|
Jörg Lanz Von Liebenfels
Adolf Josef Lanz (19 July 1874 – 22 April 1954), also known under his pseudonym as fascist agitator Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels, was an Austrian political and racial theorist and occultist, who was a pioneer of Ariosophy. He was a former monk and the founder of the magazine '' Ostara'', in which he published anti-semitic and ''völkisch'' theories. Early life He was born on 19 July 1874 in the Penzing district of Vienna in what was then Austria-Hungary, as the son of schoolmaster Johann Lanz and his wife Katharina, née Hoffenreich. His parents were middle class, and his father's ancestors had been burghers in Vienna since the early 18th century. His mother was believed to have been of Jewish ancestry, making him fail his own racial criteria. Consequently, he claimed to be the son of Baron Johannes Lancz de Liebenfels and began to call himself "Baron Adolf Georg (Jörg) Lanz Von Liebenfels Ph.D." As a young boy, he was fascinated by the myth of the Holy Grail. Liebenfels bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's own. Many pseudonym holders use pseudonyms because they wish to remain Anonymity, anonymous, but anonymity is difficult to achieve and often fraught with legal issues. Scope Pseudonyms include stage names, User (computing), user names, ring names, pen names, aliases, superhero or villain identities and code names, gamer identifications, and regnal names of emperors, popes, and other monarchs. In some cases, it may also include nicknames. Historically, they have sometimes taken the form of anagrams, Graecisms, and Latinisation (literature), Latinisations. Pseudonyms should not be confused with new names that replace old ones and become the individual's full-time name. Pseudonyms are "part-time" names, used only in certain contexts – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enlightenment (spiritual)
Used in a religious sense, enlightenment translates several Buddhist terms and concepts, most notably '' bodhi'', '' kensho,'' and '' satori''. Related terms from Asian religions are '' kaivalya'' and '' moksha'' (liberation) in Hinduism, '' Kevala Jnana'' in Jainism, and ''ushta'' in Zoroastrianism. In Christianity, the word "enlightenment" is rarely used, except to refer to the Age of Enlightenment and its influence on Christianity. Roughly equivalent terms in Christianity may be illumination, kenosis, metanoia, revelation, salvation, theosis, and conversion. Perennialists and Universalists view enlightenment and mysticism as equivalent terms for religious or spiritual insight. Asian cultures and religions Buddhism The English term ''enlightenment'' is the western translation of the abstract noun ''bodhi'', the knowledge or wisdom, or awakened intellect, of a Buddha. The verbal root ''budh-'' means "to awaken," and its literal meaning is closer to "awakening." A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious .... It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryan Race
The Aryan race is an obsolete historical race concept that emerged in the late-19th century to describe people of Proto-Indo-European heritage as a racial grouping. The terminology derives from the historical usage of Aryan, used by modern Indo-Iranians as an epithet of "noble". Anthropological, historical, and archaeological evidence does not support the validity of this concept.Arvidsson 2006:298 Arvidsson, Stefan (2006), Aryan Idols: Indo-European Mythology as Ideology and Science, translated by Sonia Wichmann, Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press. The concept derives from the notion that the original speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language were distinct progenitors of a superior specimen of humankind, and that their descendants up to the present day constitute either a distinctive race or a sub-race of the Caucasian race, alongside the Semitic race and the Hamitic race. This taxonomic approach to categorizing human population groups is now consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in media such as comics, video games, movies, anime, and television series. Belief in demons probably goes back to the Paleolithic age, stemming from humanity's fear of the unknown, the strange and the horrific. ''A Dictionary of Comparative Religion'' edited by S.G.F. Brandon 1970 In ancient Near Eastern religions and in the Abrahamic religions, including early Judaism and ancient-medieval Christian demonology, a demon is considered a harmful spiritual entity which may cause demonic possession, calling for an exorcism. Large portions of Jewish demonology, a key influence on Christianity and Islam, originated from a later form of Zoroastrianism, and was transferred to Judaism during the Persian era. Demons may or may not also be considered to be devils: minions of the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam And Eve
Adam and Eve, according to the creation myth of the Abrahamic religions, were the first man and woman. They are central to the belief that humanity is in essence a single family, with everyone descended from a single pair of original ancestors. They also provide the basis for the doctrines of the fall of man and original sin that are important beliefs in Christianity, although not held in Judaism or Islam. In the Book of Genesis of the Hebrew Bible, chapters one through five, there are two creation narratives with two distinct perspectives. In the first, Adam and Eve are not named. Instead, God created humankind in God's image and instructed them to multiply and to be stewards over everything else that God had made. In the second narrative, God fashions Adam from dust and places him in the Garden of Eden. Adam is told that he can eat freely of all the trees in the garden, except for a tree of the knowledge of good and evil. Subsequently, Eve is created from one of Ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandala
Chandala ( sa, चांडाल, caṇḍāla) is a Sanskrit word for someone who deals with disposal of corpses, and is a Hindu lower caste, traditionally considered to be untouchable. A female member of this caste is known as a ''Caṇḍālī''. History Varṇa was a hierarchical social order in ancient India, based on the Vedas. Since the Vedic corpus constitute the earliest literary source, it came to be seen as the origin of caste society. In this view of caste, ''varṇas'' were created on a particular occasion and have remained virtually unchanged. In this ordering of society, notions of purity and pollution were central, and activities were delineated in this context. ''Varṇa'' divides the society into four groups ordered in a hierarchy; beyond these, outside the system, lies a fifth group known as the ''untouchables'', of which the Chandala became a constituent part. The first mention of the fourfold ''varṇa'' division is found in the later ''Rigveda''. Vedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castration
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceutical drugs to deactivate the testes. Castration causes sterilization (preventing the castrated person or animal from reproducing); it also greatly reduces the production of hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. Surgical castration in animals is often called neutering. The term ''castration'' is sometimes also used to refer to the removal of the ovaries in the female, otherwise known as an oophorectomy, or the removal of internal testes, otherwise known as gonadectomy. The equivalent of castration for female animals is spaying. Estrogen levels drop following oophorectomy, and long-term effects of the reduction of sex hormones are significant throughout the body. Castration of animals is intended to favor a desired de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
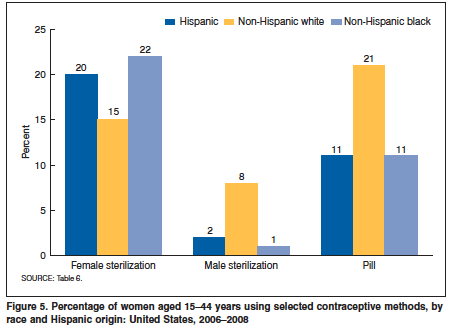
Human Sterilization (surgical Procedure)
Sterilization ( also spelled sterilisation) is any of a number of medical methods of birth control that intentionally leaves a person unable to reproduce. Sterilization methods include both surgical and non-surgical, and exist for both males and females. Sterilization procedures are intended to be permanent; reversal is generally difficult or impossible. There are multiple ways of having sterilization done, but the two that are used most frequently are tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men. There are many different ways tubal sterilization can be accomplished. It is extremely effective and in the United States surgical complications are low. With that being said, tubal sterilization is still a method that involves surgery, so there is still a danger. Women that chose a tubal sterilization may have a higher risk of serious side effects, more than a man has with a vasectomy. Pregnancies after a tubal sterilization can still occur, even many years after the procedure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theozoology
Armanism and Ariosophy are esoteric ideological systems that were developed largely by Guido von List and Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels respectively, in Austria between 1890 and 1930. The term 'Ariosophy', which means the wisdom of the Aryans, was invented by Lanz von Liebenfels in 1915, and during the 1920s it became the name of his doctrine. For research of the topic, such as Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke's book ''The Occult Roots of Nazism'', the term 'Ariosophy' is used generically to describe the Aryan/esoteric theories of a subset of the ' Völkische Bewegung'. This broader use of the word is retrospective and it was not generally current among the esotericists themselves. List actually called his doctrine 'Armanism', while Lanz used the terms 'Theozoology' and 'Ario-Christianity' before the First World War. The ideas of Von List and Lanz von Liebenfels were part of a general occult revival that occurred in Austria and Germany during the late 19th and early 20th centuries; a revival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)