|
John Whitney (animator)
John Hales Whitney, Sr. (April 8, 1917September 22, 1995) was an American animator, composer and inventor, widely considered to be one of the fathers of computer animation. Life Whitney was born in Pasadena, California and attended Pomona College. He is a descendant of the Whitney family through his father's direct line. His first works in film were 8 mm movies of a lunar eclipse which he made using a home-made telescope. In 1937-38 he spent a year in Paris, studying twelve-tone composition under René Leibowitz. In 1939 he returned to America and began to collaborate with his brother James on a series of abstract films. Their work, ''Five Film Exercises'' (1940–45) was awarded a prize for sound at the First International Experimental Film Competition in Belgium in 1949. In 1948 he was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship. During the 1950s, Whitney used his mechanical animation techniques to create sequences for television programs and commercials. In 1952, he directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasadena, California
Pasadena ( ) is a city in Los Angeles County, California, northeast of downtown Los Angeles. It is the most populous city and the primary cultural center of the San Gabriel Valley. Old Pasadena is the city's original commercial district. Its population was 138,699 at the 2020 census, making it the 44th largest city in California and the ninth-largest city in Los Angeles County. Pasadena was incorporated on June 19, 1886, becoming one of the first cities to be incorporated in what is now Los Angeles County, following the city of Los Angeles (April 4, 1850). Pasadena is known for hosting the annual Rose Bowl football game and Tournament of Roses Parade. It is also home to many scientific, educational, and cultural institutions, including Caltech, Pasadena City College, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Fuller Theological Seminary, ArtCenter College of Design, the Pasadena Playhouse, the Ambassador Auditorium, the Norton Simon Museum, and the USC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Visual Music, Los Angeles
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * Centre (department), H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Manovich
Lev Manovich ( ) is an author of books on digital culture and new media, and professor of Computer Science at the Graduate Center, City University of New York. Manovich's current research and teaching focuses on digital humanities, social computing, new media art and theory, and software studies. Manovich is also the founder and director of the Cultural Analytics Lab (called Software Studies Initiative 2007-2016), which was described in an associated press release as computational analysis of massive collections of images and video (cultural analytics). His lab was commissioned to create visualizations of cultural datasets for Google, New York Public Library, and New York's Museum of Modern Art (MoMA). One of his books, ''The Language of New Media'', has been translated into thirteen languages. Manovich's latest academic book ''Cultural Analytics'' was published in 2020 by the MIT Press. Biography Manovich was born in Moscow, USSR, where he studied painting, architecture, comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computer Animation
The history of computer animation began as early as the 1940s and 1950s, when people began to experiment with computer graphics – most notably by John Whitney. It was only by the early 1960s when digital computers had become widely established, that new avenues for innovative computer graphics blossomed. Initially, uses were mainly for scientific, engineering and other research purposes, but artistic experimentation began to make its appearance by the mid-1960s – most notably by Dr Thomas Calvert. By the mid-1970s, many such efforts were beginning to enter into public media. Much computer graphics at this time involved 2-dimensional imagery, though increasingly as computer power improved, efforts to achieve 3-dimensional realism became the emphasis. By the late 1980s, photo-realistic 3D was beginning to appear in film movies, and by mid-1990s had developed to the point where 3D animation could be used for entire feature film production. The earliest pioneers: 1940s to mid-196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirograph
Spirograph is a geometric drawing device that produces mathematical roulette curves of the variety technically known as hypotrochoids and epitrochoids. The well-known toy version was developed by British engineer Denys Fisher and first sold in 1965. The name has been a registered trademark of Hasbro Inc. since 1998 following purchase of the company that had acquired the Denys Fisher company. The Spirograph brand was relaunched worldwide in 2013, with its original product configurations, by Kahootz Toys. History In 1827, Greek-born English architect and engineer Peter Hubert Desvignes developed and advertised a "Speiragraph", a device to create elaborate spiral drawings. A man named J. Jopling soon claimed to have previously invented similar methods. When working in Vienna between 1845 and 1848, Desvignes constructed a version of the machine that would help prevent banknote forgeries, as any of the nearly endless variations of roulette patterns that it could produce were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Film Archive
The Academy Film Archive is part of the Academy Foundation, established in 1944 with the purpose of organizing and overseeing the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences’ educational and cultural activities, including the preservation of motion picture history. Although the current incarnation of the Academy Film Archive began in 1991, the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences acquired its first film in 1929. Preservation Located in Hollywood, California at the Pickford Center for Motion Picture Study, the Archive has a diverse range of moving image material. The Archive's collection comprises 107,000 titles and 230,000 separate items, including early American cinema, a vast collection of documentary films, filmed and taped interviews, amateur and private home movies of Hollywood legends, makeup and sound test reels, and a wide selection of experimental film, as well as Academy Award-winning films, Academy Award-nominated films, and a complete collection of every Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slit-scan Photography
The slit-scan photography technique is a photographic and cinematographic process where a moveable slide, into which a slit has been cut, is inserted between the camera and the subject to be photographed. More generally, "slit-scan photography" refers to cameras that use a slit, which is particularly used in scanning cameras in panoramic photography. This has numerous applications. This article discusses the manual artistic technique.{{cite web, url=https://petapixel.com/2017/10/18/role-slit-scan-image-science-art/, title=The Role of the Slit-Scan Image in Science and Art, date=18 October 2017, website=petapixel.com Use in cinematography Originally used in static photography to achieve blurriness or deformity, the slit-scan technique was perfected for the creation of spectacular animations. It enables the cinematographer to create a psychedelic flow of colors. Though this type of effect is now often created through computer animation, slit-scan is a mechanical technique. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expanded Cinema
{{italic title ''Expanded Cinema'' by Gene Youngblood (1970), the first book to consider video as an art form, was influential in establishing the field of media arts.Manovich, Lev. 2002. "Ten Key Texts on Digital Art: 1970–2000". Leonardo. 35 (5): 567–569. In the book he argues that a new, expanded cinema is required for a new consciousness. He describes various types of filmmaking utilizing new technology, including film special effects, computer art, video art, multi-media environments and holography. "Part One: The Audience and the Myth of Entertainment" In the first part of the book, Youngblood attempts to show how ''expanded cinema'' will unite art and life. "Television's elaborate movie-like subjective-camera ''simulation'' of the first moon landing" (p46) showed a generation that reality was not as real as simulation. He says that he is writing "at the end of the era of cinema as we've known it, the beginning of an era of image-exchange between man and man" (p. 49). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
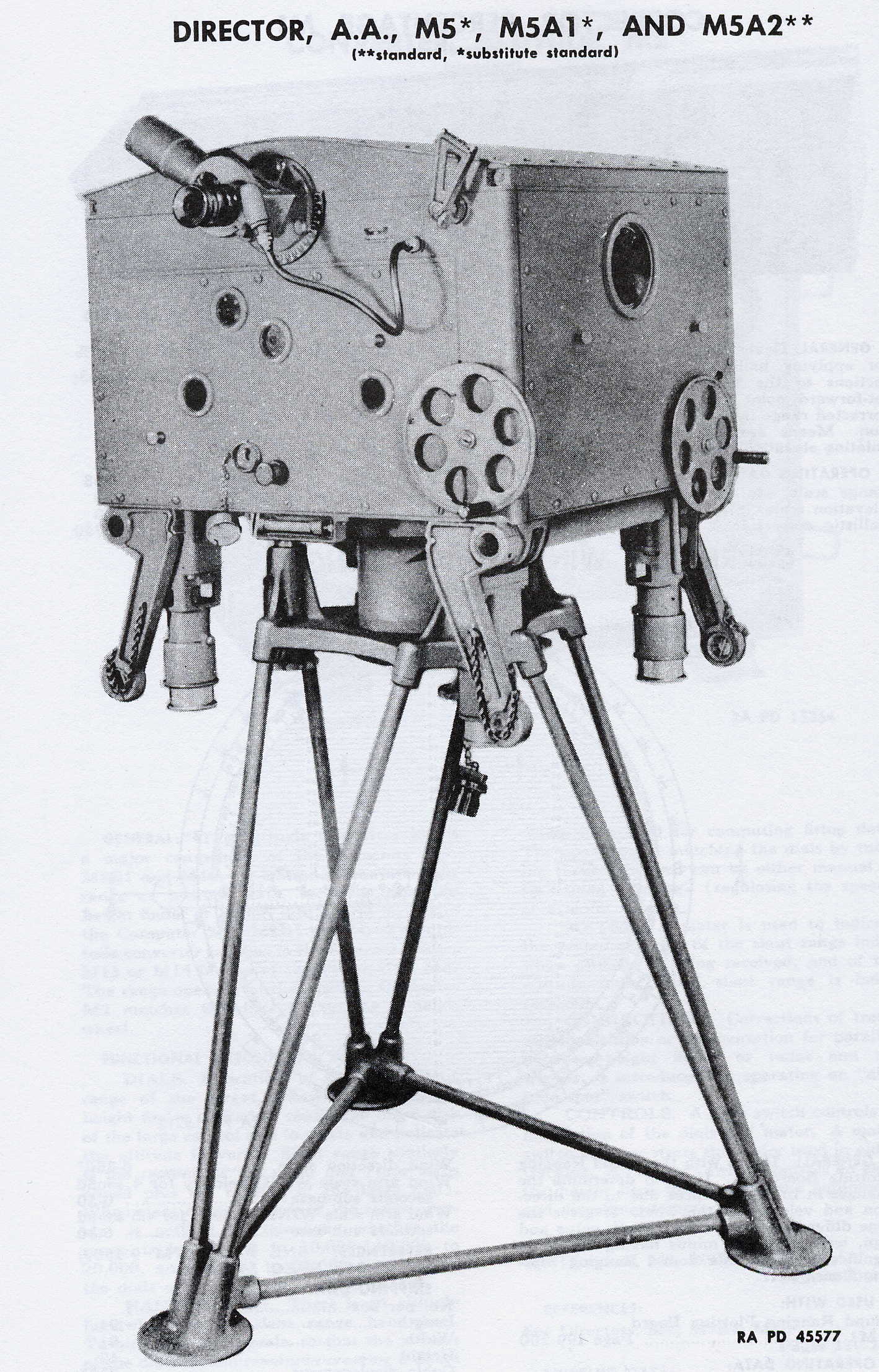
Kerrison Predictor
The Kerrison Predictor was one of the first fully automated anti-aircraft fire-control systems. It was used to automate the aiming of the British Army's Bofors 40 mm guns and provide accurate lead calculations through simple inputs on three main handwheels. The predictor could aim a gun at an aircraft based on simple inputs like the observed speed and the angle to the target. Such devices had been used on ships for gunnery control for some time, and versions such as the Vickers Predictor were available for larger anti-aircraft guns intended to be used against high-altitude bombers. Kerrison's analog computer was the first to be fast enough to be used in the demanding high-speed low-altitude role, which involved very short engagement times and high angular rates. The design was also adopted for use in the United States, where it was produced by Singer Corporation as the M5 Antiaircraft Director, later updated as the M5A1 and M5A2. The M6 was mechanically identical, differing on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guggenheim Museum
The Guggenheim Museums are a group of museums in different parts of the world established (or proposed to be established) by the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation. Museums in this group include: Locations Americas * The Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum in New York, New York, United States (1937–present)"Exhibition of Works Reflecting the Evolution of the Guggenheim's Collection Opens in Bilbao" artdaily.org, 2009, accessed April 18, 2012 ** The Guggenheim Museum SoHo, a branch of the Guggenheim Museum located in Manhattan's |