in losses for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a period of stagnation and decline. Conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of the Russian Empire as a significant European power after Peter the Great oversaw extensive modernization efforts in the early 18th century. Ultimately, however, the end of the Russo-Turkish wars came about with the dissolution of the two belligerents' respective states as a consequence of World War I: the Russian Empire collapsed in 1917 and was ultimately succeeded by the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922; while the Ottoman Empire was partitioned between 1918 and 1922 and succeeded by the Republic of Turkey in 1923. History Initial and intermediate phases (1568–1739) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire or French Empire (; ), also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 6 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815, when Napoleon was exiled to Saint Helena. Although France had already established a French colonial empire, colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a France in the early modern period, kingdom under the Bourbons and a French First Republic, republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second French Empire, Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. On 18 May 1804 (28 Floréal year XII on the French Republican calendar), Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (, ) by the French and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Fourth Coalition
The War of the Fourth Coalition () was a war spanning 1806–1807 that saw a multinational coalition fight against Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire, subsequently being defeated. The main coalition partners were Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Russian Empire, Russia with Electorate of Saxony, Saxony, Franco-Swedish War, Sweden, and United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, some members of the coalition had previously been fighting France as part of the War of the Third Coalition, Third Coalition, and there was no intervening period of general peace. On 9 October 1806, Prussia declared war on France and joined a renewed coalition, fearing the rise in French power after the defeat of Austrian Empire, Austria and establishment of the French-sponsored Confederation of the Rhine in addition to having learned of French plans to cede Prussian-desired Electorate of Hanover, Hanover to Britain in exchange for peace. Prussi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics of Turkey, population of Turkey. Istanbul is among the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest cities in Europe and List of cities proper by population, in the world by population. It is a city on two continents; about two-thirds of its population live in Europe and the rest in Asia. Istanbul straddles the Bosphorus—one of the world's busiest waterways—in northwestern Turkey, between the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea. Its area of is coterminous with Istanbul Province. Istanbul's climate is Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean. The city now known as Istanbul developed to become one of the most significant cities in history. Byzantium was founded on the Sarayburnu promontory by Greek colonisation, Greek col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |