|
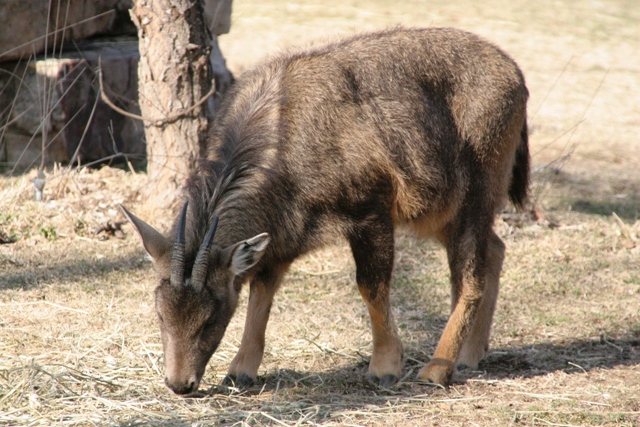
Japanese Serow
The : (''Capricornis crispus'') ( 羚羊) is a Japanese goat-antelope, an even-toed ungulate mammal. It is found in dense woodland in Japan, primarily in northern and central Honshu. The serow is seen as a national symbol of Japan, and is subject to protection in conservation areas. Adult Japanese serow stand about tall and weigh . They are black to whitish, and colouring lightens in summer. The fur is very bushy, especially the tail. Both sexes have short, backwards-curving horns, and are difficult to distinguish by sight. Japanese serow are found in dense mountain forests where they eat leaves, shoots, and acorns. They are diurnal and feed in early mornings and late afternoons. Serows are solitary, or gather in couples or small family groups. The animal marks its territory with sweet-and-sour-smelling preorbital gland secretions, and males and females have separate territories that may overlap. In the mid-20th century, the Japanese serow was hunted to near-extinction. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Swinhoe
Robert Swinhoe FRS (1 September 1836 – 28 October 1877) was an English diplomat and naturalist who worked as a Consul in Formosa. He catalogued many Southeast Asian birds, and several, such as Swinhoe's pheasant, are named after him. Biography Swinhoe was born in Calcutta where his father, who came from a Northumberland family, was a lawyer. There is no clear record of the date of his arrival in England, but it is known he attended the University of London, and in 1854 joined the China consular corps. He was stationed to the remote port of Amoy, some 300 miles to the northeast of Hong Kong, in 1855. While at this port he not only mastered the Chinese language (both official Mandarin and the local Amoy dialect), but also initiated a detailed and authoritative understanding of the ornithology of eastern China. In March, 1856, Swinhoe made an "adventurous" visit to the camphor districts of northwestern Formosa on board a lorcha, a hybrid vessel utilizing a European hull an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or (before 2001) conservation dependent. Species cannot be assigned the "Least Concern" category unless they have had their population status evaluated. That is, adequate information is needed to make a direct, or indirect, assessment of its risk of extinction based on its distribution or population status. Evaluation Since 2001 the category has had the abbreviation "LC", following the IUCN 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1). Before 2001 "least concern" was a subcategory of the "Lower Risk" category and assigned the code "LR/lc" or lc. Around 20% of least concern taxa (3261 of 15636) in the IUCN database still use the code "LR/lc", which indicates they have not been re-evalu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat ( beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the animal family Bovidae and the tribe Caprini, meaning it is closely related to the sheep. There are over 300 distinct breeds of goat.Hirst, K. Kris"The History of the Domestication of Goats".''About.com''. Accessed August 18, 2008. It is one of the oldest domesticated species of animal, according to archaeological evidence that its earliest domestication occurred in Iran at 10,000 calibrated calendar years ago. Goats have been used for milk, meat, fur, and skins across much of the world. Milk from goats is often turned into goat cheese. Female goats are referred to as ''does'' or ''nannies'', intact males are called ''bucks'' or ''billies'', and juvenile goats of both sexes are called ''kids''. Castrated males are called ''wethers''. Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
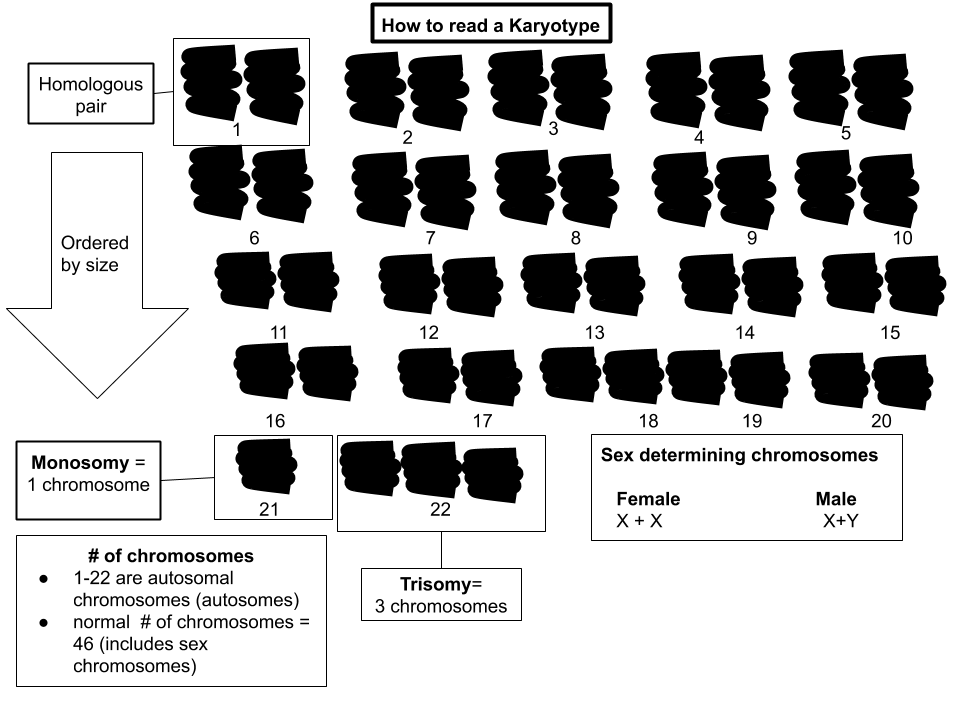
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemorhaedus Caudatus
The long-tailed goral or Amur goral (''Naemorhedus caudatus'') is a species of ungulate of the family Bovidae found in the mountains of eastern and northern Asia, including Russia, China, and Korea. A population of this species exists in the Korean Demilitarized Zone, near the tracks of the Donghae Bukbu Line. The species is classified as endangered in South Korea, with an estimated population less than 250. It has been designated South Korean natural monument 217. In 2003, the species was reported as being present in Arunachal Pradesh, in northeast India. Geographical distribution The long-tailed goral (also known as the Chinese gray goral) was and is sparsely found in the wild throughout China, Russia, and Korea, as well as the Himalayas.Crane, M., J. Willard and J. Grant. 2009. "''Naemorhedus caudatus''" (On-line), Animal Diversity Web. Accessed November 27, 2011 The main population in the wild today is found in Russia where there is a population of about 600 which is in dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaha XT 225
The Yamaha XT225, or known in some markets as the Yamaha Serow, was a dual-sport motorcycle produced by Yamaha from 1986 to 2007. The XT225 was preceded and superseded by the XT250. Power is supplied by a 223cc single-cylinder, air-cooled four-stroke engine featuring a SOHC and 2 valves. The engine produces 15 kW of power and 19Nm of torque. The XT225 has a reputation for being a lightweight dual-purpose motorcycle which is suited to many applications. (For the origin of the name, see serow The serows ( or ) are four species of medium-sized goat-like or antelope-like mammals of the genus ''Capricornis''. All four species of serow were until recently also classified under ''Naemorhedus'', which now only contains the gorals. Extant ....) External links *http://global.yamaha-motor.com/showroom/cp/collection/serow225_xt225/ References XT225 Dual-sport motorcycles Motorcycles introduced in 1986 {{Motorcycle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |