|
James Carruthers
James Carruthers (1759–1832) was a Scottish Roman Catholic priest and historian. Life He was the son of Catholic parents, Andrew Carruthers and his wife Lucy Rigg; Bishop Andrew Carruthers was his brother. He was born in New Abbey in the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright. Fr. Carruthers was educated in the Scottish College, Douai, and on his return to Scotland was ordained priest and appointed to the charge of Glenlivet. Afterwards he was successively at Buchan, in Aberdeenshire, at Preshome in the Enzie, at Dumfries, and at St Mary's, New Abbey, where he died on 14 February 1832. He was buried in the graveyard of Sweetheart Abbey. Works Carruthers wrote: * ''The History of Scotland from the earliest period of the Scottish Monarchy to the Accession of the Stewart Family, interspersed with Synoptical Reviews of Politics, Literature, and Religion throughout the World'', 2 vols., Edinburgh, 1826. * ''The History of Scotland during the reign of Queen Mary until the accession of her son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Carruthers
Andrew Carruthers (1770–1852) was a Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Bishop (Catholic Church), bishop who served as the Vicar Apostolic of the Vicariate Apostolic of the Eastern District (Scotland), Eastern District of Scotland. Born in Drumillan Miln near New Abbey in Kirkcudbrightshire on 7 February 1770, he was the son of Catholic parents, Andrew Carruthers and his wife Lucy Rigg. The priest and historian James Carruthers (historian), James Carruthers was his brother. Carruthers was Holy Orders, ordained a Priesthood (Catholic Church), priest on 25 March 1795. He was stationed first to the missionary station at Balloch on the Drummond Castle estate, in Perthshire, then in 1797 appointed as the chaplain to the Earl of Traquair at the Stuart family seat Traquair House, Traquair in Peeblesshire, and 1800 he moved to the mission at Munches, seat of the Maxwells at Dalbeattie in his native Kirkcudbrightshire. Using a bequest from the late Agnes Maxwell, who died in 1809, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
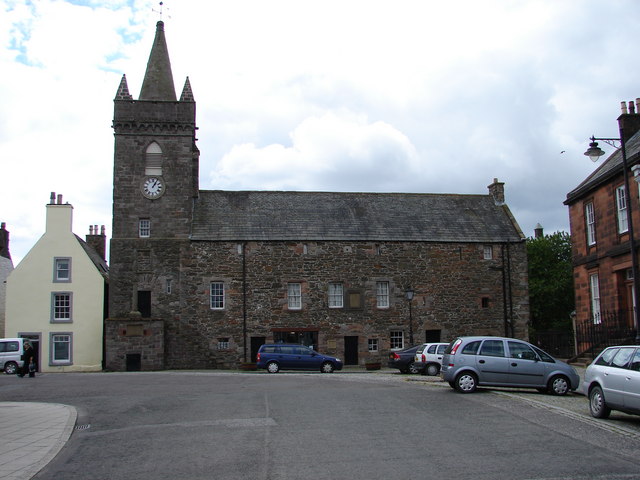
New Abbey
New Abbey ( gd, An Abaid Ùr) is a village in the historical county of Kirkcudbrightshire in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. It is south of Dumfries. The summit of the prominent hill Criffel is to the south. History The village has a wealth of history including the ruined Cistercian abbey Sweetheart Abbey, founded by Lady Dervorguilla in 1273 in memory of her husband John Balliol. She kept his embalmed heart close to her for the rest of her life. The monks named the abbey ''dulce cor'' ("sweet heart"). The village has a watermill, the New Abbey Corn Mill. Loch Kindar has a crannog and the village has the remains of Kirk Kindar (this was the parish church until just after 1633 when it was transferred to the refectory of the suppressed Sweetheart Abbey) on an island located just outside the village. New Abbey was one of five parishes from Kirkcudbrightshire included in the Nithsdale district of Dumfries and Galloway under the local government reforms of 1975 which abolished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
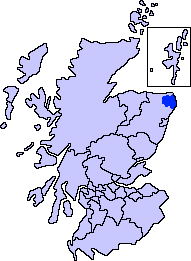
Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbright ( ; sco, Kirkcoubrie; gd, Cille Chùithbeirt) is a town, parish and a Royal Burgh from 1455 in Kirkcudbrightshire, of which it is traditionally the county town, within Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. The town lies southwest of Castle Douglas and Dalbeattie at the mouth of the River Dee, around from the Irish Sea. History An early rendition of the name of the town was Kilcudbrit; this derives from the Gaelic ''Cille Chuithbeirt'' meaning "chapel of Cuthbert", the saint whose mortal remains were kept at the town between their exhumation at Lindisfarne and reinterment at Chester-le-Street. John Spottiswoode, in his account of religious houses in Scotland, mentions that the Franciscans, or Grey Friars, had been established at Kirkcudbright from the 12th century. John Balliol was in possession of the ancient castle at Castledykes in the late 13th century and Edward I of England is said to have stayed here in 1300 during his war against Scotland. In 1455 Kirkcudb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish College, Douai
The Scottish College or Scots College at Douai was a seminary founded in Douai, France, for the training of Scottish Roman Catholic exiles for the priesthood. It was modelled on the similar English College there, founded for the same purpose. It has an unfortunate notoriety in consequence of the long dispute between the Jesuits and the secular clergy which centred around it in later times. History The Scots College was founded at Tournai, but soon transferred to Pont-à-Mousson. In 1592, Pope Clement VIII directed it to be relocated to Douai; however three years later it again moved to Louvain, where it was located next to the Jesuit College. In 1606, however, it moved again, and it was not until after several further migrations that it settled finally at Douai in 1612. At the time of the English Civil War, the Scots Colleges tended to support the crown. Many of the students were from families of the nobility and gentry and loyal to the Stuarts. A number of students interrupted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenlivet
Glenlivet (Scottish Gaelic: Gleann Lìobhait) is the glen in the Scottish Highlands through which the River Livet flows. The river rises high in the Ladder Hills, flows through the village of Tomnavoulin and onto the Bridgend of Glenlivet, passing under the remains of a late 18th-century bridge before joining the River Avon, one of the main tributaries of the River Spey. Glenlivet is known for the Glenlivet Estate and the whisky The Glenlivet. The Battle of Glenlivet was fought on 3 October 1594. Etymology The name Livet may be derived from the Gaelic Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, and Ca ... ''liobh'' + ''ait'' meaning "slippery" or "smooth" + "place". Alternatively it has been suggested that it is either an early Gaelic or pre-Gaelic name meaning "full of water" o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buchan
Buchan is an area of north-east Scotland, historically one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba. It is now one of the six committee areas and administrative areas of Aberdeenshire Council, Scotland. These areas were created by the council in 1996, when the Aberdeenshire council area was created under the Local Government etc (Scotland) Act 1994. The council area was formed by merging three districts of the Grampian Region: Banff and Buchan, Gordon and Kincardine and Deeside. The committee area of Buchan was formed from part of the former district of Banff and Buchan. Etymology The genesis of the name ''Buchan'' is shrouded in uncertainty, but may be of Pictish origin. The name may involve an equivalent of Welsh ''buwch'' meaning "a cow". American academic Thomas Clancy has noted cautiously the similarity between the territory names ''Buchan'' and ''Marr'' to those of the Welsh commotes ''Cantref Bychan'' and ''Cantref Mawr'', meaning "small-" and "large-commote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 Subdivisions of Scotland#council areas of Scotland, council areas of Scotland. It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area includes all of the area of the Counties of Scotland, historic counties of Aberdeenshire and Kincardineshire (except the area making up the City of Aberdeen), as well as part of Banffshire. The county boundaries are officially used for a few purposes, namely land registration and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy. Aberdeenshire Council is headquartered at Woodhill House, in Aberdeen, making it the only Scottish council whose headquarters are located outside its jurisdiction. Aberdeen itself forms a different council area (Aberdeen City). Aberdeenshire borders onto Angus, Scotland, Angus and Perth and Kinross to the south, Highland (council area), Highland and Moray to the west and Aber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries
Dumfries ( ; sco, Dumfries; from gd, Dùn Phris ) is a market town and former royal burgh within the Dumfries and Galloway council area of Scotland. It is located near the mouth of the River Nith into the Solway Firth about by road from the Anglo-Scottish border and just away from Cumbria by air. Dumfries is the county town of the historic county of Dumfriesshire. Before becoming King of Scots, Robert the Bruce killed his rival the Red Comyn at Greyfriars Kirk in the town on 10 February 1306. The Young Pretender had his headquarters here during a 3-day sojourn in Dumfries towards the end of 1745. During the Second World War, the bulk of the Norwegian Army during their years in exile in Britain consisted of a brigade in Dumfries. Dumfries is nicknamed ''Queen of the South''. This is also the name of the town's professional football club. People from Dumfries are known colloquially in Scots language as ''Doonhamers''. Toponymy There are a number of theories on the etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
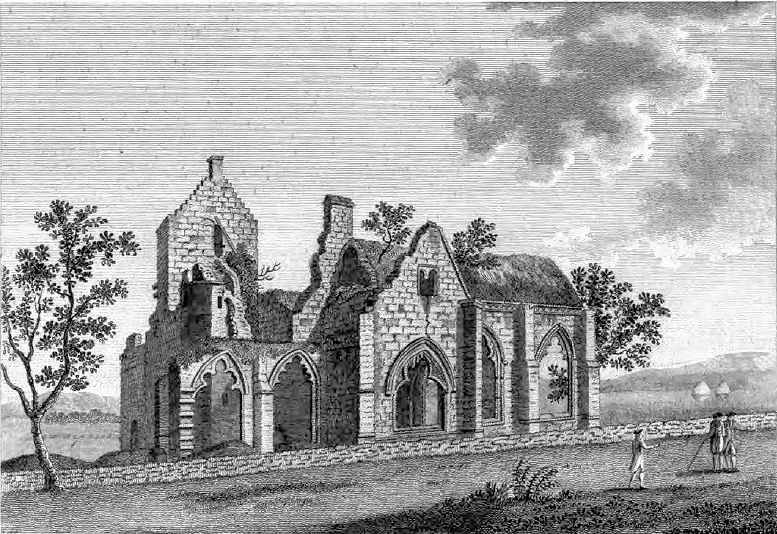
Sweetheart Abbey
The Abbey of Dulce Cor, better known as Sweetheart Abbey ( Gaelic: ''An Abaid Ur''), was a Cistercian monastery founded in 1275 in what is now the village of New Abbey, in the historical county of Kirkcudbrightshire in Dumfries and Galloway, south of Dumfries. History Founding The abbey, located on the banks of the New Abbey Pow (river), was founded by Dervorguilla of Galloway, daughter of Alan, Lord of Galloway, in memory of her husband, John de Balliol. After his death, she kept his embalmed heart, contained in a casket of ivory and silver, with her for the rest of her life, and it was buried alongside her when she died. In line with this devotion to her late husband, she named the abbey ''Dulce Cor'' (Latin for Sweet Heart). Their son, also John, became King of Scotland, but his reign was tragic and short. Under the first abbot, Henry, the abbey was built in deep-red, local sandstone in the Early English style. It was founded as a daughter house to the nearby Dundrennan A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church In Scotland
The Catholic Church in Scotland overseen by the Scottish Bishops' Conference, is part of the worldwide Catholic Church headed by the Pope. After being firmly established in Scotland for nearly a millennium, the Catholic Church was outlawed following the Scottish Reformation in 1560. Catholic Emancipation in 1793 and 1829 helped Catholics regain both religious and civil rights. In 1878, the Catholic hierarchy was formally restored. Throughout these changes, several pockets in Scotland retained a significant pre-Reformation Catholic population, including Banffshire, the Hebrides, and more northern parts of the Highlands, Galloway at Terregles House, Munches House, Kirkconnell House, New Abbey and Parton House and at Traquair in Peebleshire. In 1716, Scalan seminary was established in the Highlands and rebuilt in the 1760s by Bishop John Geddes, a well-known figure in Edinburgh during the Scottish Enlightenment. When Scottish national poet Robert Burns, who also gifted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1759 Births
In Great Britain, this year was known as the ''Annus Mirabilis'', because of British victories in the Seven Years' War. Events January–March * January 6 – George Washington marries Martha Dandridge Custis. * January 11 – In Philadelphia, the first American life insurance company is incorporated. * January 13 – Távora affair: The Távora family is executed, following accusations of the attempted regicide of Joseph I of Portugal. * January 15 – **Voltaire's satire ''Candide'' is published simultaneously in five countries. ** The British Museum opens at Montagu House in London (after six years of development). * January 27 – Battle of Río Bueno: Spanish forces, led by Juan Antonio Garretón, defeat indigenous Huilliches of southern Chile. * February 12 – Ali II ibn Hussein becomes the new Ruler of Tunisia upon the death of his brother, Muhammad I ar-Rashid. Ali reigns for 23 years until his death in 1782. * February 16 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 Deaths
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary critic. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |