|
Jordan Transverse Mercator
Jordan Transverse Mercator (JTM) (Arabic: نظام تربيع ميركاتور الأردني المستعرض) is a grid system created by the Royal Jordan Geographic Center (RJGC). This system is based on 6° belts with a Central Meridian of 37° East and a Scale Factor at Origin (mo) = 0.9998. The JTM is based on the Hayford ellipsoid adopted by the IUGG in 1924. No transformation parameters are presently offered by the government.Grids & Datums—Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan Article by Clifford J. Mugnier, C.P., C.M.S. However, Prof. Stephen H. Savage of Arizona State University provides the following parameters for the projection: Jordan Transverse Mercator Geographic Coordinate System: GCS_International_1924 Datum: D:International_1924 Spheroid: International_1924 Axis: 6378388 Flattening: 297 Prime Meridian: Greenwich Prime Meridian Longitude: 0 Units: Degree Unit Scale Factor: 0.017453292519943295 Projection: Transverse Mercator False Easting: 500,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Jordan Geographic Center
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), a 2021 reggae album * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * ''The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * ''Royal'' (Indian magazine), a men's lifestyle bimonthly * Royal Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayford Ellipsoid
The Hayford ellipsoid is a geodetic reference ellipsoid, named after the US geodesist John Fillmore Hayford (1868–1925), which was introduced in 1910. The Hayford ellipsoid was also referred to as the International ellipsoid 1924 after it had been adopted by the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics IUGG in 1924, and was recommended for use all over the world. Many countries retained their previous ellipsoids. The Hayford ellipsoid is defined by its semi-major axis = and its flattening = 1:297.00. Unlike some of its predecessors, such as the Bessel ellipsoid ( = , = 1:299.15), which was a European ellipsoid, the Hayford ellipsoid also included measurements from North America, as well as other continents (to a lesser extent). It also included isostatic measurements to reduce plumbline divergences. Hayfords ellipsoid did not reach the accuracy of Helmerts ellipsoid published 1906 ( = , = 1:298.3). It has since been replaced as the "International ellipsoid" by the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUGG
The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG; french: Union géodésique et géophysique internationale, UGGI) is an international non-governmental organization dedicated to the scientific study of Earth and its space environment using geophysical and geodetic techniques. The IUGG was established in Brussels, Belgium in 1919. Some areas within its scope are environmental preservation, reduction of the effects of natural hazards, and mineral resources. The IUGG is a member of the International Science Council (ISC), which is composed of international scholarly and scientific institutions and national academies of sciences. Objectives IUGG's objectives are the promotion and coordination of studies related to Earth's physical, chemical and mathematical representation. This includes geometrical shape, internal structure, gravity and magnetic fields, seismicity, volcanism, hydrologic cycle, glaciers, oceans, atmosphere, ionosphere, and magnetosphere of Earth. It als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public research university in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, ASU is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the U.S. One of three universities governed by the Arizona Board of Regents, ASU is a member of the Universities Research Association and classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity". ASU has nearly 150,000 students attending classes, with more than 38,000 students attending online, and 90,000 undergraduates and nearly 20,000 postgraduates across its five campuses and four regional learning centers throughout Arizona. ASU offers 350 degree options from its 17 colleges and more than 170 cross-discipline centers and institutes for undergraduates students, as well as more than 400 graduate degree and certificate programs. The Arizona State Sun Devils compete in 26 varsity-level sports in the NCAA Division I Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WGS84
The World Geodetic System (WGS) is a standard used in cartography, geodesy, and satellite navigation including GPS. The current version, WGS 84, defines an Earth-centered, Earth-fixed coordinate system and a geodetic datum, and also describes the associated Earth Gravitational Model (EGM) and World Magnetic Model (WMM). The standard is published and maintained by the United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. Definition The coordinate origin of WGS 84 is meant to be located at the Earth's center of mass; the uncertainty is believed to be less than . The WGS 84 meridian of zero longitude is the IERS Reference Meridian,European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation and IfEN: WGS 84 Implementation Manual, p. 13. 1998 5.3 arc seconds or east of the Greenwich meridian at the latitude of the Royal Observatory. (This is related to the fact that the local gravity field at Greenwich doesn't point exactly through the Earth's center of mass, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
37th Meridian East
The meridian 37° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 37th meridian east forms a great circle with the 143rd meridian west. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole, the 37th meridian east passes through: : See also * 36th meridian east *38th meridian east The meridian 38° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 38th meridian east forms a g ... {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed e037 meridian east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karameh Border Crossing
Karameh Border Crossing (Arabic: مركز حدود الكرامة) is the only border crossing between Jordan and Iraq. On the Iraqi side there is Turaibil Border Compound (Arabic: مجمع طريبيل الحدودي). The crossing served about 800,000 passengers in the year 2010 according to ''Al-Arab Al-Yawm'' newspaper. It connects the Jordanian town of Ruwaished to the Iraqi town of Turaibil. The border crossing is about 320 km (199 miles) from Jordan's capital Amman and 575 km (357 miles) from the Iraqi capital Baghdad. On 22 June 2014, the Islamic State of Iraq and Levant assaulted the border crossing and clashed with the Iraqi Army in an attempt to capture the crossing. See also * Anbar Governorate * Mafraq Governorate References Mafraq Governorate Karameh Al-Karameh ( ar, الكرامة), or simply Karameh, is a town in west-central Jordan, near the Allenby Bridge which spans the Jordan River. Karameh sits on the eastern bank of the river, along the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
39th Meridian East
The meridian 39° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 39th meridian east forms a great circle with the 141st meridian west. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole, the 39th meridian east passes through: : See also *38th meridian east The meridian 38° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 38th meridian east forms a g ... * 40th meridian east {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed e039 meridian east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
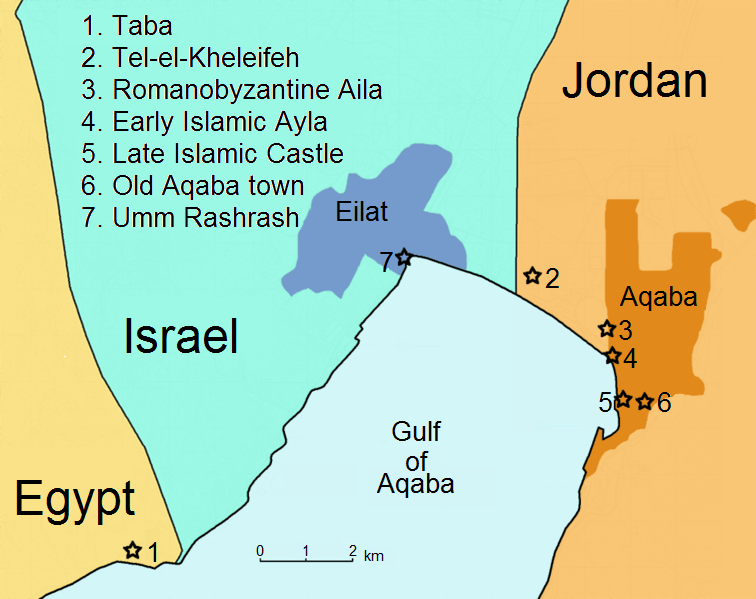
Aqaba
Aqaba (, also ; ar, العقبة, al-ʿAqaba, al-ʿAgaba, ) is the only coastal city in Jordan and the largest and most populous city on the Gulf of Aqaba. Situated in southernmost Jordan, Aqaba is the administrative centre of the Aqaba Governorate. The city had a population of 148,398 in 2015 and a land area of . Today, Aqaba plays a major role in the development of the Jordanian economy, through the vibrant trade and tourism sectors. The Port of Aqaba also serves other countries in the region. Aqaba's strategic location at the northeastern tip of the Red Sea between the continents of Asia and Africa has made its port important over the course of thousands of years. The ancient city was called ''Elath'', adopted in Latin as ''Aela'' and in Arabic as ''Ayla''. Its strategic location and proximity to copper mines made it a regional hub for copper production and trade in the Chalcolithic period. Aela became a bishopric under Byzantine rule and later became a Latin Catholic titu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35th Meridian East
The meridian 35° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 35th meridian east forms a great circle with the 145th meridian west. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole, the 35th meridian east passes through: : See also * 34th meridian east *36th meridian east The meridian 36° east of Prime Meridian, Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Europe, Asia, Africa, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 36th meridian ... {{geographical coordinates, state=collapsed e035 meridian east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |